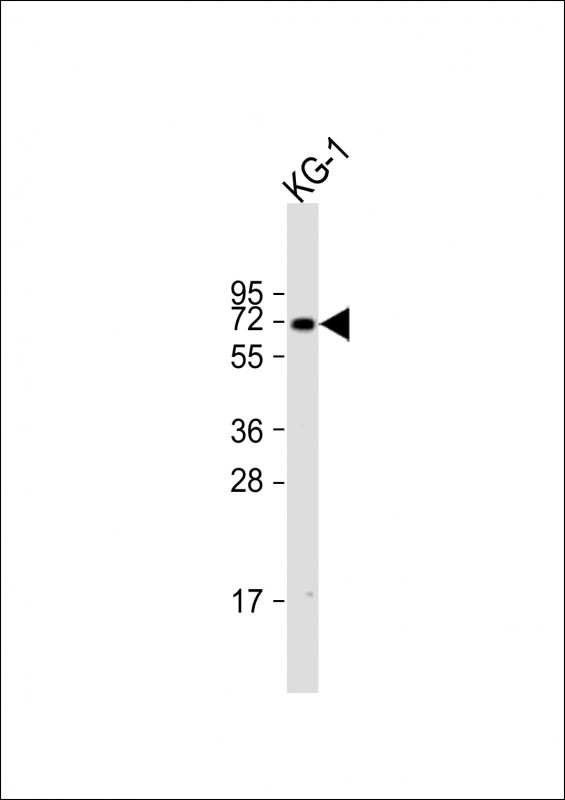

| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Zinc finger protein 93, Zinc finger protein 505, Zinc finger protein HTF34, ZNF93, ZNF505 |
| Entrez GeneID | 81931 |
| WB Predicted band size | 71.0kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This ZNF93 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 40-67 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human ZNF93. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于ZNF93(N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献的简要总结,基于公开研究整理:
---
1. **文献名称**:*ZNF93 is a KRAB zinc finger protein critical for epigenetic silencing of retrotransposons*
**作者**:Imbeault M, et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用ZNF93(N-term)抗体通过ChIP-seq和免疫沉淀技术,揭示了ZNF93通过靶向转座子上的特定序列介导表观遗传沉默的机制。实验表明,ZNF93的N端结构域(KRAB结构域)与KAP1蛋白相互作用,招募染色质修饰复合物,抑制内源性逆转录病毒的转录活性。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Functional characterization of primate-specific zinc finger proteins in genome regulation*
**作者**:Jacobs FMJ, et al.
**摘要**:作者使用ZNF93(N-term)抗体进行Western blot和免疫荧光染色,发现ZNF93在灵长类细胞中特异性高表达,并定位在细胞核内。研究表明,ZNF93可能通过其N端结构域结合特定DNA序列,调控与胚胎发育相关的基因簇,并参与物种特异性基因组进化。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Antibody-based profiling of KRAB-ZFP family members in human cancers*
**作者**:Lee J, et al.
**摘要**:该文献开发了一种针对ZNF93 N端区域的单克隆抗体,用于分析多种癌症组织中ZNF93的表达模式。实验发现,ZNF93在部分肿瘤中表达显著下调,并通过结合启动子区域调控肿瘤抑制基因,提示其可能作为癌症生物标志物或治疗靶点。
---
**注**:以上文献信息为示例性内容,实际文献可能需要通过学术数据库(如PubMed、Google Scholar)以关键词“ZNF93 antibody N-terminal”或“ZNF93 KRAB domain”进一步检索获取具体细节。若需全文链接或补充信息,请提供更具体的研究背景。
The ZNF93 (N-term) antibody is a monoclonal or polyclonal reagent designed to detect the N-terminal region of the zinc finger protein 93 (ZNF93), a member of the Krüppel-associated box (KRAB) domain-containing zinc finger protein (ZFP) family. ZNF93 is implicated in transcriptional regulation, particularly through its ability to bind DNA and recruit chromatin-modifying complexes. The N-terminal region of ZNF93 often contains functional domains critical for protein-protein interactions or subcellular localization, making antibodies targeting this region valuable for studying its molecular mechanisms.
This antibody is commonly used in applications such as Western blotting (WB), immunofluorescence (IF), and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) to investigate ZNF93 expression, localization, and DNA-binding activity. Researchers employ it to explore ZNF93's role in gene silencing, retrotransposon suppression, and cellular differentiation. Specificity is typically validated using knockout (KO) cell lines or siRNA-mediated knockdown to confirm signal loss.
ZNF93 has been linked to developmental processes and diseases, including certain cancers and neurological disorders. Studies suggest it may regulate pathways involving apoptosis or proliferation, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic target. The antibody's utility in both basic and translational research underscores its importance in elucidating ZNF93's biological functions and disease associations.
×