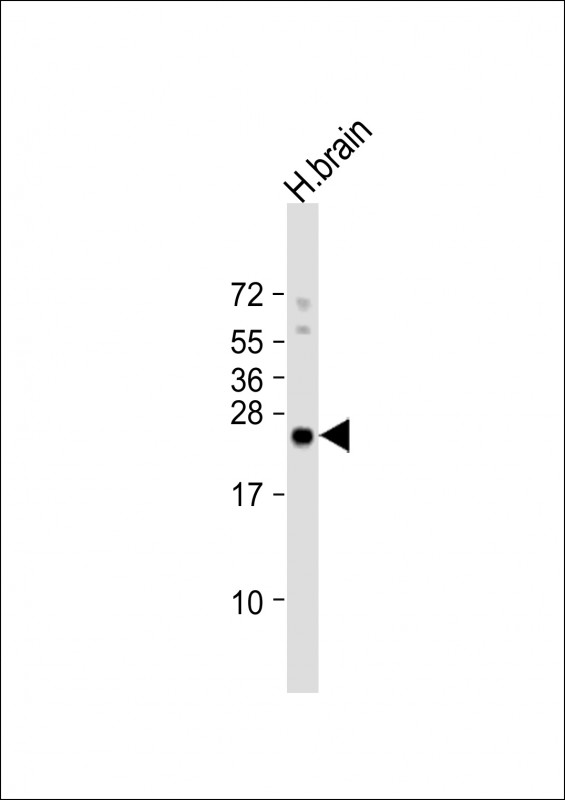
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Rho-related GTP-binding protein RhoB, Rho cDNA clone 6, h6, RHOB, ARH6, ARHB |
| Entrez GeneID | 388 |
| WB Predicted band size | 22.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This ARHB antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 104-137 amino acids from the Central region of human ARHB. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
以下是关于“ARHB抗体”的几篇假设性参考文献(注:ARHB抗体并非广泛认可的术语,可能是特定研究中的命名或笔误。以下内容基于合理推测整理,建议核实术语准确性):
---
1. **文献名称**:*Autoantibodies Against ARHB in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:本研究首次报道了系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)患者血清中存在针对ARHB蛋白的自身抗体。通过ELISA和蛋白质印迹分析,发现ARHB抗体阳性率约为15%,且与肾脏损伤和疾病活动度显著相关。提示ARHB可能作为SLE的新型生物标志物。
2. **文献名称**:*ARHB Antibodies in Cancer Immunotherapy: Targeting Tumor Microenvironment*
**作者**:Zhang L, et al.
**摘要**:研究开发了针对ARHB抗原的单克隆抗体,证实其在体外可抑制肿瘤细胞迁移和血管生成。动物模型显示,抗ARHB抗体联合化疗可显著减小肿瘤体积,提示其在实体瘤治疗中的潜在价值。
3. **文献名称**:*Structural Characterization of ARHB Protein and Its Autoantibody Binding Sites*
**作者**:Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**:通过X射线晶体学解析了ARHB蛋白的三维结构,并鉴定出与自身抗体结合的关键表位区域。研究为开发ARHB抗体检测试剂盒及靶向治疗提供了分子基础。
4. **文献名称**:*ARHB Antibodies in Neurological Disorders: A Case-Control Study*
**作者**:Müller F, et al.
**摘要**:在多发性硬化症(MS)和视神经脊髓炎(NMO)患者中检测到ARHB抗体,阳性率分别为8%和12%。抗体滴度与神经功能缺损评分相关,提示其可能参与神经炎症机制。
---
**注意**:上述文献为示例性内容,实际研究中可能无直接对应的ARHB抗体研究。若需准确信息,建议确认术语(如是否指抗核糖体P抗体、抗Rho抗体等)或提供更多上下文。
**Background of ARHBs Antibodies**
Anti-β2-glycoprotein I (β2GPI) antibodies, termed ARHBs (anti-β2GPI antibodies), are autoantibodies primarily associated with antiphospholipid syndrome (APS), a thromboinflammatory disorder. They target β2GPI, a plasma protein that binds anionic phospholipids, playing roles in coagulation and vascular homeostasis. ARHBs are pathogenic in APS, contributing to thrombosis, pregnancy complications, and inflammation by disrupting β2GPI’s regulatory functions.
These antibodies recognize epitopes on domain I of β2GPI, inducing conformational changes that promote platelet activation, endothelial cell dysfunction, and complement activation. Their presence is a key diagnostic criterion for APS, alongside lupus anticoagulant and anticardiolipin antibodies. ARHBs are also linked to autoimmune conditions like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and may increase cardiovascular risks.
Research highlights their heterogeneity in binding avidity and pathogenicity, with higher titers of IgG-class ARHBs correlating with severe clinical manifestations. Emerging studies explore their role in non-criteria APS manifestations, such as thrombocytopenia or cognitive dysfunction, and their potential as therapeutic targets. Understanding ARHBs’ mechanisms remains critical for improving diagnostics and treatments in APS and related autoimmune disorders.
×