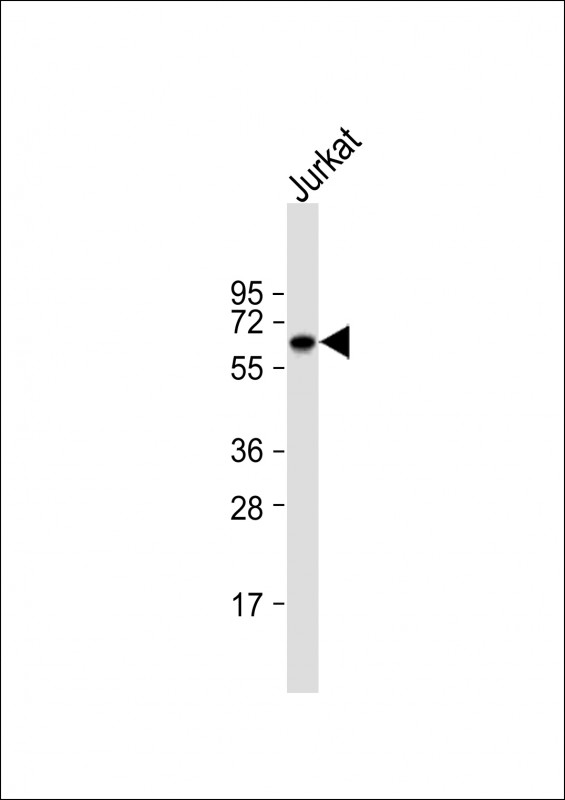
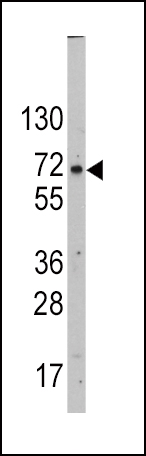
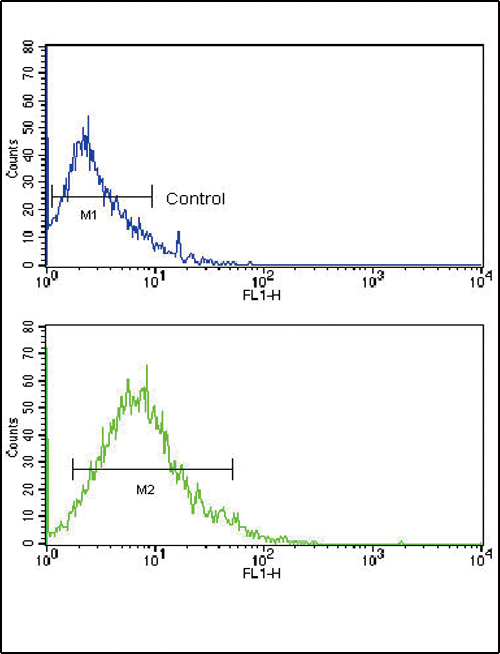
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 2, Glucose transporter type 2, liver, GLUT-2, SLC2A2, GLUT2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 6514 |
| WB Predicted band size | 57.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This GLUT2 (SLC2A2) antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 31-60 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human GLUT2 (SLC2A2). |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
以下是关于GLUT2 (SLC2A2) (N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献,包含文献名称、作者及摘要内容概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: "Cloning and functional expression in bacteria of a novel glucose transporter present in liver, intestine, kidney, and β-pancreatic islet cells"
**作者**: Thorens, B. et al.
**摘要**: 该研究首次克隆了GLUT2基因,并通过抗N端抗体在Western blot和免疫组化中验证其在肝脏、胰岛β细胞等组织中的特异性表达,揭示了其在葡萄糖感知中的关键作用。
---
2. **文献名称**: "Early diabetes and abnormal postnatal pancreatic islet development in mice lacking Glut2"
**作者**: Guillam, M.T. et al.
**摘要**: 利用N端GLUT2抗体研究GLUT2敲除小鼠,发现其胰岛β细胞发育异常及糖尿病表型,证实GLUT2对胰岛素分泌和血糖稳态的调控至关重要。
---
3. **文献名称**: "Structure and function of the human β-cell glucose transporter (GLUT2) gene promoter"
**作者**: Stümpel, F. et al.
**摘要**: 通过抗GLUT2 N端抗体进行染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP)分析,揭示了人类GLUT2基因启动子的调控机制,及其在β细胞特异性表达中的转录因子结合位点。
---
这些文献均使用了针对GLUT2 N端的抗体进行蛋白定位、功能验证或基因调控研究,涵盖疾病模型、分子机制及生理功能解析。
The GLUT2 (SLC2A2) (N-term) antibody is designed to target the N-terminal region of the glucose transporter 2 (GLUT2) protein, encoded by the SLC2A2 gene. GLUT2 is a facilitative transporter belonging to the solute carrier family 2 (SLC2), primarily expressed in metabolically active tissues such as the liver, pancreatic β-cells, small intestine, and kidneys. It plays a critical role in glucose homeostasis by mediating bidirectional glucose transport across cell membranes, functioning as a low-affinity, high-capacity transporter. Its activity is pivotal in insulin secretion (via glucose sensing in β-cells) and hepatic glucose uptake/release.
Antibodies targeting the N-terminal domain of GLUT2 are commonly used in research to study its expression, localization, and regulatory mechanisms. The N-terminal region is implicated in transporter function, including substrate interaction and conformational changes during glucose transport. Researchers employ this antibody in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to investigate GLUT2's role in metabolic disorders such as diabetes, obesity, and Fanconi-Bickel syndrome, a rare genetic condition linked to SLC2A2 mutations. Specificity is often validated using knockout controls or peptide-blocking assays. Studies may also explore GLUT2 dysregulation in cancer, as altered glucose metabolism is a hallmark of malignancies. By visualizing GLUT2 expression patterns in tissues or cell lines, this antibody aids in understanding its physiological and pathological contributions to glucose handling and disease progression.
×