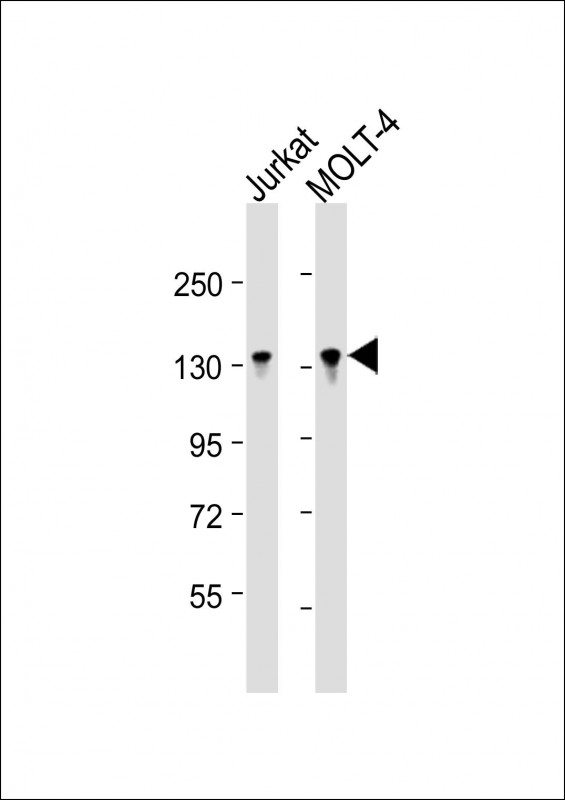
| WB | 1/16000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | B-cell lymphoma/leukemia 11B, BCL-11B, B-cell CLL/lymphoma 11B, COUP-TF-interacting protein 2, Radiation-induced tumor suppressor gene 1 protein, hRit1, BCL11B, CTIP2, RIT1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 64919 |
| WB Predicted band size | 95.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This BCL11B antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 307-334 amino acids from the Central region of human BCL11B. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于BCL11B抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*BCL11B is required for positive selection and survival of double-positive thymocytes*
**作者**:Albu, D.I. et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用BCL11B特异性抗体(如免疫沉淀和免疫荧光染色),揭示了BCL11B在T细胞发育中的关键作用,证明其缺失导致双阳性胸腺细胞存活和阳性选择缺陷,影响T细胞受体信号通路。
2. **文献名称**:*BCL11B sustains proliferation of adult T-cell leukemia cells by stabilizing STAT5A signaling*
**作者**:Liu, H. et al.
**摘要**:通过Western blot和免疫组化(使用BCL11B抗体),研究发现成人T细胞白血病中BCL11B异常高表达,并通过稳定STAT5A信号通路促进癌细胞增殖,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点。
3. **文献名称**:*Conditional ablation of Bcl11b in postnatal mice causes growth retardation and lymphoid organ atrophy*
**作者**:Punwani, D. et al.
**摘要**:利用BCL11B抗体进行组织染色和流式分析,发现小鼠中条件性敲除Bcl11B会导致胸腺萎缩、T细胞发育阻滞及外周淋巴器官功能异常,强调其对免疫系统稳态的维持作用。
4. **文献名称**:*BCL11B regulates tumor progression in human non-small cell lung cancer*
**作者**:Yu, Y. et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化(BCL11B抗体)和基因沉默实验,研究证实BCL11B在非小细胞肺癌中高表达,并通过调控细胞周期相关基因促进肿瘤增殖和转移,提示其临床预后价值。
这些研究均依赖BCL11B抗体进行蛋白定位、表达水平检测或功能分析,涵盖基础机制到疾病关联的探索。
BCL11B (B-cell lymphoma/leukemia 11B) is a zinc-finger transcription factor encoded by the BCL11B gene, primarily involved in immune regulation, neurodevelopment, and cellular differentiation. It plays critical roles in T-cell maturation, neuronal circuit formation, and hematopoietic stem cell maintenance. Dysregulation of BCL11B is linked to T-cell malignancies (e.g., T-ALL, lymphomas), neurodevelopmental disorders, and immune dysfunction.
BCL11B antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function in both normal and pathological contexts. These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence (IF), and flow cytometry to detect BCL11B protein levels in tissues or cell lines. Commercially available antibodies target specific epitopes, often validated for cross-reactivity and specificity across species (human, mouse, rat).
Research utilizing BCL11B antibodies has clarified its role in suppressing oncogenic pathways, maintaining T-cell identity, and regulating epigenetic modifiers. In diagnostics, BCL11B expression patterns aid in classifying T-cell neoplasms and assessing disease progression. Challenges include distinguishing BCL11B from its homolog BCL11A and optimizing detection in low-abundance samples. Recent studies also explore its therapeutic potential as a biomarker or target in cancers and neurological diseases.
×