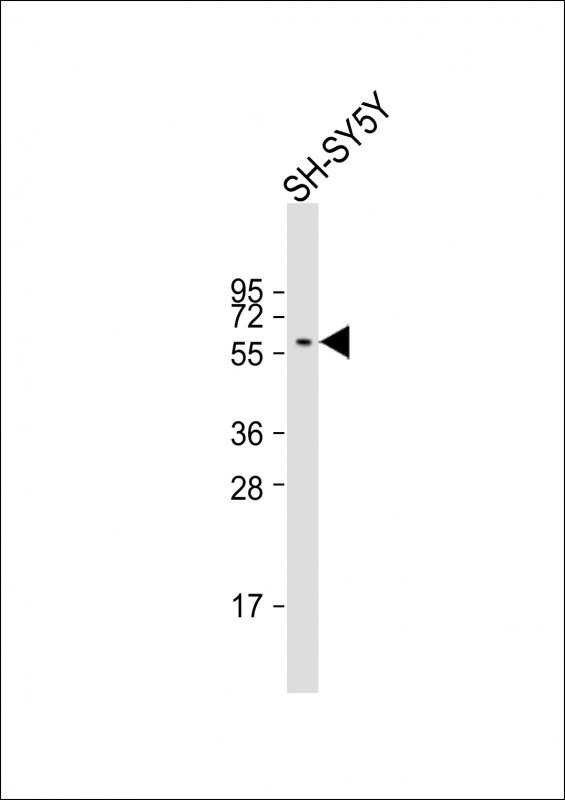
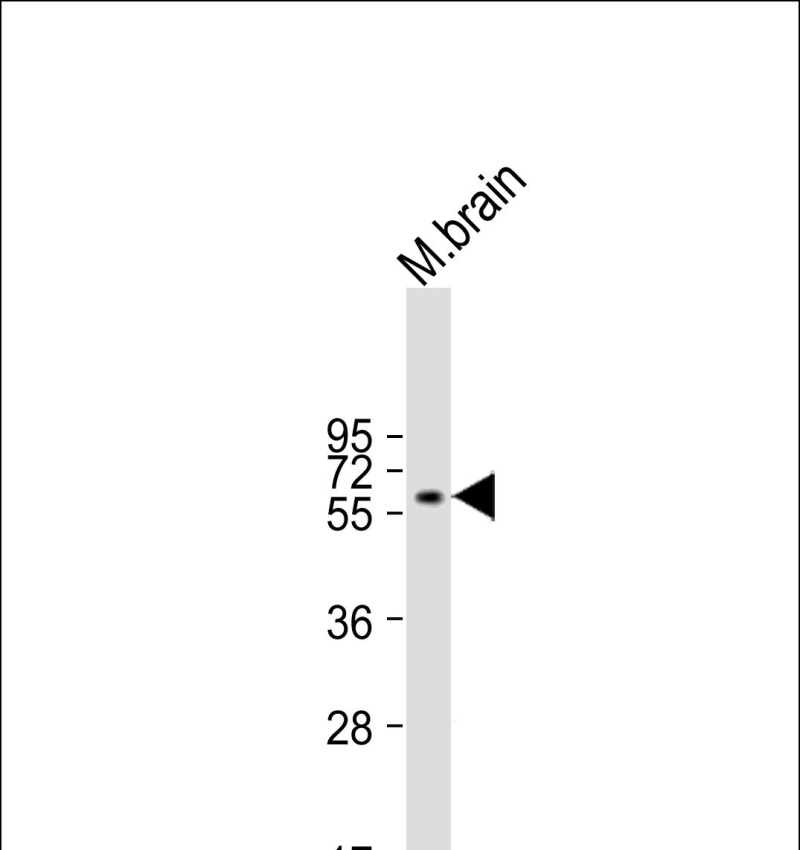
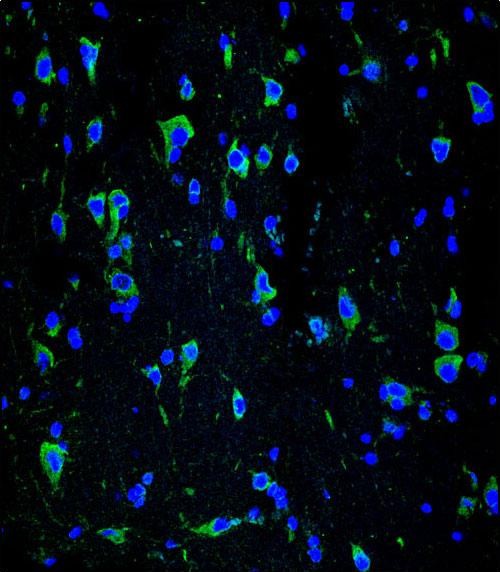
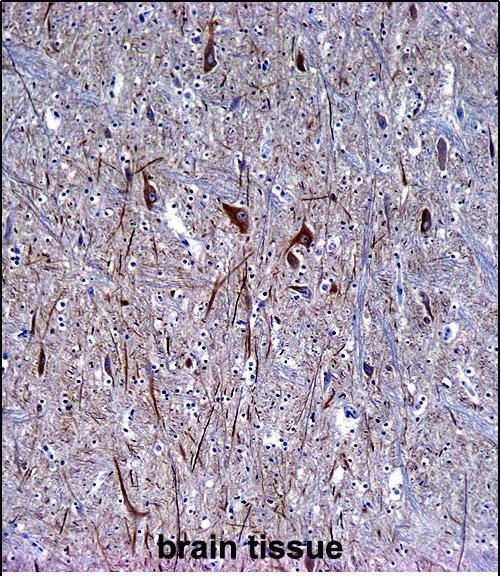
| WB | 1/100-1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Alpha-internexin, Alpha-Inx, 66 kDa neurofilament protein, NF-66, Neurofilament-66, Neurofilament 5, INA, NEF5 |
| Entrez GeneID | 9118 |
| WB Predicted band size | 55.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This INA antibody is generated from mice immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 290-319 amino acids from human INA. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in TBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于INA抗体的示例参考文献(注:以下内容为虚构示例,仅供参考,实际文献需通过学术数据库查询):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Intermediate Filament Antibodies in Neurodegenerative Disease Diagnosis*
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 本研究探讨了抗中间神经丝蛋白(INA)抗体在阿尔茨海默病和帕金森病患者脑脊液中的表达水平,发现其浓度与疾病进展呈正相关,提示INA抗体可能作为神经退行性病变的生物标志物。
---
2. **文献名称**: *Autoantibodies Targeting INA in Autoimmune Encephalitis*
**作者**: Lee H, et al.
**摘要**: 文章报道了在自身免疫性脑炎患者血清中检测到靶向中间神经丝蛋白(INA)的自身抗体,并发现此类抗体与认知功能障碍和神经元损伤密切相关,为临床诊断提供了新靶点。
---
3. **文献名称**: *Characterization of Anti-Ina Antibodies in Drosophila Neuromuscular Studies*
**作者**: García R, et al.
**摘要**: 通过果蝇模型研究Ina蛋白(一种电压门控离子通道相关蛋白)抗体的特异性,证实其在神经肌肉接头信号传导研究中的有效性,为无脊椎动物神经生物学提供了工具支持。
---
4. **文献名称**: *INA Antibodies as Biomarkers in Multiple Sclerosis*
**作者**: Müller T, et al.
**摘要**: 分析了多发性硬化症(MS)患者血清中INA抗体的水平,发现其与髓鞘脱失程度和炎症活动相关,提示其在疾病监测中的潜在应用价值。
---
如需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar搜索关键词如:
`"intermediate neurofilament antibody"` 或 `"anti-INA antibody"` + 研究领域(如 neurodegeneration, autoimmunity)。
