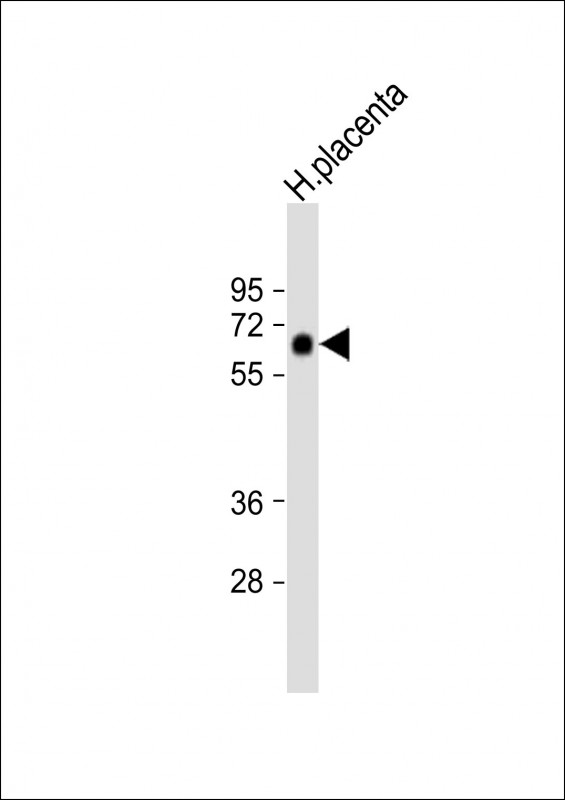
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Zinc finger protein 57 homolog, Zfp-57, Zinc finger protein 698, ZFP57, C6orf40, ZNF698 |
| Entrez GeneID | 346171 |
| WB Predicted band size | 51.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This ZFP57 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 269-296 amino acids from the Central region of human ZFP57. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于ZFP57抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要内容:
1. **"ZFP57 maintains the parent-of-origin-specific expression of the imprinted genes"**
- **作者**: Li et al.
- **摘要**: 研究利用ZFP57抗体在小鼠模型中验证了ZFP57蛋白在维持基因组印记中的作用,发现其通过结合甲基化DNA区域调控印记控制区的甲基化状态,缺失ZFP57会导致胚胎发育异常及印记基因表达失调。
2. **"ZFP57 interacts with KAP1 complex to regulate genomic imprinting"**
- **作者**: Strogantsev et al.
- **摘要**: 该文献通过ChIP实验(使用ZFP57抗体)揭示了ZFP57与KAP1蛋白复合体的相互作用机制,证明两者协同调控印记基因的甲基化及染色质修饰,为印记缺陷相关疾病提供分子机制解释。
3. **"ZFP57 is required for normal development in the early mouse embryo"**
- **作者**: Nakamura et al.
- **摘要**: 利用ZFP57抗体进行免疫荧光和Western blot分析,发现ZFP57在小鼠早期胚胎中高表达,其缺失导致胚胎停滞及印记基因(如H19和Igf2r)的甲基化丢失,提示其在胚胎发育中的关键作用。
4. **"Mutations in ZFP57 cause human imprinting disorders"**
- **作者**: Mackay et al.
- **摘要**: 研究通过患者样本中的ZFP57突变分析(结合抗体检测蛋白表达),发现ZFP57功能异常与多种印记综合征(如TNDM1)相关,强调了其在人类表观遗传调控中的重要性。
以上研究均通过ZFP57抗体进行蛋白定位、功能验证或机制探索,涵盖其在发育、疾病及表观遗传调控中的核心作用。
The ZFP57 antibody is a research tool used to study the ZFP57 protein, a zinc finger transcription factor critical in maintaining genomic imprinting during early embryonic development. ZFP57 contains a KRAB (Krüppel-associated box) domain, which facilitates interactions with co-repressors to regulate gene expression epigenetically. It specifically binds to methylated DNA regions at imprinting control regions (ICRs), ensuring the preservation of DNA methylation patterns and parental-origin-specific gene expression across cell divisions. Mutations or dysregulation of ZFP57 are linked to imprinting disorders, such as transient neonatal diabetes mellitus (TNDM) and Russell-Silver syndrome.
The antibody is widely employed in techniques like chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), immunofluorescence (IF), and Western blotting to investigate ZFP57's localization, expression levels, and interactions with target DNA sequences. It aids in elucidating mechanisms underlying epigenetic regulation, embryonic stem cell pluripotency, and developmental abnormalities. Commercial ZFP57 antibodies are typically raised in hosts like rabbits or mice, targeting specific epitopes within the protein's functional domains. Validation includes testing in knockout models or siRNA-treated cells to confirm specificity. Researchers utilize this antibody to explore ZFP57's role in diseases, reprogramming somatic cells, and maintaining epigenetic stability, making it a vital reagent in developmental biology and epigenetics studies.
×