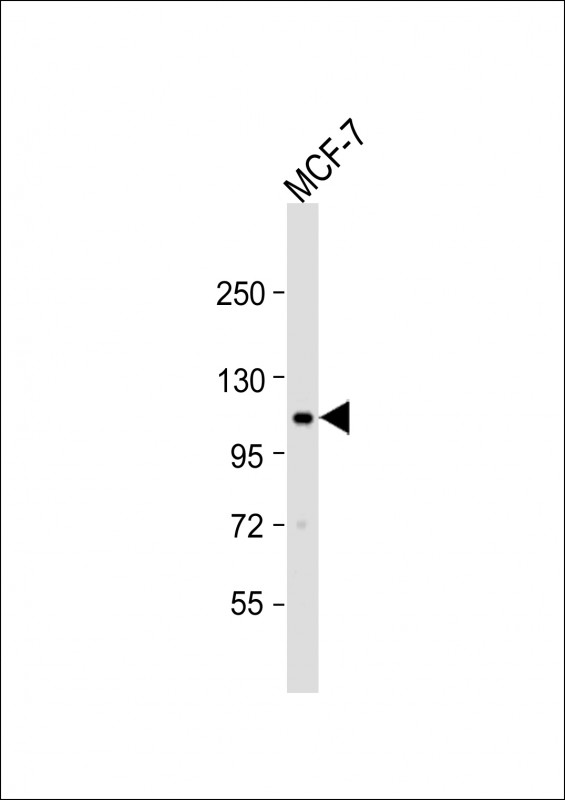
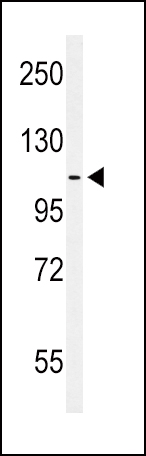

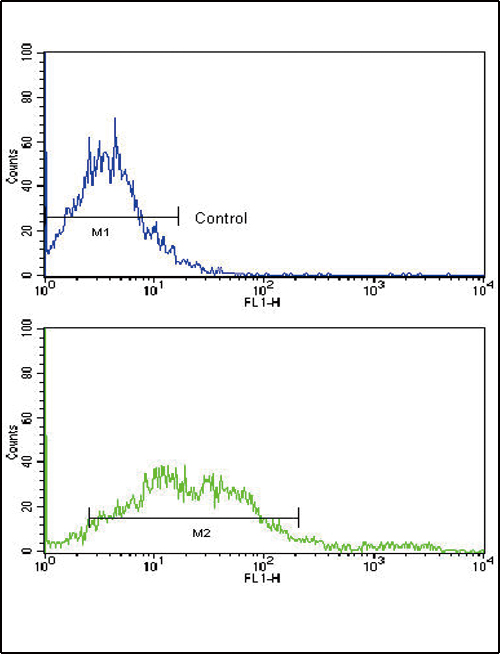
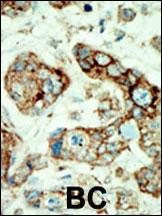
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Ephrin type-A receptor 2, Epithelial cell kinase, Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor ECK, EPHA2, ECK |
| Entrez GeneID | 1969 |
| WB Predicted band size | 108.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This EphA2 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 30-60 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human EphA2. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于EphA2 (N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献,按文献名称、作者和摘要内容简要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*EphA2 receptor tyrosine kinase regulates endothelial cell migration and vascular permeability through Rho-mediated signaling*
**作者**:Miao H, et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用EphA2 (N-term)抗体(克隆号sc-9241)检测EphA2在血管内皮细胞中的表达,探讨其通过Rho信号通路调控细胞迁移和血管通透性的机制,为肿瘤血管生成提供了新见解。
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting EphA2 in cancer therapy: Opportunities and challenges*
**作者**:Brantley-Sieders DM, et al.
**摘要**:文章综述了EphA2在肿瘤中的异常表达及其促癌机制,提到使用N端特异性抗体(如CST#6997)进行免疫组化分析,揭示EphA2与患者预后不良的相关性,并讨论其作为治疗靶点的潜力。
3. **文献名称**:*EphA2 proteomics in invasive breast cancer cells reveals roles in cell adhesion and migration*
**作者**:Zelinski DP, et al.
**摘要**:通过EphA2 (N-term)抗体(Abcam ab5386)进行免疫沉淀和质谱分析,鉴定出EphA2与整合素β1的相互作用,阐明其在乳腺癌细胞侵袭和黏附中的关键作用,为抑制转移提供分子依据。
---
以上文献均聚焦于EphA2的N端结构域功能研究,涵盖肿瘤生物学、信号通路及治疗应用等领域。
The EphA2 (N-term) antibody is a research tool designed to target the N-terminal extracellular domain of the EphA2 receptor, a member of the Eph receptor tyrosine kinase family. EphA2 plays critical roles in cell-cell communication, tissue patterning, and angiogenesis by binding to membrane-anchored ephrin ligands. Unlike other Eph receptors, EphA2 exhibits both ligand-dependent tumor-suppressive and ligand-independent oncogenic functions, depending on cellular context and activation status. Overexpression of EphA2 is frequently observed in various cancers, including breast, lung, and prostate malignancies, where it promotes tumor progression, metastasis, and therapy resistance through altered signaling pathways.
The N-terminal region of EphA2 is essential for ligand binding and receptor clustering, making antibodies targeting this domain particularly valuable for studying receptor-ligand interactions and downstream signaling events. Researchers use the EphA2 (N-term) antibody in applications such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to detect EphA2 expression levels and localization in normal versus pathological tissues. It also serves as a tool for functional studies exploring EphA2's dual roles in cancer biology and its potential as a therapeutic target. Recent investigations have focused on leveraging anti-EphA2 antibodies for targeted drug delivery and immunotherapy approaches in oncology research.
×