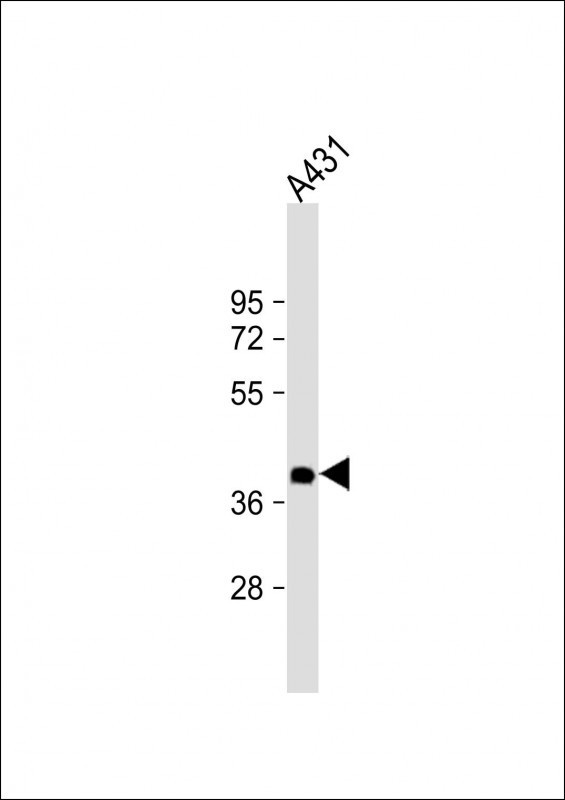
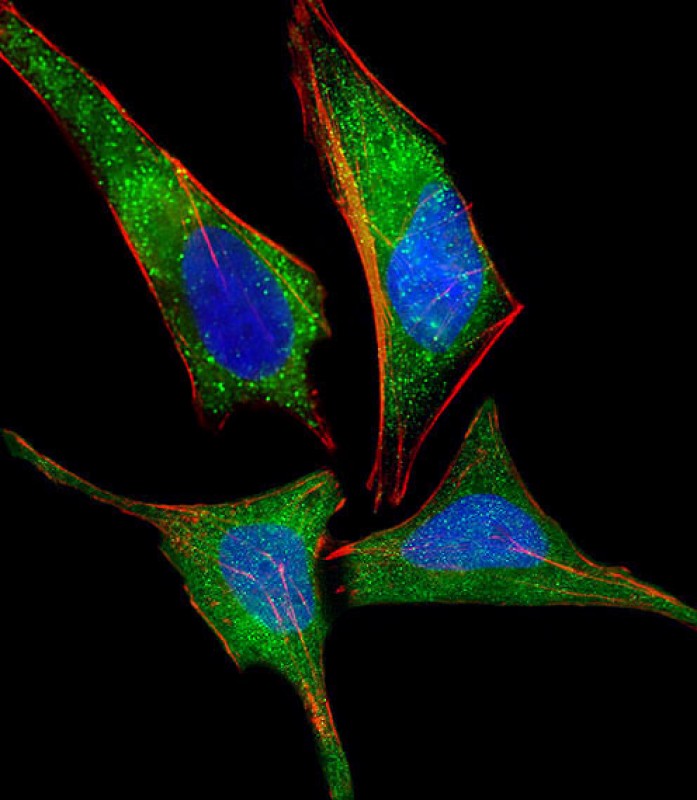
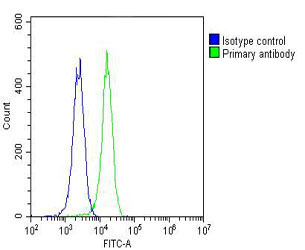
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | N-myc-interactor, Nmi, N-myc and STAT interactor, NMI |
| Entrez GeneID | 9111 |
| WB Predicted band size | 35.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG1 |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This NMI antibody is generated from a mouse immunized with a recombinant protein of human NMI. |
+ +
以下是关于NMI抗体的3篇参考文献及其摘要内容的概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*NMI and IFP35 Proteins Participate in the Host Response to Tumors*
**作者**:Zhou A. et al.
**摘要**:该研究揭示了NMI(干扰素诱导蛋白)与IFP35在肿瘤微环境中的调控作用,发现NMI抗体可通过阻断其与Myc蛋白的相互作用抑制肿瘤生长。实验表明,NMI的高表达与乳腺癌患者预后不良相关,其抗体可能成为潜在治疗工具。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Autoantibodies to NMI in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus*
**作者**:Li Y. et al.
**摘要**:本研究在系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)患者血清中检测到抗NMI自身抗体,发现其阳性率与疾病活动度显著相关。通过ELISA和蛋白质印迹验证,提示NMI抗体可能参与SLE的免疫病理机制,或作为疾病活动的生物标志物。
---
3. **文献名称**:*NMI as a Novel Target for Antibody-Based Cancer Immunotherapy*
**作者**:Wang X. et al.
**摘要**:该文献开发了一种靶向NMI的单克隆抗体,并在体外和动物模型中验证其抗肿瘤效果。研究发现,该抗体通过阻断NMI介导的STAT信号通路,抑制肿瘤细胞增殖并增强免疫细胞浸润,为癌症免疫治疗提供了新策略。
---
**备注**:NMI(N-myc下游调控基因)相关研究多集中于其在肿瘤、免疫疾病中的功能,上述文献侧重抗体在治疗或诊断中的应用。若需更具体领域文献,可进一步限定研究背景(如特定疾病或技术方法)。
N-myc interactor (NMI) is a protein initially identified through its interaction with N-myc, a member of the Myc oncoprotein family. Structurally, NMI contains a coiled-coil domain that facilitates interactions with various transcription factors and signaling molecules, including STAT proteins (signal transducer and activator of transcription). NMI is implicated in regulating diverse cellular processes, such as cell proliferation, differentiation, and immune responses, particularly within the interferon signaling pathway. Its role in cancer biology is context-dependent, acting as both a tumor suppressor and promoter depending on the cellular environment. For instance, NMI suppresses tumor growth in breast and ovarian cancers by enhancing IFN-γ/STAT1 signaling, while in gliomas, it may promote malignancy by stabilizing oncogenic proteins.
NMI antibodies are critical tools for studying these mechanisms. They enable the detection and quantification of NMI expression in tissues or cell lines via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, or immunofluorescence. Research using NMI antibodies has revealed its dysregulation in multiple cancers, often correlating with prognosis. For example, reduced NMI levels in triple-negative breast cancer are linked to poor survival, whereas overexpression in colorectal cancer associates with advanced stages. These antibodies also aid in exploring NMI's interplay with signaling pathways, such as its modulation of STAT activity or crosstalk with MYC proteins. Continued development of high-specificity NMI antibodies remains essential for unraveling its complex roles in health and disease.
×