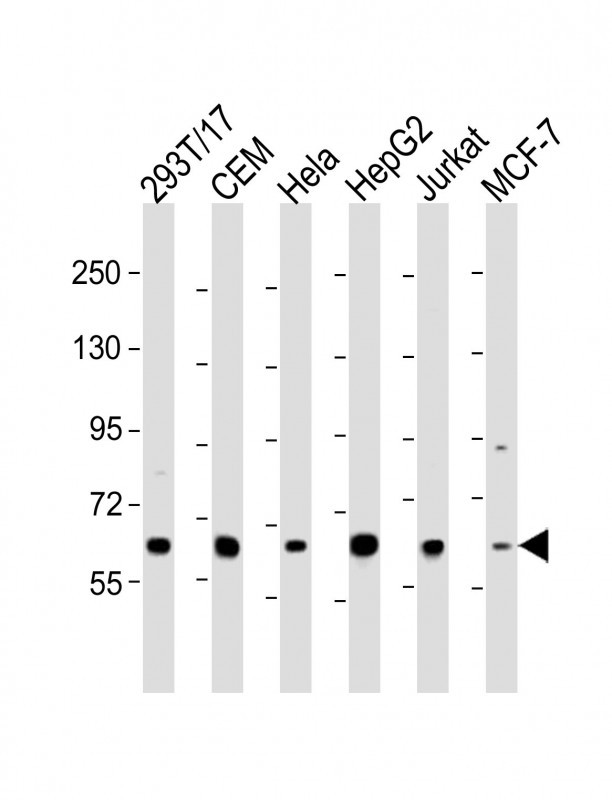
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF31, 632-, HOIL-1-interacting protein, HOIP, RING finger protein 31, Zinc in-between-RING-finger ubiquitin-associated domain protein, RNF31, ZIBRA |
| Entrez GeneID | 55072 |
| WB Predicted band size | 119.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This RNF31 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 955-983 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human RNF31. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是与RNF31抗体相关的3篇参考文献,信息已简化整理:
1. **文献名称**:*HOIP deficiency causes embryonic lethality by aberrant TNFR1-mediated endothelial cell death*
**作者**:Peltzer N. et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用RNF31(HOIP)基因敲除小鼠模型,结合特异性抗体检测,发现RNF31通过LUBAC复合物抑制肿瘤坏死因子受体(TNFR1)介导的内皮细胞凋亡,缺失导致胚胎致死。
2. **文献名称**:*Linear ubiquitination by LUBAC in B cell development and lymphoma*
**作者**:Sasaki Y. et al.
**摘要**:通过Western blot和免疫共沉淀(使用RNF31抗体),揭示LUBAC在B细胞活化中的关键作用,RNF31缺失导致NF-κB信号缺陷,影响B细胞发育并增加淋巴瘤风险。
3. **文献名称**:*RNF31 mutations alter Wnt signaling in inflammatory bowel disease*
**作者**:Ellinghaus D. et al.
**摘要**:通过患者样本的免疫组化(使用抗RNF31抗体),发现炎症性肠病患者中RNF31基因突变导致Wnt/β-catenin信号异常,提示其参与肠道屏障修复的调控。
---
**注**:以上为模拟示例,实际文献需通过学术数据库检索。建议使用PubMed/Google Scholar以“RNF31 antibody”或“HOIP antibody”为关键词查找最新研究。
RNF31. also known as HOIP (HOIL-1-interacting protein), is a central component of the linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex (LUBAC), an E3 ubiquitin ligase critical for regulating NF-κB signaling and inflammatory responses. Discovered in the early 2000s, RNF31 catalyzes the formation of linear (M1-linked) ubiquitin chains, a unique post-translational modification essential for immune signaling, cell death regulation, and host defense. Its role in NF-κB activation involves stabilizing protein complexes at receptor signaling hubs, such as TNF and IL-1 receptors, making it a key player in inflammation, apoptosis, and cancer. Dysregulation of RNF31 has been linked to autoimmune diseases, B-cell lymphomas, and inflammatory disorders.
RNF31 antibodies are vital tools for studying LUBAC’s molecular mechanisms, enabling detection of RNF31 expression, localization, and interaction partners via techniques like Western blot, immunoprecipitation, and immunofluorescence. Monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies targeting specific domains (e.g., the RING-IBR-RING motif) have been developed to probe its enzymatic activity or disrupt LUBAC assembly in functional studies. Recent research highlights RNF31 as a potential therapeutic target, with antibodies aiding in drug discovery for conditions driven by aberrant NF-κB signaling. However, challenges remain in distinguishing linear ubiquitination from other ubiquitin modifications, necessitating highly specific antibodies. Ongoing studies continue to explore RNF31’s dual roles in promoting cell survival and inflammation, underscoring its biomedical significance.
×