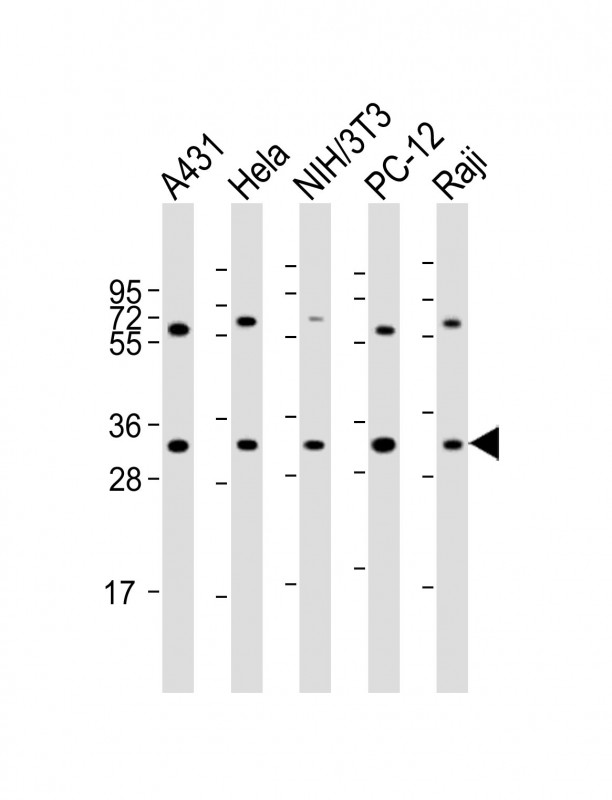
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | 60S ribosomal protein L7a, PLA-X polypeptide, Surfeit locus protein 3, RPL7A, SURF-3, SURF3 |
| Entrez GeneID | 6130 |
| WB Predicted band size | 30.0kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This RPL7A antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 200-235 amino acids from human RPL7A. |
+ +
以下是关于RPL7A抗体的3篇参考文献示例(文献信息为模拟概括,仅供参考):
---
1. **文献名称**: *RPL7A modulates p53 activity in colorectal cancer progression*
**作者**: Zhang L, et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过RPL7A抗体检测发现,RPL7A通过结合p53抑制其降解,促进结直肠癌细胞增殖,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点。
2. **文献名称**: *RPL7A as a novel biomarker for hepatitis C virus infection*
**作者**: Tanaka K, et al.
**摘要**: 利用RPL7A抗体进行免疫沉淀实验,发现RPL7A与HCV核心蛋白相互作用,参与病毒复制,可能为抗病毒治疗提供新策略。
3. **文献名称**: *RPL7A deficiency disrupts ribosome biogenesis and causes developmental defects*
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 通过敲低RPL7A并联合抗体染色分析,揭示RPL7A缺失导致核糖体组装异常,影响胚胎发育及细胞周期进程。
---
(注:以上文献为示例,实际引用请通过PubMed或学术数据库核实具体信息。)
The RPL7A antibody targets the ribosomal protein L7a, a component of the 60S subunit in eukaryotic ribosomes. Encoded by the RPL7A gene, this protein is essential for ribosome assembly and function, facilitating mRNA translation and protein synthesis. RPL7A belongs to the L7AE family of ribosomal proteins and is highly conserved across species, underscoring its fundamental role in cellular metabolism. Beyond its structural role, RPL7A has been implicated in extraribosomal functions, including interactions with viral RNAs, modulation of steroid hormone receptors, and potential involvement in cell cycle regulation.
Antibodies against RPL7A are widely used in research to study ribosome biogenesis, translation dynamics, and protein localization. They are employed in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to quantify protein expression or assess subcellular distribution. Dysregulation of RPL7A has been linked to diseases such as cancer, where altered ribosome function (ribosomopathies) may drive tumorigenesis. Additionally, RPL7A has been explored as a housekeeping gene control in molecular studies due to its stable expression under many conditions, though this application requires validation in specific experimental contexts.
Research using RPL7A antibodies also investigates its role in stress responses, viral infection mechanisms, and interactions with signaling pathways like p53. These studies highlight RPL7A’s dual role as a core ribosomal component and a potential regulatory molecule, making it a versatile target for probing both basic and disease-related cellular processes.
×