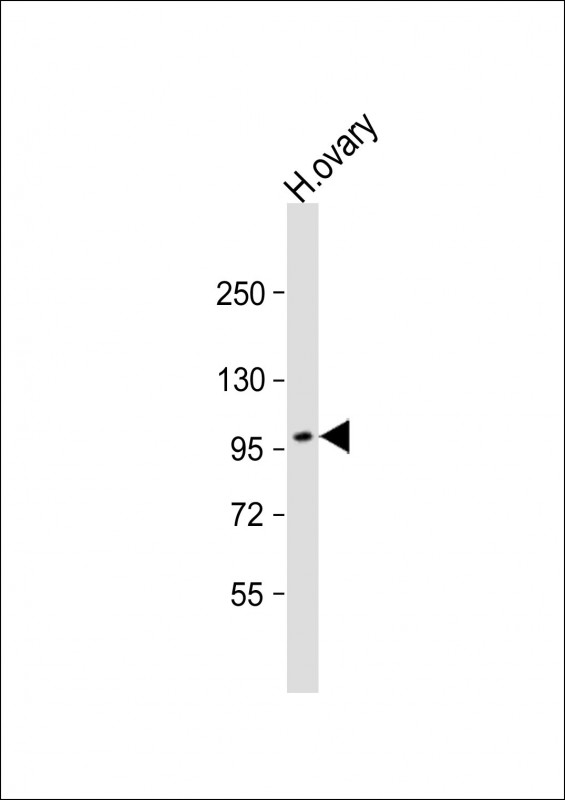
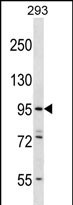

| WB | 1/500-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Espin-like protein, ESPNL |
| Entrez GeneID | 339768 |
| WB Predicted band size | 108.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This ESPNL antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 903-932 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human ESPNL. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于ESPNL(Espin-like)抗体的3篇代表性文献,包含文献名称、作者及摘要概述:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Espin: An actin cytoskeletal regulator essential for hearing and balance*
**作者**:Sekerková, G., Zheng, L., Loomis, P.A., Mugnaini, E., Bartles, J.R.
**摘要**:本文揭示了Espin蛋白通过调控肌动蛋白束的形成,对耳蜗毛细胞静纤毛的结构和功能至关重要。研究使用特异性抗体验证了Espin在内耳组织中的定位,并发现其突变可导致听力损失。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against espin*
**作者**:Zheng, L., Sekerková, G., Bartles, J.R.
**摘要**:该研究报道了针对Espin蛋白的单克隆抗体的制备与表征。通过免疫印迹和免疫荧光验证了抗体在检测内耳组织及转染细胞中Espin的特异性,为后续功能研究提供工具。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Espin gene mutations cause autosomal dominant hearing loss*
**作者**:Naz, S., Griffith, A.J., Riazuddin, S., et al.
**摘要**:文章发现ESPN基因显性突变与非综合征型听力障碍相关,通过Espin抗体检测患者成纤维细胞,显示突变导致蛋白表达异常,提示其在内耳发育中的关键作用。
---
**备注**:ESPNL抗体相关研究多集中于“Espin”蛋白(听觉相关),若需更特定于“ESPNL”的文献,建议补充基因编号或研究背景以精准检索。
The ESPN-like (ESPNL) protein, a member of the espin family, is an actin-binding protein involved in regulating cytoskeletal dynamics, particularly in specialized cell structures like stereocilia of inner ear hair cells and microvilli. Espins are critical for maintaining the structure and function of these mechanosensory organelles, which are essential for hearing and balance. Mutations in espin genes, including ESPN, are linked to hereditary deafness and vestibular dysfunction. ESPNL shares functional similarities with espin, including actin-bundling activity, but its distinct expression patterns and regulatory roles remain under investigation.
ESPNL antibodies are valuable tools for studying the protein's localization, expression levels, and interactions in tissues. They are used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to explore ESPNL's role in cellular morphogenesis, mechanotransduction, and disease mechanisms. Research has focused on its contribution to hearing loss models, neuroepithelial development, and pathologies involving cytoskeletal defects, such as neurodegenerative disorders. These antibodies also aid in characterizing ESPNL isoforms and post-translational modifications, providing insights into its functional diversity. By enabling precise detection, ESPNL antibodies support efforts to unravel its physiological significance and potential as a therapeutic target for sensory disorders.
×