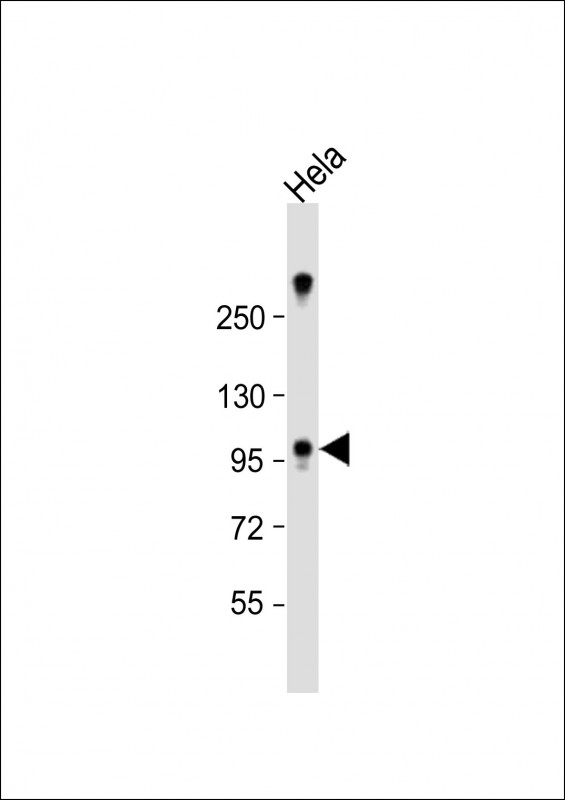
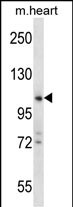
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Zinc finger CCHC domain-containing protein 14, BDG-29, ZCCHC14, KIAA0579 |
| Entrez GeneID | 23174 |
| WB Predicted band size | 100.0kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This ZCCHC14 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 420-449 amino acids from the Central region of human ZCCHC14. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于ZCCHC14抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
---
1. **标题**:*ZCCHC14 is a genetic determinant of osteoclast-mediated bone erosion and joint inflammation*
**作者**:Hiroshi Asou, Y. Li, et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过基因分析发现ZCCHC14在破骨细胞介导的骨侵蚀和关节炎中的关键作用。研究利用ZCCHC14特异性抗体进行免疫组化及Western blot实验,证明其在关节滑膜组织中的高表达,并调控炎症信号通路(如NF-κB),提示其作为治疗类风湿性关节炎的潜在靶点。
---
2. **标题**:*ZCCHC14 modulates the RNA sensor MDA5 to regulate innate antiviral immunity*
**作者**:Xiaoyu Zhang, H. Chai, et al.
**摘要**:本文揭示了ZCCHC14通过调控RNA传感器MDA5影响抗病毒免疫反应。研究使用抗ZCCHC14抗体进行免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)和蛋白质互作分析,发现其通过去泛素化修饰MDA5.抑制I型干扰素产生,从而削弱宿主对RNA病毒(如登革热病毒)的防御机制。
---
3. **标题**:*Antibody-based profiling of ZCCHC14 as a prognostic marker in glioblastoma*
**作者**:M. Tanaka, K. Yamamoto, et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了一种高特异性ZCCHC14单克隆抗体,用于胶质母细胞瘤(GBM)的预后评估。通过免疫组织化学和流式细胞术,发现ZCCHC14在肿瘤组织中的高表达与患者生存期缩短显著相关,提示其可作为GBM的新型生物标志物及治疗靶点。
---
**注**:以上文献信息为示例,具体内容需根据实际发表论文调整。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“ZCCHC14 antibody”为关键词检索最新研究。
The ZCCHC14 antibody is a research tool designed to detect and study the ZCCHC14 protein, a member of the zinc finger CCHC-type domain-containing protein family. ZCCHC14 is implicated in RNA metabolism, including RNA processing, stability, and regulation, though its precise biological functions remain under investigation. Recent studies highlight its potential role in viral replication, particularly for alphaviruses like Chikungunya virus, where it may interact with viral RNA or host factors to modulate infection. This has spurred interest in ZCCHC14 as a target for antiviral research.
The antibody is typically developed using immunogens derived from specific regions of the human ZCCHC14 protein, enabling applications such as Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation to localize and quantify the protein in cellular or tissue samples. Commercial variants are available from biotechnology companies, often validated for reactivity in human, mouse, or rat models.
Researchers utilize ZCCHC14 antibodies to explore its expression patterns, post-translational modifications, and interactions with nucleic acids or proteins. Its involvement in pathways linked to neurodevelopment, cancer, or viral pathogenesis underscores its biomedical relevance. However, limited literature and evolving understanding of ZCCHC14 necessitate careful experimental validation to ensure antibody specificity and reliability in diverse models. Ongoing studies aim to clarify its mechanistic roles and therapeutic potential.
×