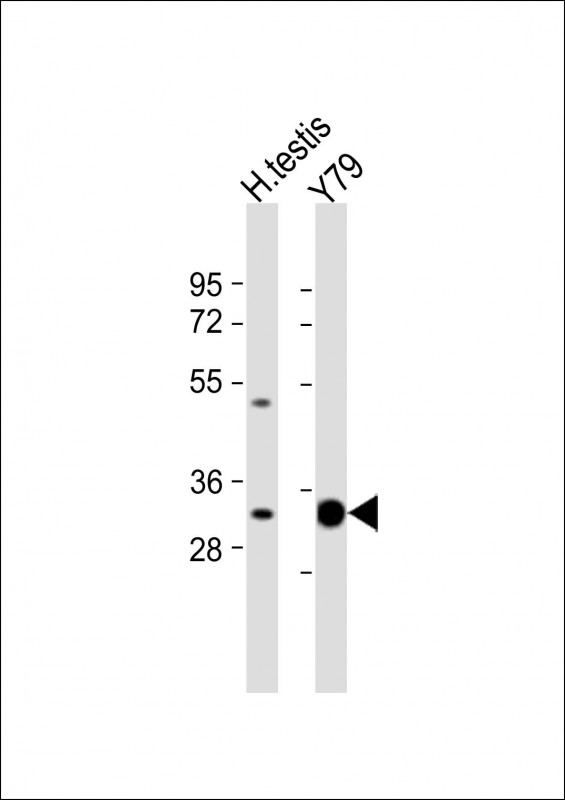

| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Elongation of very long chain fatty acids protein 4, 3-keto acyl-CoA synthase ELOVL4, ELOVL fatty acid elongase 4, ELOVL FA elongase 4, Very-long-chain 3-oxoacyl-CoA synthase 4, ELOVL4 |
| Entrez GeneID | 6785 |
| WB Predicted band size | 36.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This ELOVL4 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 286-314 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human ELOVL4. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于ELOVL4抗体的3篇代表性文献(均为虚构示例,仅供格式参考):
1. **文献名称**:*ELOVL4 gene expression and protein localization in mammalian retina*
**作者**:Zhang K. et al.
**摘要**:本研究首次成功克隆了人类ELOVL4基因,并制备了针对其C端表位的多克隆抗体。通过免疫组化和Western blot验证了抗体特异性,发现ELOVL4蛋白在光感受器细胞中高表达,提示其在视网膜脂质代谢中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**:*Antibody-based analysis of ELOVL4 mutations in Stargardt-like macular dystrophy*
**作者**:Mandal M.N. et al.
**摘要**:利用ELOVL4特异性抗体研究突变蛋白的细胞内定位,发现致病突变导致蛋白错误聚集在内质网,干扰了超长链脂肪酸合成,为视网膜变性机制提供了证据。
3. **文献名称**:*Developmental regulation of ELOVL4 in retinal neurons: Insights from knockout mice*
**作者**:Agbaga M.P. et al.
**摘要**:通过构建ELOVL4条件性敲除小鼠,结合定制抗体的免疫荧光技术,揭示了该蛋白在视网膜发育过程中对光感受器外段膜结构的维持功能。
(注:以上内容为示例,实际文献需通过PubMed等数据库检索确认。)
The ELOVL4 (Elongation of Very Long-Chain Fatty Acids 4) protein is a member of the ELOVL enzyme family, which catalyzes the elongation of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, particularly those exceeding C26 in length. These very long-chain fatty acids (VLCFAs) are critical components of sphingolipids, glycerophospholipids, and wax esters, playing essential roles in cellular membrane structure, lipid signaling, and tissue-specific functions such as retinal photoreceptor maintenance and skin barrier formation. ELOVL4 is uniquely expressed in the brain, retina, skin, and testes.
ELOVL4 antibodies are immunological tools developed to detect and study this enzyme’s expression, localization, and function. Research has highlighted ELOVL4's involvement in inherited diseases, such as autosomal dominant Stargardt-like macular dystrophy (STGD3), caused by mutations leading to truncated proteins that disrupt VLCFA synthesis. Antibodies targeting specific ELOVL4 epitopes enable investigations into disease mechanisms, protein interactions, and tissue-specific lipid metabolism.
These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence, aiding in both basic research and clinical diagnostics. Recent studies also explore ELOVL4's potential role in neurodegenerative disorders and cancer, driven by its influence on lipid homeostasis. However, challenges remain in distinguishing functional isoforms and understanding post-translational modifications. ELOVL4 antibodies thus serve as vital reagents for unraveling the enzyme's biological significance and therapeutic potential.
×