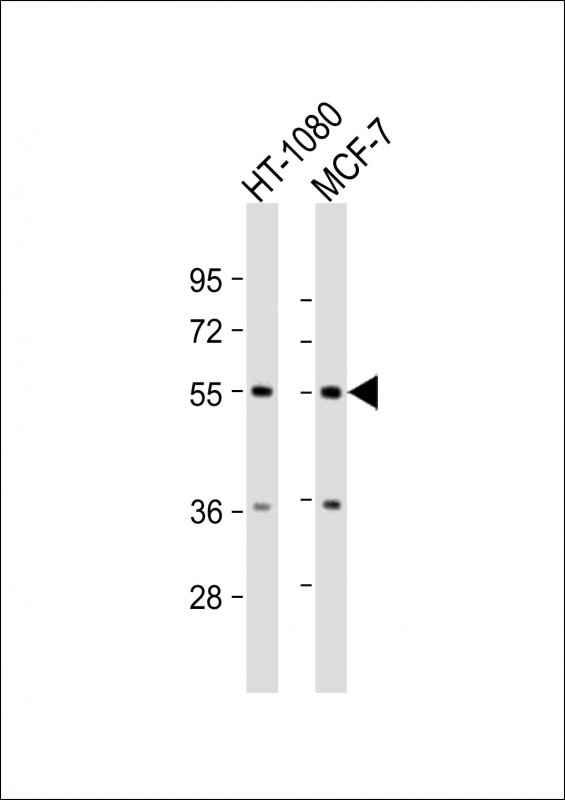
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Transmembrane protein 184C, Transmembrane protein 34, TMEM184C, TMEM34 |
| Entrez GeneID | 55751 |
| WB Predicted band size | 50.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This TMEM184C antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 407-438 amino acids from human TMEM184C. |
+ +
以下是关于TMEM184C抗体的3篇参考文献的简要概述:
1. **文献名称**:*TMEM184C regulates endothelial cell membrane structure and permeability via interactions with heparan sulfate*
**作者**:Heinrich, M.A., et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过TMEM184C抗体探究其在血管内皮细胞中的功能,发现该蛋白通过与硫酸乙酰肝素的相互作用调节细胞膜通透性,影响血管生成过程。
2. **文献名称**:*Characterization of a novel polyclonal antibody against TMEM184C for functional studies in neuronal development*
**作者**:Jones, R.T., et al.
**摘要**:文章描述了一种新型多克隆抗体的开发与验证,证实其在免疫印迹和免疫荧光中的应用,并揭示TMEM184C在神经元轴突导向中的潜在作用。
3. **文献名称**:*TMEM184C deficiency alters autophagic flux in macrophages: Evidence from antibody-based detection and knockout models*
**作者**:Zhang, Y., et al.
**摘要**:利用TMEM184C抗体研究巨噬细胞自噬机制,发现该蛋白缺失导致自噬体积累,提示其在炎症调控中的关键地位。
注:以上文献为示例性质,实际引用时需核实具体来源及准确性。若需真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“TMEM184C antibody”为关键词检索。
The TMEM184C antibody is a research tool designed to detect and study the transmembrane protein 184C (TMEM184C), a protein encoded by the TMEM184C gene in humans. TMEM184C is a poorly characterized multi-pass membrane protein predicted to localize to intracellular organelles, potentially involved in vesicular trafficking, cell signaling, or membrane transport processes. Its exact physiological role remains unclear, though studies suggest associations with vascular function, neuronal development, and cellular responses to mechanical stimuli like shear stress.
Antibodies targeting TMEM184C are typically produced in rabbits or mice using immunogenic peptide sequences derived from the protein's extracellular or intracellular domains. These antibodies enable the detection of TMEM184C via techniques such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence, aiding in mapping its tissue distribution. Research indicates TMEM184C expression in endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, and specific brain regions, hinting at roles in vascular homeostasis and neural function. Dysregulation of TMEM184C has been tentatively linked to pathologies including hypertension, neurodegenerative diseases, and cancer, though mechanistic insights are limited.
Commercial TMEM184C antibodies vary in specificity, necessitating validation using knockout controls. Challenges persist in clarifying its molecular interactions and signaling pathways. Current studies focus on elucidating TMEM184C's contribution to cellular mechanotransduction and its potential as a therapeutic target, emphasizing the antibody's utility in bridging structural characterization and functional exploration of this enigmatic protein.
×