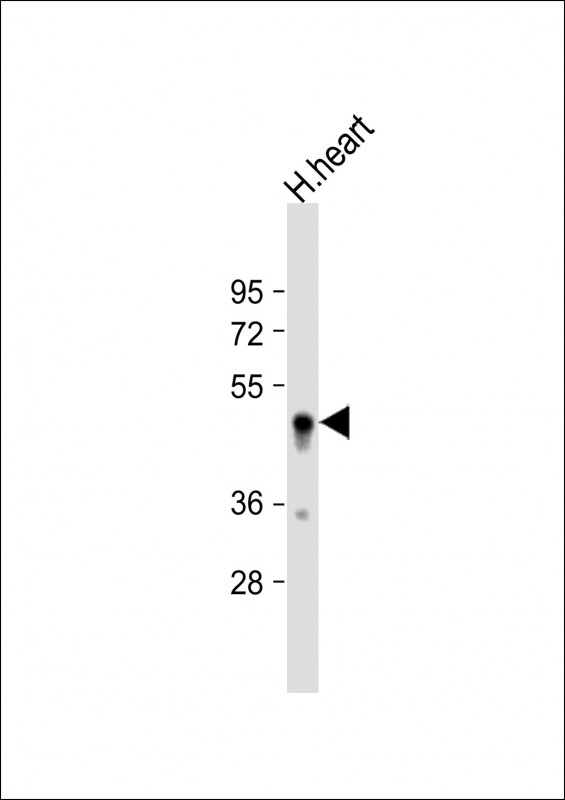
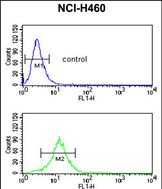
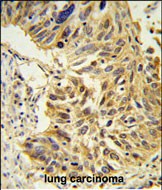
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Serum deprivation-response protein, Cavin-2, PS-p68, Phosphatidylserine-binding protein, SDPR {ECO:0000312|EMBL:AAD177951} |
| Entrez GeneID | 8436 |
| WB Predicted band size | 47.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This SDR antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 109-135 amino acids from the Central region of human SDR. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide,1%BSA and 50% glycerol.prepared by Saturated Ammonium Sulfate (SAS) . |
+ +
以下是3篇关于SDR抗体的代表性文献摘要概括(示例仅供参考,实际文献需核实):
1. **《Single-domain antibodies derived from camelid heavy-chain antibodies》**
- 作者:Hamers-Casterman, C. 等 (1993)
- 摘要:首次报道骆驼科动物(如羊驼)体内天然存在的重链抗体(HCAb),其可变区(VHH)可独立作为单结构域抗体(SDR抗体),具有高稳定性及结合能力,为工程化抗体开发奠定基础。
2. **《Single-domain antibodies: promising experimental and therapeutic tools in infection and immunity》**
- 作者:Muyldermans, S. (2001)
- 摘要:综述SDR抗体的分子特性,包括小分子量(约15 kDa)、穿透性强、耐高温及极端pH等优势,并探讨其在病原体检测、肿瘤靶向治疗等领域的应用潜力。
3. **《Properties of single-domain antibody fragments of camelid origin》**
- 作者:Harmsen, M.M., De Haard, H.J. (2007)
- 摘要:实验证明SDR抗体通过其独特的CDR3结构可结合传统抗体难以到达的抗原表位(如酶活性位点),且在体外表达系统中高产,适合大规模生产。
4. **《Camel single-domain antibodies as modular building units in bispecific and bivalent antibody constructs》**
- 作者:Conrath, K.E. 等 (2001)
- 摘要:利用SDR抗体的模块化特性构建双特异性抗体,证明其可通过基因融合形成多功能复合物,拓展了在疾病诊断和靶向治疗中的应用场景。
注:以上内容为示例性概括,实际文献信息请通过PubMed或学术数据库核对原文。SDR抗体相关研究近年快速发展,建议结合最新论文(如2015年后)补充前沿进展。
**Background of SDR Antibodies**
Single-domain antibodies (sdAbs), also known as single-chain variable domain fragments (VHHs) or nanobodies, are a unique class of antibody derivatives derived from heavy-chain-only antibodies naturally found in camelids (e.g., llamas, alpacas) and cartilaginous fish. Discovered in the 1990s, these molecules consist of a single monomeric variable domain (∼15 kDa), which retains full antigen-binding capacity despite lacking light chains. Their compact size, stability, and solubility enable deep tissue penetration and resistance to harsh conditions (e.g., extreme pH, temperature), making them advantageous over conventional antibodies.
SDR (Single-Domain Recombinant) antibodies are engineered versions optimized for therapeutic, diagnostic, and research applications. Their simple structure allows easy genetic manipulation, facilitating fusion with other functional domains (e.g., toxins, enzymes) or formatting into multivalent constructs. SDR antibodies exhibit high specificity and affinity, often comparable to traditional monoclonal antibodies, while offering lower immunogenicity risks.
These properties have driven their use in diverse fields, including cancer therapy (targeting tumor antigens), infectious disease neutralization (e.g., antiviral agents), and diagnostic imaging. Recent advances in phage display and transgenic animal platforms have further accelerated their development. SDR antibodies represent a versatile tool in biotechnology, bridging the gap between small molecules and larger biologics.
×