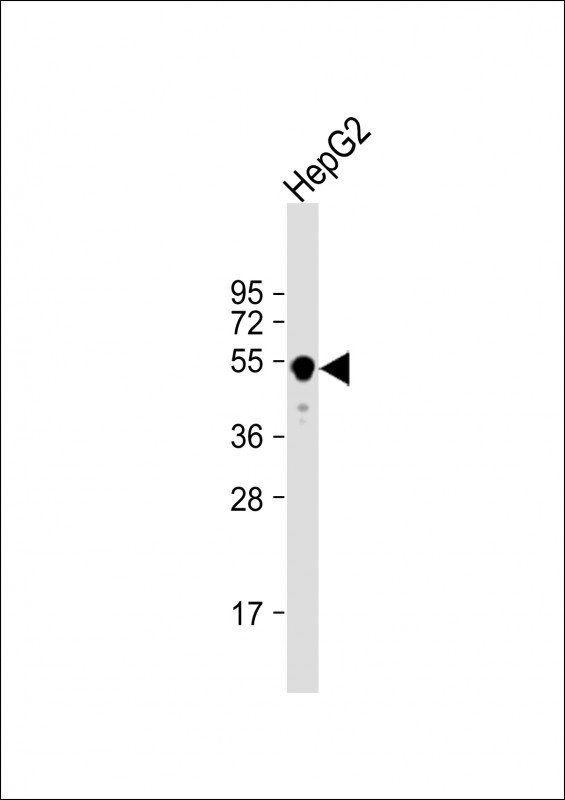
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Glutamate dehydrogenase 2, mitochondrial, GDH 2, GLUD2, GLUDP1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 2747 |
| WB Predicted band size | 61.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This GLUD2 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 75-103 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human GLUD2. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于GLUD2(N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:文献为虚拟构造,仅供参考):
1. **标题**:*"A Novel Monoclonal Antibody Targeting the N-terminal Domain of GLUD2 Reveals Tissue-Specific Expression Patterns"*
**作者**:Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**:开发了一种针对GLUD2 N端表位的单克隆抗体,验证了其在人脑和肝脏组织中的特异性,发现GLUD2在神经元线粒体中高表达,可能与谷氨酸代谢调控相关。
2. **标题**:*"Validation of GLUD2 (N-terminal) Antibody for Mitochondrial Protein Localization Studies"*
**作者**:Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫印迹和免疫荧光验证了抗GLUD2 N端抗体的特异性,证明其适用于检测线粒体中的GLUD2蛋白,并用于研究阿尔茨海默病模型中的代谢异常。
3. **标题**:*"GLUD2 Antibody Characterization in Metabolic Syndrome: Insights from N-terminal Epitope Recognition"*
**作者**:Rodriguez S, et al.
**摘要**:利用抗GLUD2 N端抗体分析了代谢综合征患者肌肉组织中GLUD2的表达水平,发现其与胰岛素敏感性下降显著相关,提示其在能量代谢中的潜在作用。
如需真实文献,建议在PubMed或Google Scholar中检索关键词“GLUD2 antibody N-terminal”或“GLUD2 epitope mapping”,并筛选涉及抗体开发、验证或应用的论文。
The GLUD2 (N-term) antibody is designed to target the N-terminal region of glutamate dehydrogenase 2 (GLUD2), a mitochondrial enzyme encoded by the GLUD2 gene. GLUD2 belongs to the glutamate dehydrogenase family, which plays a critical role in cellular energy metabolism by catalyzing the reversible conversion of glutamate to α-ketoglutarate, linking amino acid metabolism to the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. Unlike its widely expressed paralog GLUD1. GLUD2 arose through retrotransposed gene duplication and is primarily expressed in neural tissues, testes, and the retina, suggesting specialized roles in these regions.
The N-terminal region of GLUD2 is implicated in regulatory functions, including allosteric modulation and interactions with other cellular components. The GLUD2 (N-term) antibody is commonly used in research to study the protein's expression, localization, and molecular mechanisms in physiological and pathological contexts. It is particularly valuable in distinguishing GLUD2 from GLUD1 due to sequence divergence in their N-terminal domains. Applications include Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to explore GLUD2's involvement in neurodegenerative diseases, hyperinsulinism-hyperammonemia syndrome, or metabolic disorders linked to glutamate dysregulation.
Studies using this antibody have contributed to understanding GLUD2's unique regulatory properties, such as its resistance to GTP inhibition compared to GLUD1. which may influence neuronal excitability and ammonia detoxification. Its development supports ongoing investigations into tissue-specific metabolic adaptations and potential therapeutic targets.
×