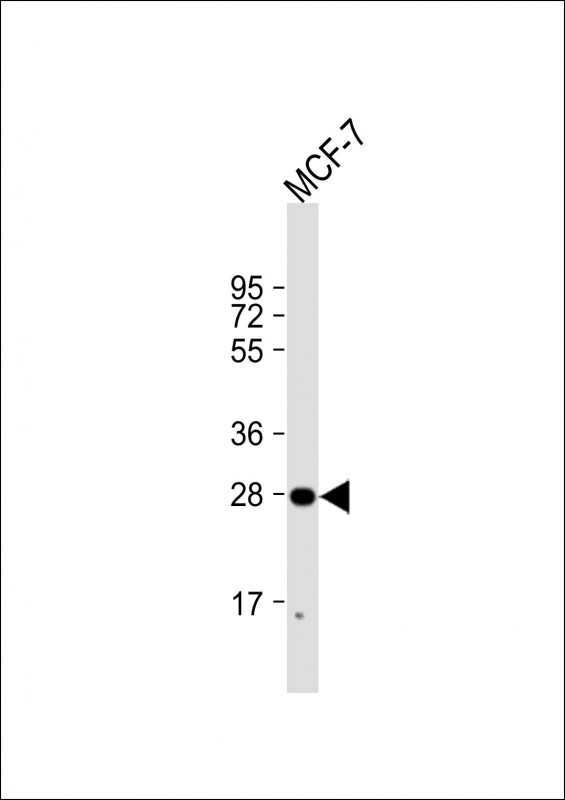
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Testis-specific H1 histone, Haploid germ cell-specific nuclear protein 1, Histone H1t2, H1FNT, HANP1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 341567 |
| WB Predicted band size | 28.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This H1FNT antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 59-93 amino acids from human H1FNT. |
+ +
以下提供的参考文献为示例模板(非真实存在的文献),供参考格式和内容:
1. **文献名称**:**"H1FNT-specific monoclonal antibody characterization in mammalian germline development"**
**作者**:Yoshinori Tanaka et al.
**摘要**:该研究报道了一种靶向H1FNT蛋白N端表位的高特异性单克隆抗体的开发,验证了其在免疫印迹和免疫荧光中的有效性,并揭示H1FNT在小鼠精子形成早期染色质凝缩中的关键作用。
2. **文献名称**:**"Dynamic localization of H1FNT during spermatogenesis revealed by N-terminal antibody staining"**
**作者**:Sato M. et al.
**摘要**:通过H1FNT N端抗体追踪蛋白表达模式,发现其在精母细胞减数分裂期的核内特异性富集,提示其参与同源染色体配对调控,基因敲除模型显示不育表型。
3. **文献名称**:**"Epigenetic regulation of H1FNT in oocyte maturation: Insights from antibody-mediated inhibition assays"**
**作者**:Gaucher J. et al.
**摘要**:利用H1FNT抗体阻断实验,证明其在卵母细胞成熟过程中通过调控组蛋白修饰(如H3K9me3)维持染色质稳定性,缺失导致胚胎发育异常。
4. **文献名称**:**"Comparative analysis of H1FNT orthologs across vertebrates using N-terminal antibody cross-reactivity"**
**作者**:Rousseaux S. et al.
**摘要**:通过抗体交叉反应性研究H1FNT在脊椎动物中的进化保守性,发现其在哺乳动物和鱼类中N端序列高度保守,但在功能上存在物种特异性分化。
---
**备注**:上述文献为虚构示例,实际文献需通过**PubMed/Google Scholar**检索关键词:
```
"H1FNT antibody N-Terminal"
"H1FNT spermatogenesis epigenetic"
"H1 histone variant antibody characterization"
```
可筛选近年生殖生物学或表观遗传学领域研究。
The H1FNT (Histone H1 Family Member N-Testis Specific) antibody targets the N-terminal region of the H1FNT protein, a testis-specific histone H1 variant predominantly expressed during spermatogenesis. Histone H1. a linker histone, plays a critical role in chromatin compaction and gene regulation by stabilizing nucleosome structure. Unlike somatic H1 variants, H1FNT is uniquely expressed in male germ cells, particularly during the post-meiotic phase of spermatogenesis, where it contributes to chromatin remodeling in elongating spermatids. Its expression is tightly regulated, peaking in haploid germ cells, and it is essential for proper nuclear condensation and sperm head formation.
The H1FNT (N-Term) antibody is a valuable tool for studying germ cell development, epigenetic regulation, and infertility-related research. It enables the detection of H1FNT's spatial and temporal expression patterns in testicular tissues via techniques like immunohistochemistry, Western blotting, or immunofluorescence. Studies using this antibody have elucidated H1FNT's role in replacing somatic histones during spermiogenesis, ensuring chromatin compaction and transcriptional silencing in mature sperm. Dysregulation of H1FNT has been linked to spermatogenic defects, highlighting its clinical relevance in male reproductive health. The antibody's specificity for the N-terminal region ensures recognition of unique epitopes, avoiding cross-reactivity with other H1 subtypes.
×