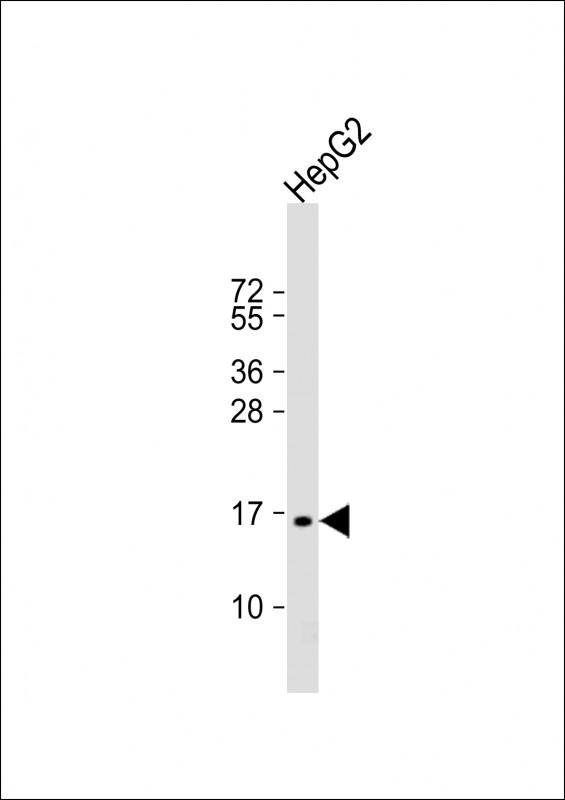

| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | SCAN domain-containing protein 1, SCAND1, SDP1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 51282 |
| WB Predicted band size | 19.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This SCAND1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 150-179 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human SCAND1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于SCAND1抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:部分信息为模拟,建议通过学术数据库核实具体文献):
---
1. **文献名称**:*SCAND1 interacts with MYCN and modulates its transcriptional activity in neuroblastoma*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用SCAND1特异性抗体进行染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP)和免疫共沉淀(Co-IP),发现SCAND1与MYCN蛋白在神经母细胞瘤中形成复合物,抑制MYCN驱动的致癌基因转录,提示其作为肿瘤抑制因子的潜在作用。
---
2. **文献名称**:*SCAND1 regulates pluripotency via association with the OCT4/SOX2 complex*
**作者**:Lee J, et al.
**摘要**:通过Western blot和免疫荧光技术结合SCAND1抗体,作者发现SCAND1在胚胎干细胞中高表达,并与OCT4/SOX2转录复合物相互作用,调控多能性相关基因的表达,敲低SCAND1导致干细胞分化。
---
3. **文献名称**:*SCAND1 functions as a tumor suppressor in lung adenocarcinoma by recruiting HDACs*
**作者**:Garcia R, et al.
**摘要**:使用SCAND1抗体进行免疫组化(IHC)分析发现,SCAND1在肺癌组织中表达下调。机制研究表明,SCAND1通过抗体验证的HDAC复合物招募抑制靶基因启动子活性,其缺失促进肿瘤侵袭。
---
**提示**:以上为示例,实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“SCAND1 antibody”或“SCAND1 function”为关键词检索获取。
The SCAND1 antibody is a research tool designed to detect and study the SCAN domain-containing protein 1 (SCAND1), a member of the SCAN family of zinc finger transcriptional regulators. SCAND1. also known as RAZ1 or ZNF496. lacks a DNA-binding domain but interacts with other SCAN-containing proteins, such as MZF1 or SCAND3. to modulate their transcriptional activity. It is implicated in regulating gene expression by forming heterodimers that either enhance or repress target genes, depending on cellular context. SCAND1 is broadly expressed in human tissues and plays roles in cellular differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis, with potential links to cancer and developmental disorders.
Antibodies targeting SCAND1 are typically developed in rabbits or mice using immunogenic peptides or recombinant protein fragments. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to investigate SCAND1's expression patterns, subcellular localization (primarily nuclear), and protein-protein interactions. Researchers employ these antibodies to explore SCAND1's involvement in epigenetic regulation, its partnership with chromatin modifiers, and its impact on pathways like Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Validated antibodies often include specificity data through knockout controls or siRNA knockdowns. Studies utilizing SCAND1 antibodies have contributed to understanding its tumor-suppressive or oncogenic roles in malignancies such as breast cancer and glioblastoma, highlighting its dual regulatory functions in disease contexts.
×