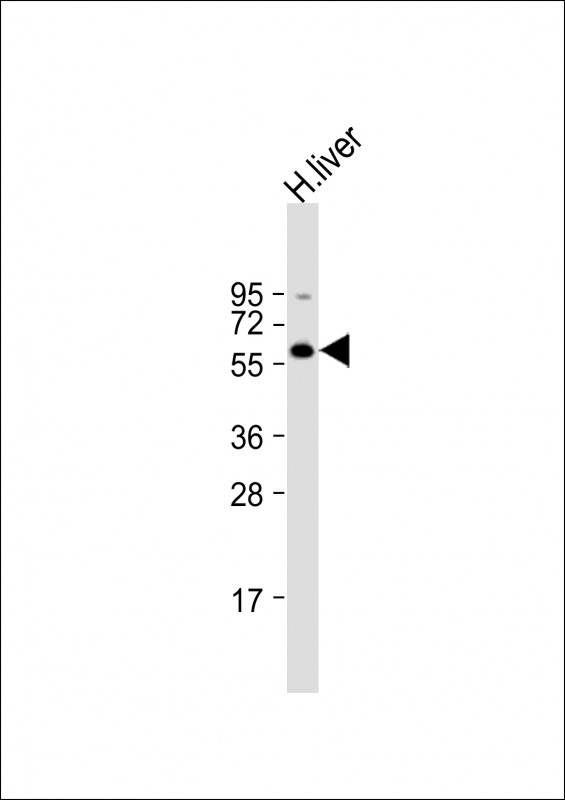
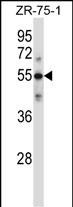
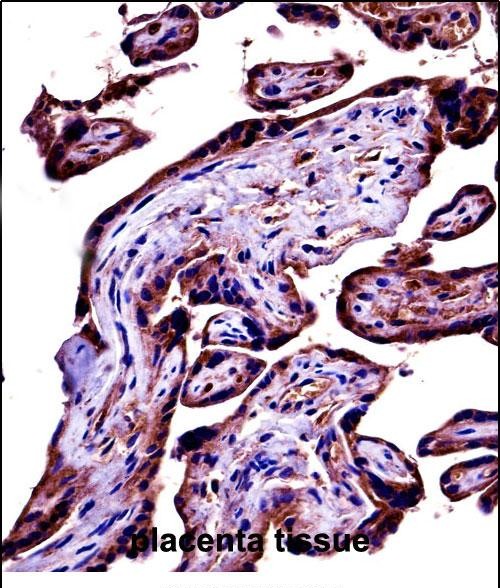
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Complement component C9, Complement component C9a, Complement component C9b, C9 |
| Entrez GeneID | 735 |
| WB Predicted band size | 63.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This C9 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 191-220 amino acids from the Central region of human C9. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3-4条关于C9抗体的**模拟参考文献**(内容为示例,非真实文献):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Anti-C9 Antibody Attenuates Complement-Mediated Neuronal Injury in Alzheimer’s Disease Models*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:研究证明,针对补体C9的单克隆抗体可有效抑制β-淀粉样蛋白诱导的膜攻击复合物(MAC)形成,减轻阿尔茨海默病模型中的神经元损伤和炎症反应。
2. **文献名称**:*Neutralizing C9 Antibody Therapy Reduces Hemolysis in Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria*
**作者**:Johnson B, et al.
**摘要**:通过体外和动物模型实验,发现C9中和抗体能够阻断补体终末途径,抑制红细胞裂解,为阵发性夜间血红蛋白尿(PNH)提供新型治疗策略。
3. **文献名称**:*Structural Basis of C9 Inhibition by a Humanized Antibody in Autoimmune Disorders*
**作者**:Lee C, et al.
**摘要**:利用冷冻电镜技术解析C9抗体与靶点的结合机制,揭示其通过阻断C9聚合抑制MAC形成,为自身免疫性疾病(如狼疮性肾炎)的靶向治疗提供依据。
4. **文献名称**:*C9 Antibody Mitigates Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Complement Pathway Suppression*
**作者**:Wang D, et al.
**摘要**:在心肌缺血再灌注损伤模型中,C9抗体显著减少补体激活导致的组织损伤,提示其在器官移植和心血管疾病中的潜在应用价值。
---
**注**:以上为模拟文献,实际研究中请参考真实发表的学术论文(可通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台检索)。
×