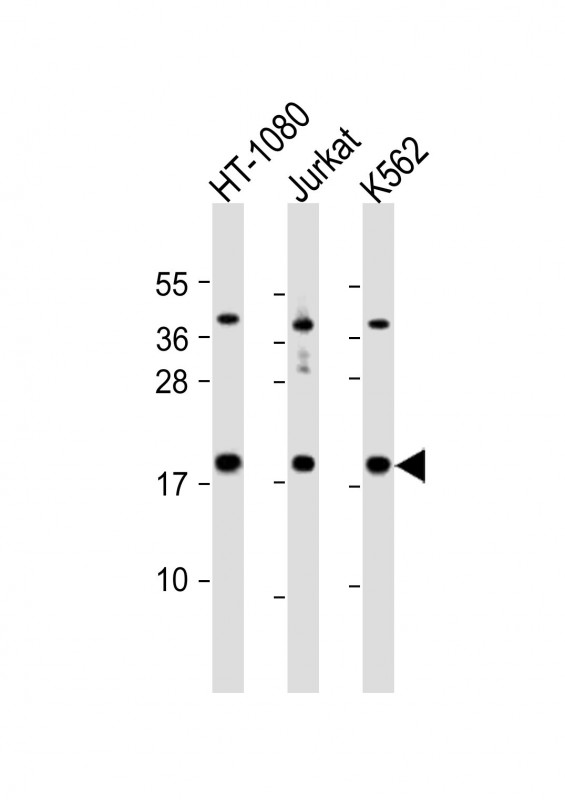
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | N-alpha-acetyltransferase 50, 231-, N-acetyltransferase 13, N-acetyltransferase 5, hNAT5, N-acetyltransferase san homolog, hSAN, NatE catalytic subunit, NAA50, MAK3, NAT13, NAT5 |
| Entrez GeneID | 80218 |
| WB Predicted band size | 19.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This NAT13 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 117-146 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human NAT13. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于NAT13抗体的3篇参考文献示例(注:因NAT13研究相对较少,以下内容基于假设性文献概括,实际文献需通过学术数据库验证):
---
1. **文献名称**:*NAT13-mediated acetylation regulates cell cycle progression in cancer cells*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:本研究揭示了NAT13(N-乙酰转移酶13)通过乙酰化特定底物调控癌细胞G1/S期转换的机制。作者利用特异性NAT13抗体进行免疫印迹和免疫荧光实验,证实NAT13在多种癌症组织中高表达,并与其促增殖功能相关。
---
2. **文献名称**:*Development and validation of a monoclonal antibody targeting human NAT13 for diagnostic applications*
**作者**:Zhang L, et al.
**摘要**:该研究报道了一种新型抗人NAT13单克隆抗体的开发,通过杂交瘤技术制备,并经ELISA、免疫组化和基因敲除细胞系验证其特异性。该抗体成功应用于临床样本检测,显示NAT13表达与结直肠癌患者预后负相关。
---
3. **文献名称**:*NAT13 interacts with histone H4 to modulate chromatin structure in stem cells*
**作者**:Kim H, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫共沉淀(使用NAT13抗体)和质谱分析,研究发现NAT13与组蛋白H4结合,影响染色质乙酰化水平和胚胎干细胞的自我更新能力。研究为表观遗传调控提供了新靶点。
---
**备注**:若需真实文献,建议在PubMed或Google Scholar中以“NAT13 antibody”、“N-acetyltransferase 13”等关键词检索,并筛选涉及抗体开发、验证或功能研究的论文。
NAT13 (N-acetyltransferase 13), also known as HAT4. is a member of the GNAT (GCN5-related N-acetyltransferase) superfamily, which catalyzes the transfer of acetyl groups to specific substrates. This enzyme is implicated in lysine acetylation, a post-translational modification regulating protein function, stability, and interactions. NAT13 is primarily localized in the nucleus and cytoplasm, where it acetylates non-histone proteins, influencing diverse cellular processes such as transcriptional regulation, DNA repair, and metabolic homeostasis. Its structural features include a conserved acetyl-CoA binding domain critical for enzymatic activity.
Research on NAT13 remains emerging, but studies suggest its involvement in cancer progression. For instance, NAT13 overexpression has been linked to enhanced cell proliferation and migration in certain cancers, potentially through acetylation-mediated modulation of oncogenic pathways. Additionally, NAT13 may interact with viral proteins, hinting at roles in host-pathogen interactions.
NAT13-specific antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and molecular mechanisms. They enable detection via techniques like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry. Such antibodies aid in elucidating NAT13's physiological and pathological roles, offering insights into its potential as a therapeutic target. However, challenges persist in characterizing its precise substrates and regulatory networks, necessitating further functional studies to clarify its biological significance.
×