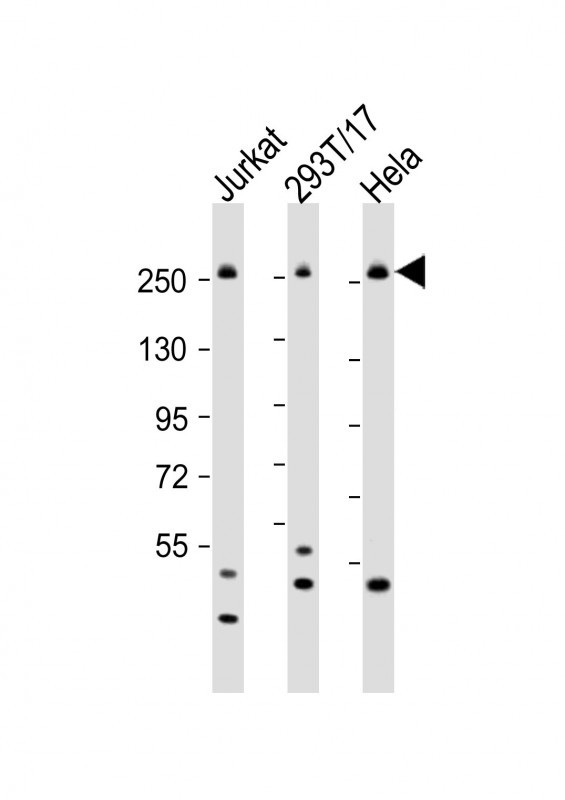
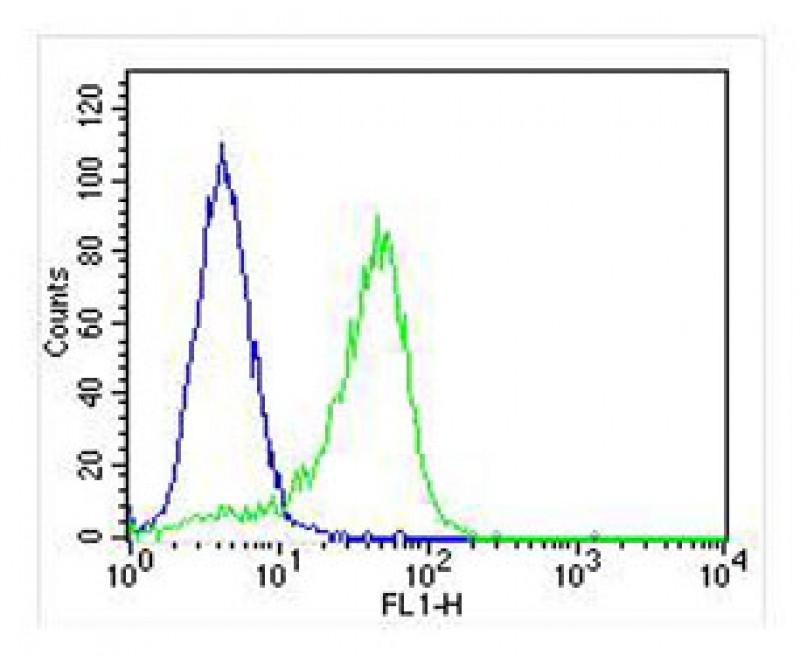
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | CAD protein, Glutamine-dependent carbamoyl-phosphate synthase, Aspartate carbamoyltransferase, Dihydroorotase, CAD |
| Entrez GeneID | 790 |
| WB Predicted band size | 243.0kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This CAD antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 780-809 amino acids from the Central region of human CAD. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CAD抗体(冷凝集素病相关抗体)的3篇参考文献,简要概述如下:
---
1. **文献名称**:*Rituximab for Chronic Cold Agglutinin Disease: A Prospective Study of 20 Patients*
**作者**:Berentsen, S., et al.
**摘要**:该研究评估了利妥昔单抗(抗CD20单克隆抗体)治疗慢性冷凝集素病的疗效。20名患者接受治疗后,60%表现出显著临床缓解,血红蛋白水平上升,提示利妥昔单抗可作为CAD的一线治疗方案。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Cold Agglutinin Disease: Current Challenges and Future Prospects*
**作者**:Jäger, U., et al.
**摘要**:本文综述了CAD的病理机制,强调抗红细胞I/i抗原的IgM抗体在溶血中的作用,并探讨了新型靶向疗法(如补体抑制剂)的潜力,为改善患者预后提供理论依据。
---
3. **文献名称**:*Diagnosis and Treatment of Primary Chronic Cold Agglutinin Disease: A Retrospective Analysis of 24 Patients*
**作者**:Randen, U., et al.
**摘要**:通过对24例原发性CAD患者的回顾性分析,研究指出骨髓淋巴增殖性疾病(如淋巴瘤)与CAD的关联,并强调联合化疗对合并血液系统恶性肿瘤患者的有效性。
---
**备注**:CAD抗体通常指冷凝集素病中靶向红细胞I/i抗原的IgM自身抗体,上述文献涵盖治疗策略、病理机制及诊断关联,为临床与研究提供参考。如需扩展,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“Cold Agglutinin Disease”或“CAD antibody”检索近五年文献。
CAD antibodies, primarily associated with paraneoplastic neurological syndromes (PNS), target the collapsin response mediator protein 5 (CRMP5), a neuronal cytosolic protein involved in axonal guidance and differentiation. First identified in the 1990s, these autoantibodies are often detected in patients with underlying malignancies, particularly small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) and thymoma. Their presence signals an immune-mediated attack on the nervous system triggered by cross-reactivity between tumor antigens (onconeural antigens) and neuronal proteins—a phenomenon termed "molecular mimicry."
Clinically, CAD antibodies are linked to diverse neurological manifestations, including encephalomyelitis, cerebellar ataxia, optic neuropathy, and peripheral neuropathy. Symptoms typically emerge subacutely, preceding cancer diagnosis in many cases. Detection relies on indirect immunofluorescence or immunoblotting using neural tissue or recombinant CRMP5. often paired with cerebrospinal fluid analysis and imaging to confirm neurological involvement. While CAD antibodies aid in early cancer detection and guide treatment, their pathogenic role remains debated. Some evidence suggests direct involvement in neuronal dysfunction, while others propose they are disease markers. Treatment focuses on immunosuppression (e.g., corticosteroids, IVIg) and addressing the underlying malignancy. Prognosis varies, with outcomes influenced by cancer stage and neurological damage severity. Research continues to clarify their pathophysiological mechanisms and optimize therapeutic strategies.
×