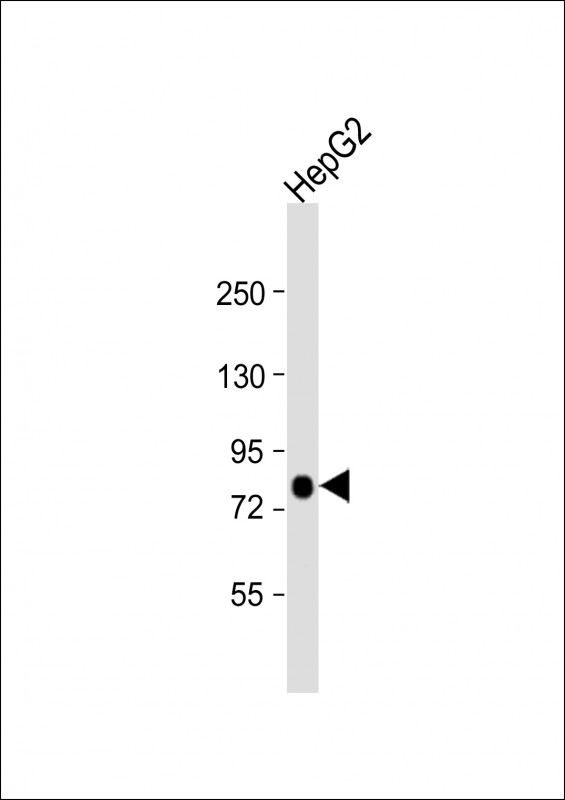
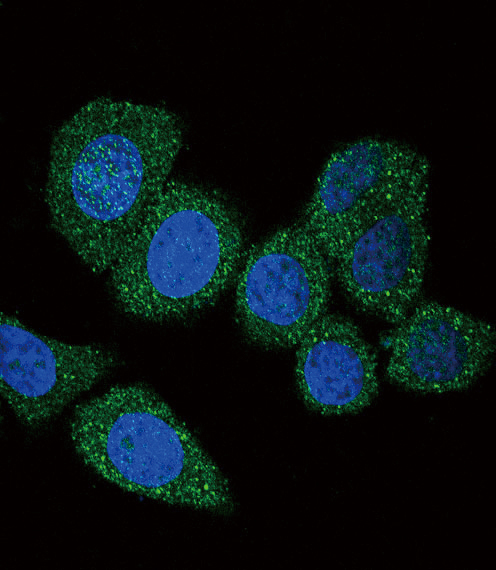
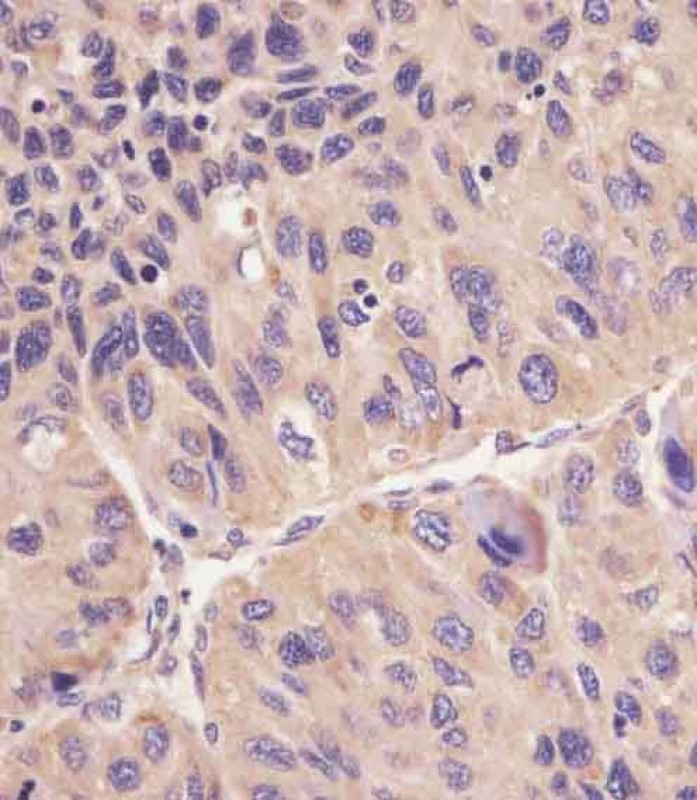
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Long-chain-fatty-acid--CoA ligase 4, Long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase 4, LACS 4, ACSL4, ACS4, FACL4, LACS4 |
| Entrez GeneID | 2182 |
| WB Predicted band size | 79.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This ACSL4 (FACL4) antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 236-267 amino acids from the Central region of human ACSL4 (FACL4). |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
以下是关于ACSL4(FACL4)抗体的3篇参考文献,包含文献名称、作者及摘要概括:
1. **文献名称**:*ACSL4 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by shaping cellular lipid composition*
**作者**:Doll, S. et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过ACSL4特异性抗体(Western blot和免疫荧光)揭示ACSL4在调控细胞铁死亡(ferroptosis)中的关键作用。发现ACSL4通过促进多不饱和脂肪酸(PUFA)的酯化,驱动脂质过氧化,从而决定细胞对铁死亡的敏感性。
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting ACSL4 suppresses tumor growth in hepatocellular carcinoma*
**作者**:Yuan, H. et al.
**摘要**:研究利用ACSL4抗体(免疫组化)分析肝癌组织中ACSL4的表达水平,发现其高表达与患者不良预后相关。通过基因敲低实验证明抑制ACSL4可减少肿瘤细胞增殖并诱导凋亡,提示其作为肝癌治疗靶点的潜力。
3. **文献名称**:*ACSL4 is overexpressed in triple-negative breast cancer and promotes metastasis via Wnt/β-catenin signaling*
**作者**:Wu, X. et al.
**摘要**:通过ACSL4抗体(Western blot和免疫荧光)检测三阴性乳腺癌细胞系及组织样本,发现ACSL4高表达与肿瘤转移相关。机制研究表明,ACSL4通过激活Wnt/β-catenin通路增强肿瘤细胞的侵袭能力。
4. **文献名称**:*FACL4. a new gene encoding long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase 4. is induced by retinoids and modifies lipid metabolism in mammalian cells*
