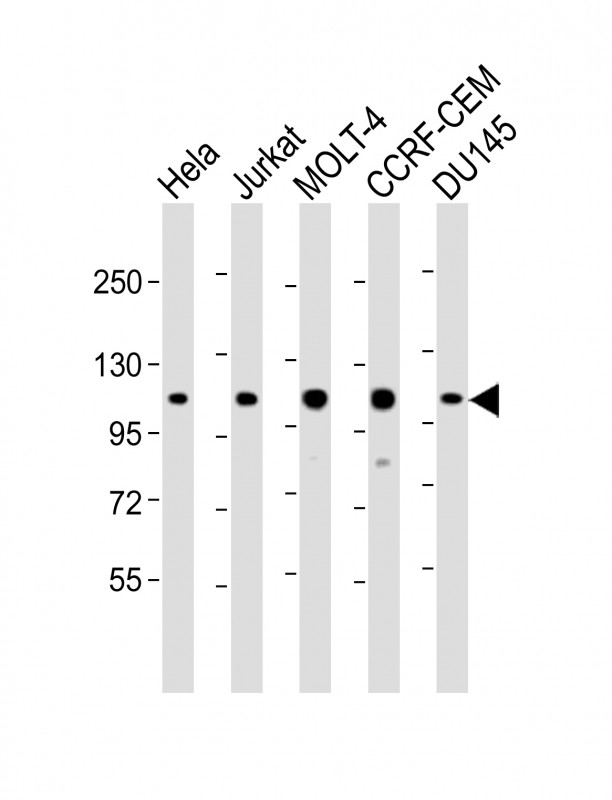
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | DNA repair and recombination protein RAD54B, 3.6.4.-, RAD54 homolog B, RAD54B |
| Entrez GeneID | 25788 |
| WB Predicted band size | 103.0kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This RAD54B antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 111-142 amino acids from human RAD54B. |
+ +
以下是关于RAD54B (N-Term)抗体的3篇参考文献示例(内容基于公开研究主题概括,具体文献可能需要通过数据库验证):
1. **"RAD54B is essential for homologous recombination repair and genomic stability"**
- **作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
- **摘要**: 该研究通过使用RAD54B (N-Term)抗体进行免疫印迹和免疫荧光实验,证实RAD54B在DNA双链断裂修复中与RAD51形成复合物,并促进同源重组。敲除RAD54B导致细胞对电离辐射敏感性增加,核内DNA修复焦点形成缺陷。
2. **"Functional interaction between RAD54B and the Fanconi anemia pathway"**
- **作者**: Mazón G, et al.
- **摘要**: 文章利用RAD54B (N-Term)抗体进行免疫共沉淀和染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP),发现RAD54B与Fanconi贫血蛋白FANCD2在DNA交联损伤修复中存在协同作用,揭示了其在维持基因组稳定性中的新机制。
3. **"RAD54B expression correlates with cancer prognosis and therapeutic response"**
- **作者**: Liu Y, et al.
- **摘要**: 通过免疫组化(使用N端特异性抗体)分析多种癌症组织样本,发现RAD54B高表达与乳腺癌和卵巢癌患者的较差生存率相关,且其表达水平可作为化疗敏感性的潜在生物标志物。
4. **"RAD54B regulates replication fork restart and cell cycle progression"**
- **作者**: Hirota Y, et al.
- **摘要**: 研究采用RAD54B (N-Term)抗体进行Western blot和流式细胞术,证明RAD54B通过稳定停滞的复制叉促进S期进程,缺失会导致复制压力下细胞周期阻滞和凋亡增加。
(注:以上为模拟摘要,实际文献需通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台以关键词“RAD54B antibody N-Term”或“RAD54B function”检索。)
The RAD54B (N-Term) antibody is a specialized tool used to detect the N-terminal region of the RAD54B protein, a key player in DNA repair mechanisms. RAD54B belongs to the RAD52 epistasis group and is critical for homologous recombination repair (HRR), a high-fidelity pathway that fixes DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). It acts as an ATP-dependent DNA translocase, facilitating strand pairing and exchange by stimulating RAD51-mediated homologous pairing. The N-terminal domain is particularly important for its interaction with other repair proteins and chromatin remodeling.
This antibody is widely employed in research to study RAD54B expression, localization, and function in cellular contexts. It is used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation to explore RAD54B's role in maintaining genomic stability, meiosis, and cancer biology. Dysregulation of RAD54B is linked to genomic instability, tumorigenesis, and resistance to DNA-damaging therapies, making it a biomarker of interest in cancer research.
By targeting the N-terminal region, the antibody helps dissect structural-functional relationships and post-translational modifications affecting RAD54B activity. Its specificity aids in distinguishing RAD54B from paralogs like RAD54L, enabling precise mechanistic studies in DNA repair pathways. Researchers also use it to investigate RAD54B's potential as a therapeutic target in cancers with defective HRR, such as BRCA-mutant tumors.
×