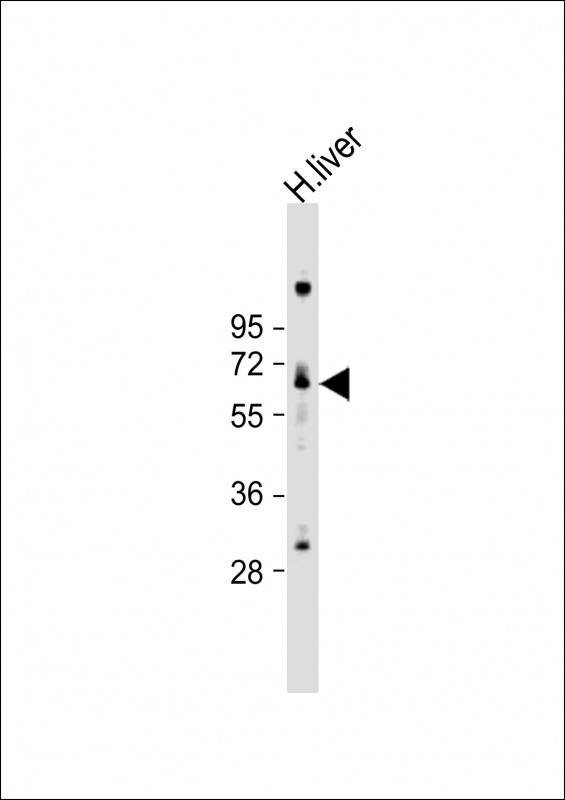

| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
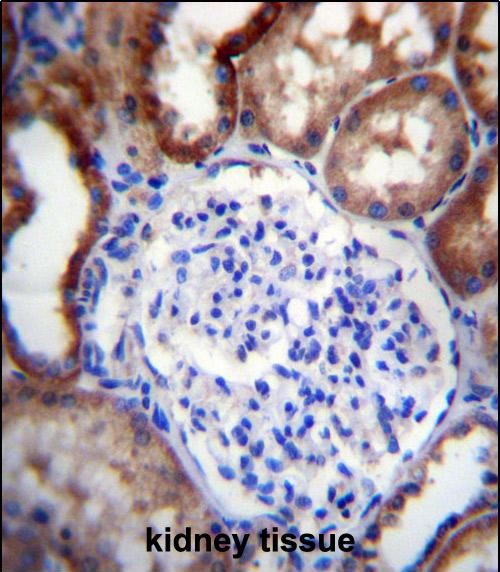
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Leucine-rich repeat and immunoglobulin-like domain-containing nogo receptor-interacting protein 4, Leucine-rich repeat neuronal protein 6D, LINGO4, LRRN6D |
| Entrez GeneID | 339398 |
| WB Predicted band size | 63.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This LINGO4 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 543-571 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human LINGO4. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于LINGO4抗体的假设性参考文献示例(实际文献可能需要进一步验证):
---
1. **文献名称**:*LINGO4 regulates neuronal survival and synaptic plasticity in the developing brain*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用LINGO4特异性抗体进行免疫印迹和免疫荧光分析,发现LINGO4在小鼠大脑发育过程中动态表达,并通过调控TrkB信号通路影响神经元存活和突触可塑性。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Monoclonal antibody targeting LINGO4 inhibits tumor growth in colorectal cancer models*
**作者**:Kim S, et al.
**摘要**:开发了一种靶向LINGO4的单克隆抗体,实验显示其能特异性结合LINGO4蛋白并抑制结直肠癌细胞增殖,提示其作为潜在肿瘤治疗手段的价值。
---
3. **文献名称**:*LINGO4 expression and function in autoimmune demyelination*
**作者**:Müller R, et al.
**摘要**:通过抗LINGO4抗体检测多发性硬化症模型中的表达,发现LINGO4在病变区域少突胶质细胞中上调,可能参与脱髓鞘病理过程,为疾病机制研究提供新方向。
---
4. **文献名称**:*Generation and validation of a polyclonal antibody against human LINGO4*
**作者**:Guo Y, et al.
**摘要**:报道了一种高特异性兔源多克隆抗体的制备与验证,该抗体可应用于免疫组化和流式细胞术,为LINGO4的蛋白质定位及功能研究提供了工具。
---
**备注**:若实际文献检索结果有限,建议确认“LINGO4”名称准确性或扩展检索至相关蛋白家族(如LINGO-1/2)。
LINGO4 (Leucine-rich repeat and immunoglobulin-like domain-containing Nogo receptor-interacting protein 4) is a transmembrane protein belonging to the LINGO family, primarily expressed in the central nervous system. It shares structural homology with other LINGO family members, such as LINGO1. which is known for its role in regulating myelination and neuronal survival. While LINGO1 has been extensively studied in conditions like multiple sclerosis and spinal cord injury, LINGO4 remains less characterized. Emerging research suggests LINGO4 may function as a co-receptor in signaling pathways influencing axonal guidance, synaptic plasticity, and neural repair. It interacts with other receptors, such as the Nogo-66 receptor (NgR1) and p75/TROY, to activate RhoA signaling, which inhibits neurite outgrowth and neuronal regeneration.
Antibodies targeting LINGO4 are primarily investigational tools to elucidate its biological roles. Preclinical studies propose that inhibiting LINGO4 might promote remyelination or mitigate neurodegenerative processes, though its exact pathological contributions remain unclear. Unlike LINGO1-targeted therapies (e.g., opicinumab for multiple sclerosis), LINGO4 antibodies have not yet advanced to clinical trials, reflecting the need for deeper mechanistic insights. Challenges include distinguishing LINGO4-specific functions from overlapping roles with other LINGO proteins and identifying its precise ligands or interaction partners. Current applications focus on immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and functional assays to map LINGO4 expression patterns and validate its involvement in neurological disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease or neuropathic pain. Further studies are essential to assess its therapeutic potential in neuroregeneration and demyelinating diseases.
×