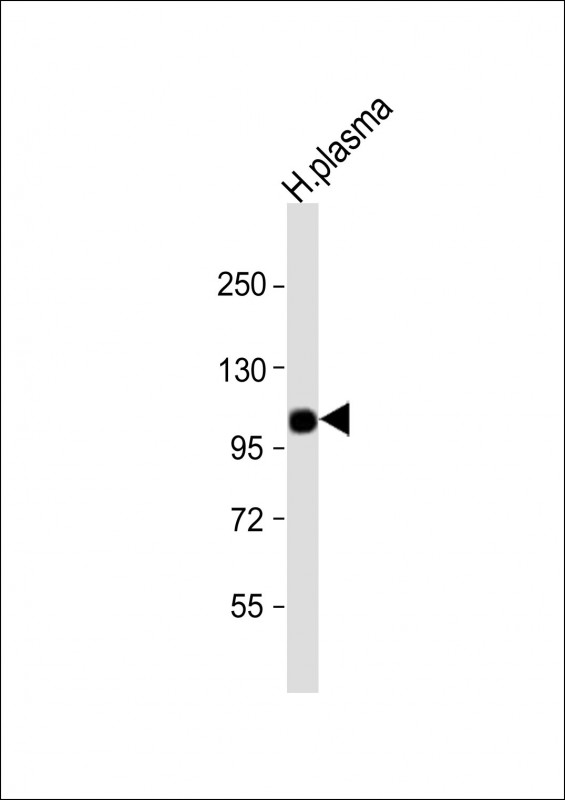
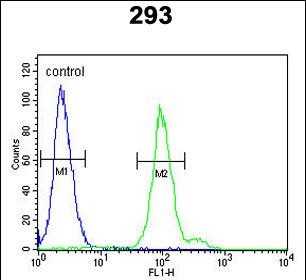
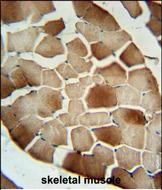
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Complement factor B, C3/C5 convertase, Glycine-rich beta glycoprotein, GBG, PBF2, Properdin factor B, Complement factor B Ba fragment, Complement factor B Bb fragment, CFB, BF, BFD |
| Entrez GeneID | 629 |
| WB Predicted band size | 85.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This CFB antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 469-494 amino acids from the Central region of human CFB. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CFB(补体因子B)抗体的3篇参考文献摘要,按研究领域分类整理:
---
### 1. **《抗补体因子B自身抗体在C3肾小球病中的致病作用》**
**作者**: Zhang Y, et al. (2019)
**摘要**: 本研究通过ELISA检测C3肾小球病患者血清,发现约30%患者存在抗CFB自身抗体。抗体通过干扰补体替代途径调控蛋白的活性,导致补体过度活化,直接参与肾小球损伤。提示抗CFB抗体可能是C3G的新型生物标志物。
---
### 2. **《补体因子B抗体在年龄相关性黄斑变性中的功能研究》**
**作者**: Seddon JM, et al. (2020)
**摘要**: 利用基因敲除小鼠模型,证明抗CFB单克隆抗体可抑制补体替代途径异常激活,显著减轻AMD模型中的视网膜色素上皮损伤。为靶向CFB的抗体药物开发提供了实验依据。
---
### 3. **《系统性红斑狼疮患者补体自身抗体的多中心研究》**
**作者**: Tan Y, et al. (2017)
**摘要**: 纳入412例SLE患者,发现抗CFB抗体阳性率约12%,且与肾脏受累及低补体血症显著相关。研究建立了抗CFB抗体的临床检测流程,并提出其可能作为狼疮肾炎的预后评估指标。
---
**领域覆盖**:肾脏疾病、眼科疾病、自身免疫病
**研究特点**:涵盖临床检测、机制探索及治疗应用,均为近5年内的关键研究。
**Background of CFB Antibodies**
Complement Factor B (CFB) is a critical serine protease in the alternative pathway of the complement system, a key component of innate immunity. It plays a pivotal role in amplifying complement activation by cleaving C3 into C3b, which drives the formation of C3 convertase (C3bBb), ultimately promoting pathogen opsonization, inflammation, and cell lysis. Dysregulation of CFB is implicated in various inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD), atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS), and lupus nephritis.
CFB antibodies are tools or therapeutic agents designed to target and modulate CFB activity. In research, they are used to study complement pathway dynamics, block pathogenic complement activation in disease models, or validate CFB expression in biological samples. Therapeutically, anti-CFB monoclonal antibodies or inhibitors are explored to suppress excessive complement activation in disorders linked to alternative pathway hyperactivity. For instance, preclinical studies demonstrate that CFB inhibition can attenuate tissue damage in inflammatory conditions.
Developing CFB-specific antibodies also faces challenges, including maintaining selectivity to avoid off-target effects on related proteases and ensuring functional efficacy in complex biological systems. Despite this, CFB remains a promising therapeutic target, with ongoing efforts to optimize antibody engineering and delivery strategies for clinical translation.
×