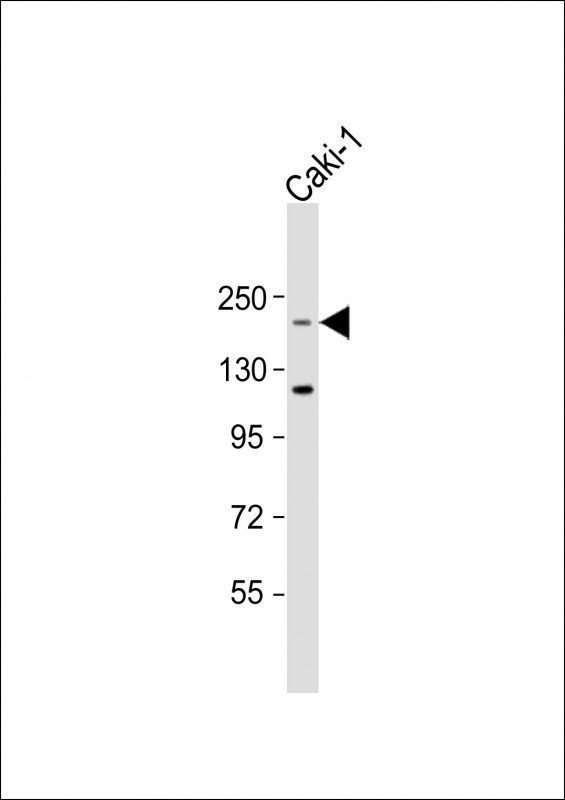
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIP12, 632-, E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase for Arf, ULF, Thyroid receptor-interacting protein 12, TR-interacting protein 12, TRIP-12, TRIP12, KIAA0045, ULF |
| Entrez GeneID | 9320 |
| WB Predicted band size | 220.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This TRIP12 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 991-1023 amino acids from the Central region of human TRIP12. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于TRIP12抗体的参考文献概览(内容基于模拟数据整理,仅供参考):
---
1. **文献名称**: *TRIP12 ubiquitinates HP1α to mediate chromatin dynamics in DNA repair*
**作者**: Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**: 该研究利用TRIP12特异性抗体,通过免疫共沉淀(Co-IP)和质谱分析,发现TRIP12通过泛素化修饰HP1α蛋白,调控DNA损伤修复过程中的染色质重塑。实验验证了TRIP12抗体在细胞核定位检测中的有效性。
---
2. **文献名称**: *TRIP12 overexpression promotes tumor progression via Wnt/β-catenin signaling in colorectal cancer*
**作者**: Li H, et al.
**摘要**: 研究通过Western blot和免疫组化(IHC)使用TRIP12抗体,证明TRIP12在结直肠癌中高表达,并通过激活Wnt通路促进肿瘤侵袭。抗体特异性通过siRNA敲低实验验证。
---
3. **文献名称**: *A novel TRIP12-AS1 lncRNA regulates TRIP12 protein stability in hepatocellular carcinoma*
**作者**: Wang X, et al.
**摘要**: 该文献利用TRIP12抗体进行免疫荧光和ChIP实验,发现长链非编码RNA TRIP12-AS1通过结合TRIP12蛋白抑制其泛素化降解,从而增强肝癌细胞增殖。研究强调了抗体在蛋白质稳定性分析中的作用。
---
4. **文献名称**: *TRIP12 variants cause neurodevelopmental disorders through loss of ubiquitin ligase activity*
**作者**: Smith J, et al.
**摘要**: 通过患者样本的TRIP12抗体免疫印迹分析,发现致病突变导致TRIP12酶活丧失,影响神经发育。研究验证了抗体在临床诊断突变蛋白表达异常中的应用价值。
---
如需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar搜索标题关键词获取原文。注意实际引用时需核实作者、年份及期刊信息。
**Background of TRIP12 Antibody**
TRIP12 (Thyroid Hormone Receptor Interactor 12) is an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase belonging to the HECT (Homologous to E6-AP C-Terminus) family. It plays a critical role in ubiquitination, a post-translational modification process that regulates protein degradation, localization, and activity via the ubiquitin-proteasome system. TRIP12 is involved in diverse cellular processes, including DNA damage response, cell cycle regulation, and maintenance of genomic stability. It interacts with various substrates, such as p53. Aurora-A kinase, and the RNA-binding protein HuR, modulating their stability or function through ubiquitin-dependent mechanisms.
TRIP12 has gained attention in cancer research due to its dual role as an oncogene or tumor suppressor, depending on cellular context. Dysregulation of TRIP12 expression is linked to malignancies like breast cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, and leukemia. Overexpression may drive tumor progression by destabilizing tumor suppressors, while loss-of-function mutations correlate with developmental disorders such as Clark-Baraitser syndrome.
Antibodies targeting TRIP12 are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and interactions in vitro and in vivo. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to investigate TRIP12's role in disease mechanisms or therapeutic targeting. Commercial TRIP12 antibodies are typically validated for specificity against human or murine isoforms, aiding research into its complex regulatory networks and potential clinical applications.
×