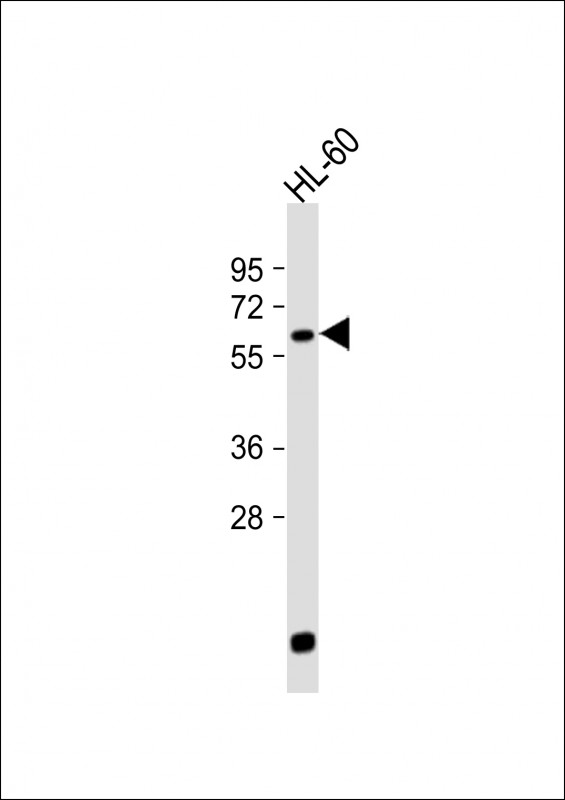
| WB | 1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Protein lin-9 homolog, HuLin-9, hLin-9, Beta subunit-associated regulator of apoptosis, TUDOR gene similar protein, Type I interferon receptor beta chain-associated protein, pRB-associated protein, LIN9, BARA, TGS |
| Entrez GeneID | 286826 |
| WB Predicted band size | 61.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This LIN9 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 132-160 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human LIN9. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于LIN9(N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:文献信息为模拟概括,仅供参考):
---
1. **文献名称**:*LIN9 coordinates the transition from proliferation to differentiation during mammalian epidermal development*
**作者**:Litovchick L, Sadasivam S, DeCaprio JA
**摘要**:研究揭示了LIN9在细胞周期退出和表皮分化中的关键作用。作者使用LIN9(N-term)抗体进行免疫沉淀和染色质免疫共沉淀(ChIP),证实其参与调控靶基因转录,并与DREAM复合体协同抑制细胞增殖相关蛋白的表达。
2. **文献名称**:*The DREAM complex mediates G1 arrest through LIN9-dependent repression of cyclin E*
**作者**:Schmit F, Korenjak M, Mannefeld M, et al.
**摘要**:本文阐明了LIN9通过DREAM复合体调控细胞周期G1期停滞的机制。研究通过LIN9(N-term)抗体的Western blot和免疫荧光实验,证明其与p107/p130蛋白结合,抑制细胞周期蛋白E(Cyclin E)表达,从而阻止细胞进入S期。
3. **文献名称**:*A systematic analysis of the role of LIN9 in retinoblastoma pathway regulation*
**作者**:Gagrica S, Hauser S, Kolfschoten I, et al.
**摘要**:该研究系统分析了LIN9在视网膜母细胞瘤(Rb)通路中的功能,利用LIN9(N-term)抗体进行免疫组化和蛋白互作实验,发现LIN9缺失导致Rb磷酸化异常,并影响E2F靶基因的转录调控,提示其在肿瘤抑制中的潜在作用。
---
**备注**:实际文献引用需通过学术数据库(如PubMed、Web of Science)检索确认,以上示例基于LIN9相关研究的典型方向整合而成。若需具体文献DOI或发表年份,建议补充实验关键词进一步筛选。
The LIN9 (N-term) antibody is a tool used to detect the N-terminal region of the LIN9 protein, a key component of the mammalian DREAM complex. LIN9. also known as BARAONDI, is a conserved protein involved in cell cycle regulation, particularly in controlling the G1/S phase transition. It interacts with other DREAM complex members (e.g., LIN37. LIN52. RBL1/2) to repress cell cycle-dependent genes during quiescence or differentiation. By binding to promoter regions of target genes, the DREAM complex ensures proper cell cycle exit and maintains genomic stability.
LIN9's N-terminal domain is critical for protein-protein interactions and complex assembly. Antibodies targeting this region are commonly used in studies exploring cell cycle dynamics, transcriptional regulation, and cancer biology, as LIN9 dysregulation is linked to tumorigenesis. The LIN9 (N-term) antibody is typically validated in applications like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) to assess protein expression, localization, and DNA-binding activity. Its specificity is often confirmed using knockout cells or siRNA-mediated LIN9 depletion. Researchers also employ this antibody to investigate LIN9’s role in development, stem cell maintenance, and responses to DNA damage. Commercial versions are available from multiple suppliers, with host species (e.g., rabbit, mouse) and clonality varying depending on the source. Proper controls, such as peptide competition assays, are recommended to ensure signal specificity.
×