**作者**:Meloni, I. et al.
**摘要**:早期研究利用FACL4(ACSL4)抗体鉴定其在哺乳动物细胞中的表达模式,发现视黄酸可显著上调FACL4表达。进一步实验表明FACL4参与脂质代谢重编程,影响细胞膜磷脂组成及信号传导。
这些研究均通过ACSL4抗体验证其在疾病机制或代谢调控中的功能,涵盖肿瘤生物学、细胞死亡和脂代谢等领域。
The ACSL4 (Acyl-CoA Synthetase Long Chain Family Member 4), also known as FACL4. is an enzyme encoded by the ACSL4 gene. It belongs to the acyl-CoA synthetase family, which catalyzes the activation of long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs) into acyl-CoA esters, a critical step in lipid metabolism. These acyl-CoA derivatives are utilized in diverse cellular processes, including membrane phospholipid synthesis, energy production via β-oxidation, and lipid-mediated signaling pathways. ACSL4 exhibits a distinct substrate preference for polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), such as arachidonic acid, influencing membrane composition and inflammatory responses.
ACSL4 antibodies are widely used in research to study the enzyme's expression, localization, and function. They help detect ACSL4 in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Studies have linked ACSL4 dysregulation to pathologies, including cancers (e.g., breast, liver, and prostate), where its overexpression often correlates with tumor progression, metastasis, and therapy resistance. Additionally, ACSL4 plays a key role in ferroptosis, a form of iron-dependent cell death driven by lipid peroxidation, making it a therapeutic target in cancer and neurodegenerative diseases.
Genetic variants in ACSL4 are also associated with neurodevelopmental disorders, such as X-linked intellectual disability and autism spectrum disorders. Research using ACSL4 antibodies aims to unravel its tissue-specific roles and regulatory mechanisms, offering insights into metabolic reprogramming in disease contexts.
×