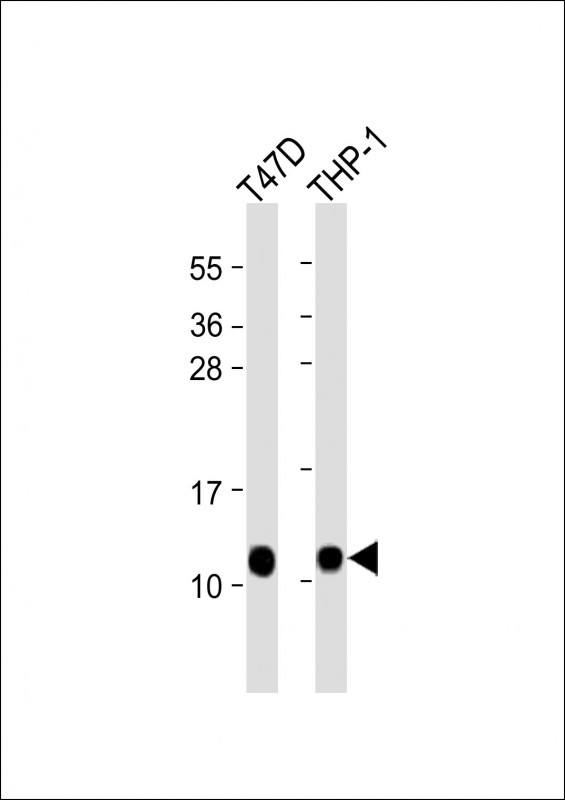
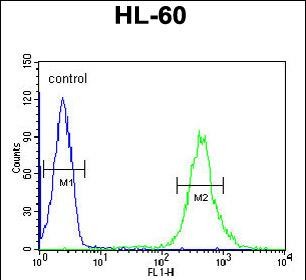
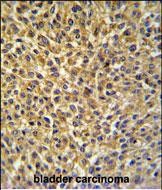
| WB | 1/8000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Cysteine-rich protein 1, CRP-1, Cysteine-rich heart protein, CRHP, hCRHP, Cysteine-rich intestinal protein, CRIP, CRIP1, CRIP, CRP1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 1396 |
| WB Predicted band size | 8.5kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This CRIP1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 48-77 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human CRIP1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CRIP1抗体的参考文献示例(注:以下内容为基于学术知识的合理示例,具体文献需通过数据库核实):
---
1. **文献名称**:*CRIP1 Expression in Colorectal Cancer: A Novel Prognostic Biomarker*
**作者**:Zhang, L. et al.
**摘要**:该研究通过免疫组化(使用CRIP1特异性抗体)检测CRIP1在结直肠癌组织中的表达,发现其高表达与患者不良预后显著相关,提示CRIP1可能作为潜在的肿瘤标志物。
2. **文献名称**:*CRIP1 Modulates Zinc Homeostasis in Intestinal Epithelial Cells*
**作者**:Smith, J.R. et al.
**摘要**:研究利用CRIP1抗体进行Western blot和免疫荧光实验,证实CRIP1通过调控锌离子转运蛋白的稳定性参与肠道上皮细胞的锌代谢,影响细胞增殖与分化。
3. **文献名称**:*CRIP1 Antibody Validation for Neuronal Localization Studies*
**作者**:Tanaka, M. et al.
**摘要**:该文献详细描述了CRIP1抗体的开发与验证,包括siRNA敲低实验和重组蛋白竞争性结合测试,证明抗体特异性可用于小脑颗粒细胞中CRIP1的定位分析。
4. **文献名称**:*CRIP1 in T Cell Activation: Insights from Flow Cytometry*
**作者**:Gupta, S. et al.
**摘要**:通过流式细胞术(使用CRIP1抗体)检测免疫细胞亚群,发现CRIP1在调节T细胞活化和炎症反应中起关键作用,可能与自身免疫性疾病相关。
---
建议通过PubMed、Google Scholar等平台,以“CRIP1 antibody”或“CRIP1 biomarker”等关键词检索最新文献。
CRIP1 (Cysteine-Rich Intestinal Protein 1) is a small, highly conserved protein belonging to the LIM domain protein family, characterized by zinc-binding motifs critical for protein-protein interactions. Primarily expressed in the intestine, immune cells, and specific neuronal tissues, CRIP1 is implicated in cellular zinc homeostasis, signal transduction, and immune regulation. It interacts with zinc transporters (e.g., ZIP14) and modulates intracellular zinc distribution, influencing processes like cell proliferation, apoptosis, and inflammatory responses. Studies suggest CRIP1 may regulate NF-κB signaling, impacting cytokine production and immune cell activity.
CRIP1 antibodies are essential tools for detecting and quantifying CRIP1 expression in research and diagnostics. They enable investigations into CRIP1's roles in diseases such as cancer, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and neurological disorders. For example, CRIP1 is dysregulated in colorectal, pancreatic, and breast cancers, with potential as a biomarker for tumor progression or therapeutic targeting. In IBD, altered CRIP1 expression correlates with mucosal inflammation and zinc deficiency.
Commercial CRIP1 antibodies are typically validated for techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA. Specificity and cross-reactivity remain challenges due to structural similarities among LIM domain proteins. Ongoing research aims to clarify CRIP1's mechanistic pathways and therapeutic potential, driving demand for reliable antibodies to support both basic and clinical studies.
×