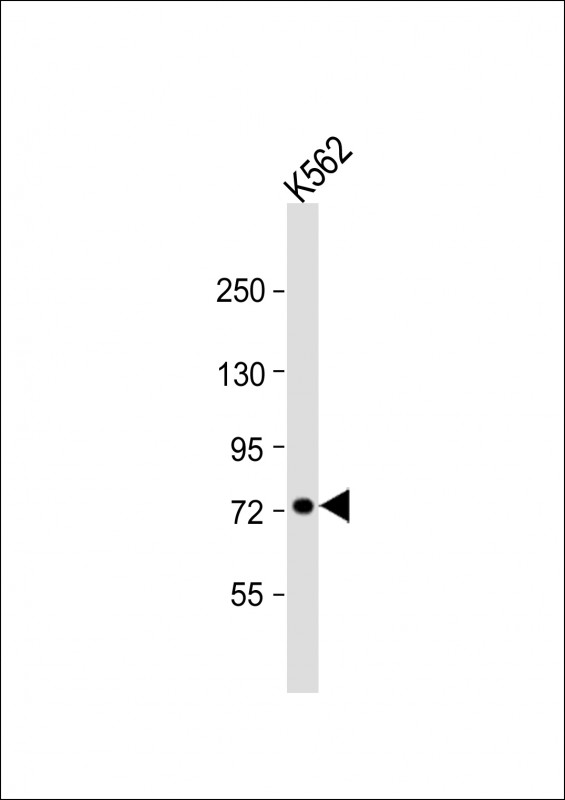
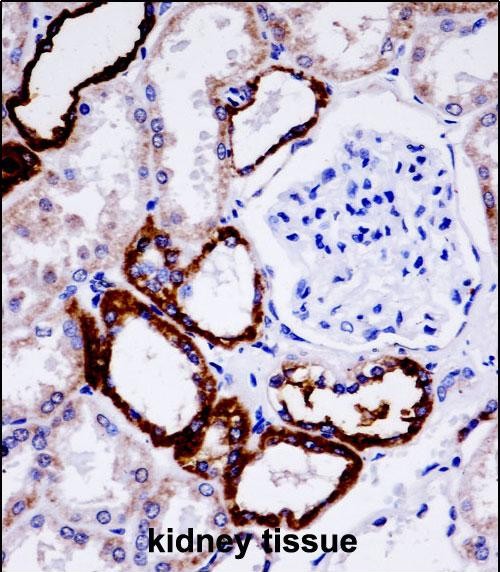
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Uromodulin, Tamm-Horsfall urinary glycoprotein, THP, Uromodulin, secreted form, UMOD |
| Entrez GeneID | 7369 |
| WB Predicted band size | 69.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This UMOD antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 352-380 amino acids from the Central region of human UMOD. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于UMOD抗体的3篇参考文献,按您的要求整理:
1. **文献名称**: "Uromodulin in Kidney Injury: Pathogenesis and Diagnostic Potential"
**作者**: Schaeffer C, et al.
**摘要**: 探讨UMOD在急性肾损伤中的表达变化,验证其作为生物标志物的潜力。研究通过Western blot和免疫组化证实UMOD抗体在检测肾小管损伤中的特异性。
2. **文献名称**: "Autoantibodies to Uromodulin in Patients with Tubulointerstitial Nephritis"
**作者**: Vyletal P, et al.
**摘要**: 发现部分间质性肾炎患者血清中存在UMOD自身抗体,提出其可能通过免疫复合物沉积加剧肾脏炎症,采用ELISA和免疫荧光法验证抗体存在。
3. **文献名称**: "Structural Insights into UMOD Polymerization and Pathogenic Mutations"
**作者**: Bokhove M, et al.
**摘要**: 解析UMOD蛋白聚合机制及突变影响,利用单克隆抗体定位关键结构域,揭示ADTKD相关突变导致UMOD异常聚集的分子机制。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例性内容,实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词(如"UMOD antibody"、"uromodulin diagnostics")获取。如需具体文章链接或补充年份/期刊信息,可进一步说明。
The uromodulin (UMOD) antibody is a tool used to detect uromodulin, a glycoprotein also known as Tamm-Horsfall protein. UMOD is primarily synthesized in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle in the kidney and is the most abundant urinary protein under physiological conditions. It plays roles in kidney defense, ion transport regulation, and innate immunity. UMOD forms filamentous polymers that trap pathogens and modulate inflammatory responses. Mutations in the *UMOD* gene are linked to autosomal dominant tubulointerstitial kidney diseases (ADTKD-UMOD), characterized by progressive renal dysfunction.
UMOD antibodies are essential in research and diagnostics to study UMOD expression, localization, and function. They are employed in techniques like immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, and ELISA to investigate UMOD-related pathologies, including chronic kidney disease, urinary tract infections, and nephrolithiasis. Additionally, UMOD antibodies aid in exploring UMOD's potential as a biomarker for kidney injury, as urinary UMOD levels correlate with tubular health. Recent studies also suggest its involvement in metabolic and inflammatory conditions, expanding its clinical relevance.
Despite its utility, UMOD antibody specificity can vary, requiring validation for accurate interpretation. Research continues to unravel UMOD's complex roles, driving demand for reliable antibodies to advance understanding of renal physiology and disease mechanisms.
×