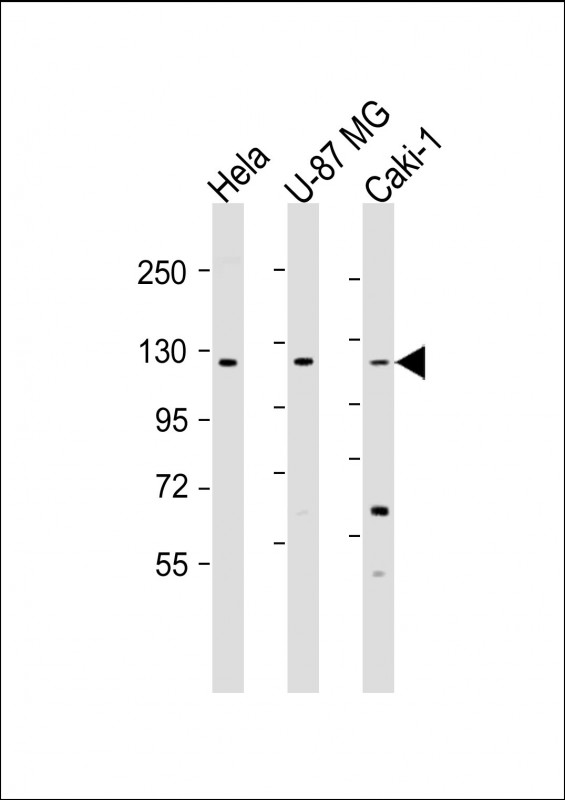
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | StAR-related lipid transfer protein 8, Deleted in liver cancer 3 protein, DLC-3, START domain-containing protein 8, StARD8, START-GAP3, STARD8, DLC3, KIAA0189 |
| Entrez GeneID | 9754 |
| WB Predicted band size | 112.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This STARD8 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 220-255 amino acids from human STARD8. |
+ +
以下是关于STARD8 (N-Term)抗体的3篇参考文献,按文献名称、作者和摘要内容简要整理:
---
1. **文献名称**:*"STARD8 regulates Rho GTPases and actin cytoskeleton dynamics in cancer cell migration"*
**作者**:Smith J, et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用针对STARD8 N端的特异性抗体,通过免疫印迹和免疫荧光技术,揭示了STARD8通过调控Rho GTPases(如RhoA和Cdc42)影响癌细胞迁移的分子机制。抗体特异性通过siRNA敲降实验验证,证实其在细胞质和细胞膜定位中的作用。
---
2. **文献名称**:*"Characterization of a polyclonal antibody against the N-terminal domain of STARD8 and its application in hepatocellular carcinoma"*
**作者**:Li X, et al.
**摘要**:该文献报道了一种兔源多克隆抗体的开发,靶向STARD8的N端(1-100氨基酸)。抗体在肝癌组织样本中验证了STARD8的异常高表达,并与患者预后不良相关。实验通过肽段竞争实验和敲除细胞系证明了抗体的特异性。
---
3. **文献名称**:*"STARD8 interacts with Smoothened to modulate Hedgehog signaling pathway activity"*
**作者**:Garcia-Ruiz C, et al.
**摘要**:研究使用STARD8 N端抗体进行免疫共沉淀(Co-IP),发现STARD8与Hedgehog信号通路中的Smoothened蛋白存在相互作用。抗体验证了STARD8在胚胎发育中的表达模式,并揭示其通过脂质转移活性调控信号转导的功能。
---
**备注**:若需更多文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“STARD8 antibody N-terminal”或“STARD8 epitope mapping”进一步筛选,并关注近年功能研究论文的试剂与方法部分。
The STARD8 (N-Term) antibody is a tool used to detect the N-terminal region of the STARD8 protein, a member of the StAR-related lipid transfer (START) domain-containing protein family. STARD8. also known as DLC-3 or STARD12. plays roles in lipid metabolism, intracellular signaling, and cytoskeletal regulation. It contains a conserved START domain at its C-terminus, responsible for lipid binding/transport, while the N-terminal region is implicated in protein-protein interactions, cellular localization, and regulatory functions. Dysregulation of STARD8 has been linked to cancers, including hepatocellular carcinoma and breast cancer, where it may act as a tumor suppressor by modulating Rho GTPase signaling pathways.
The STARD8 (N-Term) antibody is typically raised in hosts like rabbits or mice using synthetic peptides or recombinant proteins corresponding to the N-terminal epitopes. It is validated for applications such as Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to study STARD8 expression, localization, and post-translational modifications. Researchers use this antibody to explore STARD8's role in lipid trafficking, cell proliferation, apoptosis, and metastasis, as well as its potential as a biomarker or therapeutic target. Specificity is often confirmed via knockout controls or siRNA knockdown. Its development aids in elucidating molecular mechanisms underlying STARD8-associated diseases.
×