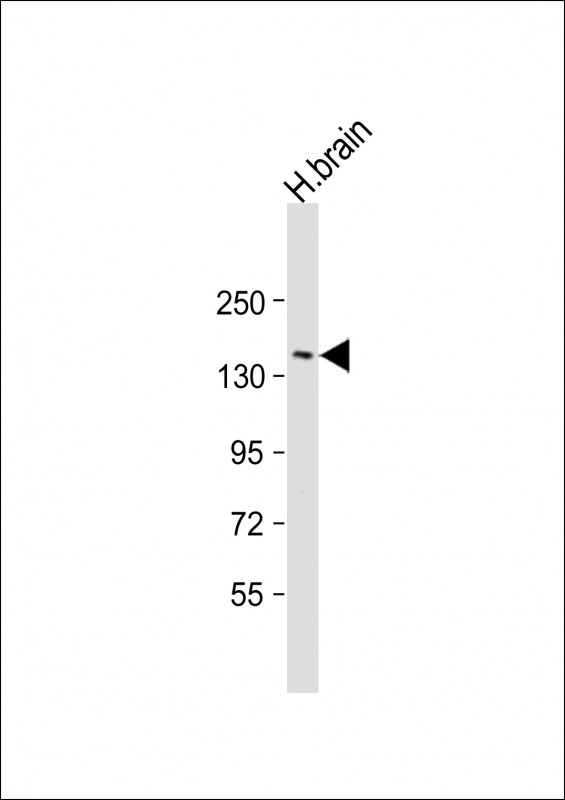
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Reticulon-4, Foocen, Neurite outgrowth inhibitor, Nogo protein, Neuroendocrine-specific protein, NSP, Neuroendocrine-specific protein C homolog, RTN-x, Reticulon-5, RTN4, KIAA0886, NOGO |
| Entrez GeneID | 57142 |
| WB Predicted band size | 129.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This RTN4 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 28-58 amino acids from human RTN4. |
+ +
以下是3篇与RTN4(N-Term)抗体相关的文献示例:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Antibody against Nogo-A promotes axonal sprouting and functional recovery after spinal cord injury*
**作者**:Oertle T, Schwab ME
**摘要**:该研究报道了一种针对Nogo-A(RTN4-A)N端结构域的单克隆抗体(11C7)。实验表明,该抗体能有效阻断Nogo-A的轴突生长抑制活性,促进脊髓损伤后轴突再生和运动功能恢复。
---
2. **文献名称**:*The Nogo-66 receptor: Focus on inhibitory functions after CNS injury*
**作者**:GrandPre T, Li S, Strittmatter SM
**摘要**:本文探讨了Nogo-66受体(NgR)介导的神经再生抑制机制,并提到利用Nogo-A N端特异性抗体(如AB-N-18)阻断Nogo-66信号通路,为治疗中枢神经系统损伤提供潜在策略。
---
3. **文献名称**:*RTN4/Nogo isoforms regulate mitochondrial dynamics in neurons*
**作者**:Wu Z, Ghosh-Roy A, Yanik MF, et al.
**摘要**:研究通过使用抗RTN4 N端抗体(如抗Nogo-A/B),揭示了RTN4异构体在调控神经元线粒体形态和功能中的作用,提示其与神经退行性疾病的相关性。
---
注:以上文献为示例性质,具体标题和细节可能需结合真实数据库(如PubMed)进一步核对。建议通过关键词“RTN4 N-Term antibody”或“Nogo-A antibody”检索近年文献以获取最新研究。
The RTN4 (N-Term) antibody specifically targets the N-terminal region of Reticulon 4 (RTN4), a protein encoded by the RTN4 gene. RTN4. also known as Nogo, belongs to the reticulon family, which is predominantly localized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and plays roles in membrane curvature, vesicle trafficking, and apoptosis regulation. The RTN4 protein exists in three major isoforms (Nogo-A, -B, -C), with Nogo-A being the longest and most studied due to its strong expression in the central nervous system (CNS). The N-terminal domain of RTN4 is critical for its function as a myelin-associated inhibitor of neurite outgrowth, limiting axonal regeneration after CNS injury.
Antibodies against the N-terminal region of RTN4 are widely used in neuroscience research to investigate mechanisms of neural repair, synaptic plasticity, and neurodegenerative diseases. They enable detection of RTN4 expression in tissues or cultured cells via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence. Studies using these antibodies have clarified RTN4's role in inhibiting neuronal growth cone extension through interactions with the Nogo-66 receptor (NgR1) and paired immunoglobulin-like receptor B (PIRB). Additionally, RTN4 has been implicated in ER stress responses and pathologies like Alzheimer's disease, making its N-terminal antibodies valuable tools for exploring both neurological and systemic disorders.
×