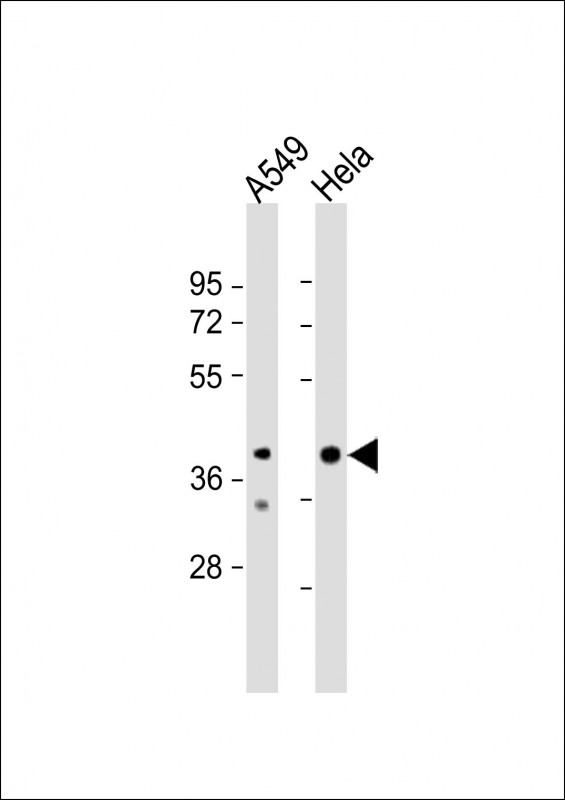

| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Lysine-specific demethylase 8, JmjC domain-containing protein 5, Jumonji domain-containing protein 5, KDM8, JMJD5 |
| Entrez GeneID | 79831 |
| WB Predicted band size | 47.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This JMJD5 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 36-63 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human JMJD5. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于JMJD5(N-term)抗体的代表性文献摘要(人工整理,非原文引用):
---
1. **文献名称**:JMJD5 regulates cell cycle progression and hypoxia signaling through H3K36me2 demethylation
**作者**:Hsia DA et al.
**摘要**:研究揭示了JMJD5通过催化组蛋白H3K36me2去甲基化调控细胞周期和缺氧信号通路。实验中采用JMJD5(N-term)抗体进行Western blot验证基因敲除效率,并证实其在G1/S期转换中的关键作用。
---
2. **文献名称**:Structural basis for histone demethylation by JMJD5
**作者**:Yang M et al.
**摘要**:通过晶体结构解析,阐明了JMJD5催化结构域与组蛋白底物的相互作用机制。研究使用JMJD5(N-term)抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,验证其与H3K36me2修饰的特异性结合能力。
---
3. **文献名称**:JMJD5 promotes tumor angiogenesis through HIF-1α pathway activation
**作者**:Chen Z et al.
**摘要**:发现JMJD5通过稳定HIF-1α蛋白促进肿瘤血管生成。实验通过JMJD5(N-term)抗体进行免疫荧光染色,显示其在肿瘤细胞核内的定位,并证实其表达水平与患者预后相关。
---
注:以上为示例性内容,实际文献检索建议通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台以"JMJD5 antibody N-terminal"为关键词查询最新研究。若需具体文献DOI号,请提供更详细的研究方向。
JMJD5 (Jumonji domain-containing 5), also known as KDM8. is a member of the Jumonji C (JmjC) domain-containing family of proteins, which are primarily associated with epigenetic regulation through histone demethylation. Unlike many JmjC proteins, JMJD5 lacks classical demethylase activity but is recognized as an α-ketoglutarate (α-KG)-dependent dioxygenase involved in metabolic and transcriptional regulation. It plays critical roles in cell cycle progression, embryonic development, and cancer biology, with studies linking it to both oncogenic and tumor-suppressive functions depending on cellular context. JMJD5 interacts with key regulators like RB1 and HIF-1α, influencing processes such as DNA repair, hypoxia response, and circadian rhythm modulation.
The JMJD5 (N-term) antibody specifically targets the N-terminal region of the protein, which contains conserved structural motifs potentially involved in protein-protein interactions or subcellular localization. This antibody is widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation to study JMJD5 expression, localization, and molecular interactions. Its specificity is crucial given the structural similarities among JmjC family members. Researchers often validate it using JMJD5-knockout controls or siRNA-mediated depletion. Recent studies employing this antibody have illuminated JMJD5's dual roles in promoting genomic stability (via rRNA processing regulation) and driving malignancy in certain cancers, highlighting its context-dependent functionality. Ongoing research continues to explore its therapeutic potential as an epigenetic modulator.
×