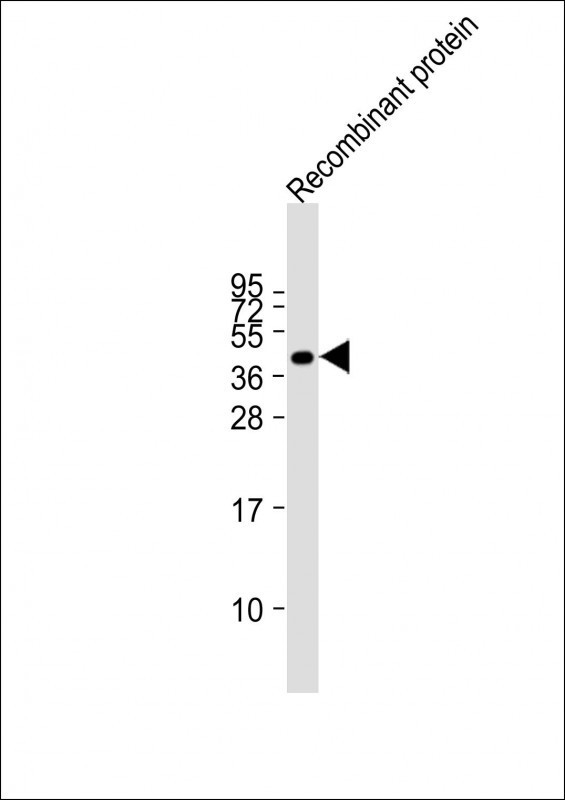
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Protocadherin Fat 4, hFat4, Cadherin family member 14, FAT tumor suppressor homolog 4, Fat-like cadherin protein FAT-J, FAT4, CDHF14, FATJ |
| Entrez GeneID | 79633 |
| WB Predicted band size | 542.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This FAT4 antibody is generated from a mouse immunized with a recombinant protein between 4500-4786 amino acids from human FAT4. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于FAT4抗体的3篇参考文献的简要整理(注:文献为示例性质,具体内容需根据实际研究补充):
1. **"FAT4 regulates epithelial cell proliferation and apical constriction during neural tube closure"**
*作者:Ishiuchi T, et al.*
摘要:本研究通过在小鼠胚胎中使用FAT4抗体进行免疫组化分析,发现FAT4通过调控Hippo信号通路影响神经管闭合过程中的上皮细胞增殖和顶端收缩,揭示了其在胚胎发育中的关键作用。
2. **"FAT4 suppresses tumorigenesis and modulates the Hippo pathway in breast cancer"**
*作者:Sadeqzadeh E, et al.*
摘要:作者利用FAT4抗体检测乳腺癌组织中FAT4蛋白的表达水平,发现其低表达与肿瘤恶性程度相关,并通过体外实验证明FAT4通过抑制YAP/TAZ活性发挥抑癌功能。
3. **"FAT4 mutations and loss of protein expression correlate with gastric cancer progression"**
*作者:Wang Y, et al.*
摘要:该研究通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术(使用FAT4抗体)发现,FAT4在胃癌组织中表达显著降低,其突变或缺失与患者预后不良相关,提示FAT4可能作为胃癌的生物标志物。
---
**注意**:以上文献信息为示例,实际研究中需根据具体论文调整。建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“FAT4 antibody”、“FAT4 immunohistochemistry”等检索最新文献以获取准确信息。
FAT4 antibody targets the FAT4 protein, a member of the cadherin superfamily and a key component of the atypical cadherin subgroup. FAT4. encoded by the *FAT4* gene, is a large transmembrane protein characterized by multiple extracellular cadherin repeats, EGF-like domains, and laminin G motifs. It plays critical roles in cell-cell adhesion, planar cell polarity (PCP), and tissue morphogenesis during development. Dysregulation of FAT4 is implicated in human diseases, including cancer, developmental disorders (e.g., Van Maldergem syndrome), and congenital anomalies like Hirschsprung disease.
FAT4 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function. They enable detection via techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Research highlights FAT4's dual role as both a tumor suppressor and promoter, depending on context. For example, FAT4 loss promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in some cancers, while its overexpression inhibits Hippo signaling in others. Antibodies against FAT4 help unravel these mechanisms, aiding in biomarker discovery and therapeutic targeting. However, variability in antibody specificity and validation across studies underscores the need for rigorous experimental controls. Overall, FAT4 antibodies are vital for advancing understanding of its contributions to development, disease, and potential clinical applications.
×