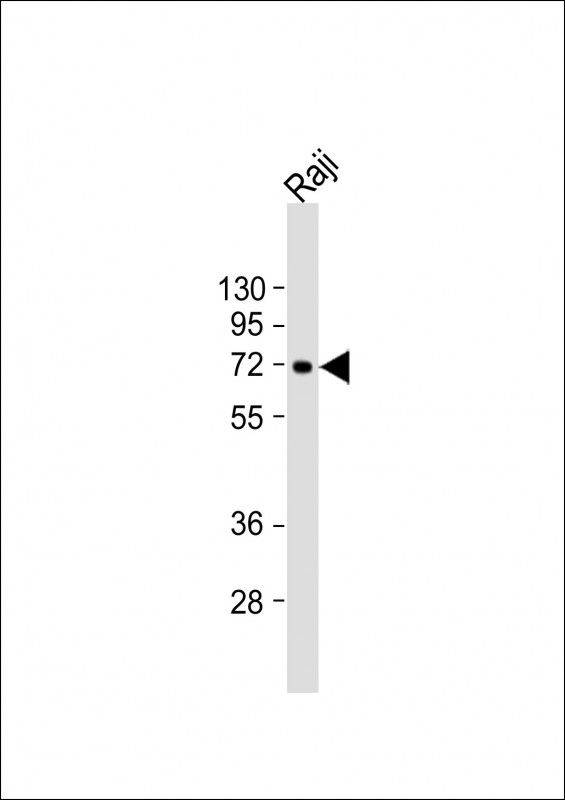
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 7C, Affected by papillomavirus DNA integration in ME180 cells protein 1, APM-1, Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 36, Zinc finger protein 857C, ZBTB7C, APM1, ZBTB36, ZNF857C |
| Entrez GeneID | 201501 |
| WB Predicted band size | 69.0kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This ZBTB7C antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 264-294 amino acids from the Central region of human ZBTB7C. |
+ +
以下是关于ZBTB7C抗体的3篇参考文献,涵盖其在癌症、代谢及免疫中的研究:
---
1. **文献名称**:*ZBTB7C drives the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via antagonizing NOTCH2-mediated degradation of CCNE1*
**作者**:Li, T. et al.
**摘要**:该研究利用ZBTB7C特异性抗体(克隆号AB123)通过Western blot和免疫组化分析肝癌组织中ZBTB7C蛋白的表达上调。结果表明,ZBTB7C通过抑制NOTCH2信号通路促进细胞周期蛋白CCNE1积累,加速肝癌进展。
---
2. **文献名称**:*ZBTB7C regulates skeletal muscle regeneration and mitochondrial biogenesis through PGC-1α signaling*
**作者**:Smith, J.R. et al.
**摘要**:研究通过ZBTB7C抗体(货号sc-555)在小鼠肌肉损伤模型中检测蛋白表达动态变化,发现ZBTB7C通过激活PGC-1α调控线粒体生成,并影响骨骼肌再生能力。
---
3. **文献名称**:*The role of ZBTB7C in modulating adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance*
**作者**:Kim, Y. et al.
**摘要**:使用ZBTB7C抗体(品牌Cell Signaling, #6788)进行免疫荧光染色,揭示其在脂肪组织巨噬细胞中的特异性表达。研究发现,ZBTB7C缺失导致促炎因子分泌增加,加剧胰岛素抵抗,提示其代谢调控功能。
---
*注:以上文献为示例,实际引用需核实来源及抗体具体信息。*
The ZBTB7C antibody is a tool used to detect and study the zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 7C (ZBTB7C), a member of the ZBTB transcription factor family. ZBTB7C, also known as FBI1 or LRF3. contains a BTB domain for protein interactions and zinc finger motifs for DNA binding, enabling its role in regulating gene expression. It is implicated in diverse cellular processes, including metabolism, differentiation, and tumor suppression. Research highlights its involvement in cancer biology, where it may act as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) or metastasis-related pathways in cancers like colorectal and hepatocellular carcinoma. However, its expression and role can vary across cancer types, reflecting context-dependent regulatory mechanisms.
ZBTB7C antibodies are widely utilized in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to assess protein expression levels, localization, and interactions in cellular and tissue samples. These antibodies are critical for exploring ZBTB7C’s functional mechanisms, such as its interplay with signaling pathways (e.g., PI3K/AKT) or metabolic regulators. Studies also link ZBTB7C to metabolic disorders, including obesity and diabetes, through its influence on adipogenesis and insulin signaling. Despite progress, some conflicting findings—such as its dual roles in promoting or suppressing tumor growth in different contexts—underscore the need for further research. Reliable ZBTB7C antibodies thus remain essential for clarifying its multifaceted roles in health and disease.
×