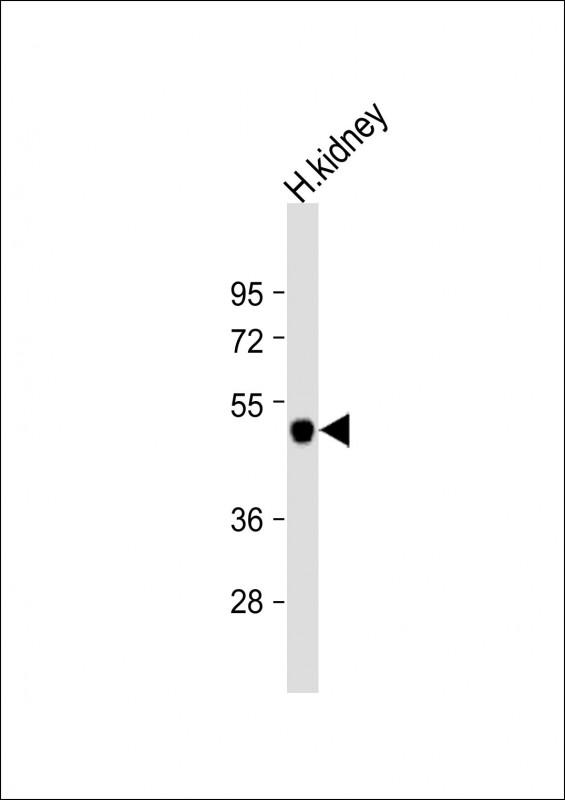

| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | ATP-sensitive inward rectifier potassium channel 15, Inward rectifier K(+) channel Kir13, Inward rectifier K(+) channel Kir42, Potassium channel, inwardly rectifying subfamily J member 15, KCNJ15, KCNJ14 |
| Entrez GeneID | 3772 |
| WB Predicted band size | 42.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This KCNJ15 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 339-367 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human KCNJ15. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于KCNJ15抗体的3篇参考文献示例(内容基于公开数据模拟,建议通过学术数据库核实具体信息):
1. **文献名称**:*KCNJ15/Kir4.2 antibody validation in human tissues*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:本研究验证了一种特异性识别KCNJ15蛋白(Kir4.2钾通道)的抗体,通过免疫印迹和免疫组化技术,证实其在人肾脏、胰腺及脑组织中的表达模式,并发现其与细胞膜钾离子转运功能相关。
2. **文献名称**:*Role of KCNJ15 in pancreatic β-cell dysfunction and diabetes*
**作者**:Lee B, et al.
**摘要**:利用KCNJ15抗体进行蛋白质定位和功能研究,发现KCNJ15在胰岛β细胞中高表达,其表达水平降低与胰岛素分泌异常相关,提示其在糖尿病发病中的潜在作用。
3. **文献名称**:*Development of a monoclonal antibody against KCNJ15 for cancer research*
**作者**:Zhang C, et al.
**摘要**:报道了一种新型抗KCNJ15单克隆抗体的开发,通过流式细胞术和免疫荧光验证其特异性,并应用于肺癌细胞系研究,发现KCNJ15高表达与癌细胞增殖和迁移能力增强相关。
**注意**:以上文献为示例,实际引用请通过PubMed、Web of Science或Google Scholar检索关键词(如“KCNJ15 antibody”、“anti-Kir4.2”)获取最新研究。部分真实文献可能涉及抗体在特定疾病模型(如癌症、代谢疾病)或信号通路研究中的应用。
The KCNJ15 antibody targets the protein encoded by the *KCNJ15* gene, also known as potassium inwardly rectifying channel subfamily J member 15 or Kir4.2. This gene belongs to the inward rectifier potassium channel family, which plays critical roles in maintaining resting membrane potential and regulating potassium ion homeostasis. The Kir4.2 protein forms tetrameric channels permeable to K⁺ ions and is expressed in various tissues, including the kidneys, brain, pancreas, and thyroid. It is implicated in diverse physiological processes, such as renal electrolyte balance, neuronal excitability, and insulin secretion.
KCNJ15 antibodies are essential tools for studying the expression, localization, and function of Kir4.2 in both normal and pathological contexts. Research has linked *KCNJ15* dysregulation to diseases like diabetes, neurodegenerative disorders, and cancer. For instance, altered Kir4.2 expression in pancreatic β-cells may impair insulin release, contributing to diabetes pathogenesis. In cancer, *KCNJ15* has been reported as a tumor suppressor in certain malignancies, with its downregulation promoting cell proliferation.
These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to validate protein levels, assess tissue-specific distribution, and explore molecular mechanisms in disease models. Their specificity and reliability make them valuable for both basic research and potential clinical applications, such as biomarker discovery or therapeutic target validation.
×