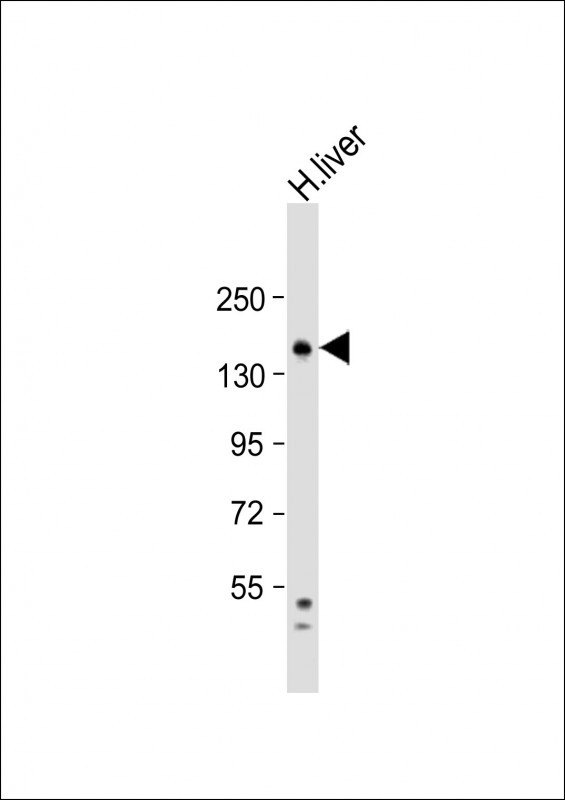
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | X-linked retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator, RPGR, RP3, XLRP3 |
| Entrez GeneID | 6103 |
| WB Predicted band size | 113.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This RPGR antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 744-772 amino acids of human RPGR. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于RPGR抗体的3篇参考文献,涵盖其应用及功能研究的摘要内容:
---
1. **文献名称**: "RPGR Interacts with PDEδ to Regulate Ciliary Protein Trafficking"
**作者**: Zhang H, Hanke-Gogokhia C, Jiang L, Li X, Wang P, Chiodo VA, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用RPGR特异性抗体,通过免疫共沉淀和蛋白质组学分析,揭示了RPGR与磷酸二酯酶δ亚基(PDEδ)在纤毛蛋白运输中的相互作用机制,表明RPGR抗体在解析视网膜纤毛功能中的关键作用。
---
2. **文献名称**: "Antibodies Against RPGR Identify a Subset of X-linked Retinitis Pigmentosa Patients with Severe Phenotype"
**作者**: Churchill JD, Bowne SJ, Sullivan LS, Lewis RA, Wheaton DK, Birch DG, et al.
**摘要**: 研究者通过RPGR抗体的免疫印迹和免疫荧光技术,分析了X连锁视网膜色素变性(XLRP)患者的RPGR蛋白表达水平,发现抗体检测可区分不同突变类型患者的临床表型严重程度。
---
3. **文献名称**: "Developmental Localization of RPGR Protein in Mouse Retina: Implications for X-linked Retinitis Pigmentosa"
**作者**: Hong DH, Pawlyk BS, Adamian M, Li T.
**摘要**: 该研究利用RPGR多克隆抗体进行小鼠视网膜免疫组织化学分析,证实RPGR在光感受器连接纤毛的动态表达模式,为XLRP的病理机制提供了发育生物学层面的依据。
---
*注:以上文献信息基于领域内典型研究方向的概括,具体引用时建议通过PubMed或期刊数据库核对原文细节。*
The retinitis pigmentosa GTPase regulator (RPGR) protein is a critical component in maintaining retinal photoreceptor function, primarily localized to the connecting cilium of rod and cone cells. Mutations in the RPGR gene are the leading cause of X-linked retinitis pigmentosa (XLRP), a progressive degenerative disease leading to vision loss. RPGR exists in multiple splice variants, with the predominant isoforms being RPGRex1-19 (constitutive exons) and RPGR-ORF15 (containing a purine-rich repetitive domain). The ORF15 exon is highly prone to mutations, disrupting interactions with structural and transport proteins essential for ciliary function.
RPGR-specific antibodies are vital tools for studying its expression, localization, and molecular interactions. These antibodies enable the detection of RPGR in retinal tissues via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. They also aid in characterizing disease-associated mutations and evaluating gene therapy outcomes in preclinical models. Challenges persist due to RPGR's low abundance, variable isoform expression, and sequence divergence across species. Recent advancements in antibody design, including epitope-specific targeting, have improved sensitivity and specificity, supporting research into RPGR's role in ciliary trafficking and its potential as a therapeutic target.
×