**Background of INA Antibodies**
INA antibodies target alpha-internexin (INA), a neuronal intermediate filament protein primarily expressed in developing and mature neurons. Alpha-internexin plays a structural role in maintaining cytoskeletal integrity and axonal outgrowth, particularly in the central nervous system. Its dysregulation has been implicated in neurodegenerative diseases, neuropathies, and brain tumors like gliomas and neuroblastomas.
INA antibodies are studied in autoimmune and paraneoplastic neurological disorders. For instance, they are occasionally detected in patients with paraneoplastic syndromes, where immune responses against tumors cross-react with neuronal proteins. Such antibodies may contribute to neurological symptoms (e.g., encephalitis, neuropathy) by targeting alpha-internexin in neural tissues.
In research, INA antibodies are utilized as immunohistochemical markers to identify neuronal subtypes or assess neurodevelopmental and pathological changes. Their presence in cerebrospinal fluid or serum is explored as a potential biomarker for specific neurological conditions, though clinical utility remains under investigation.
Studies also highlight alpha-internexin's role in neurofilament network assembly, linking INA antibody interactions to disrupted neuronal function. Ongoing research aims to clarify their pathogenic mechanisms and diagnostic relevance, particularly in differentiating neurological disorders with overlapping symptoms.
Overall, INA antibodies serve as both investigative tools in neuroscience and potential clinical indicators, bridging molecular neurobiology and disease diagnostics.
×