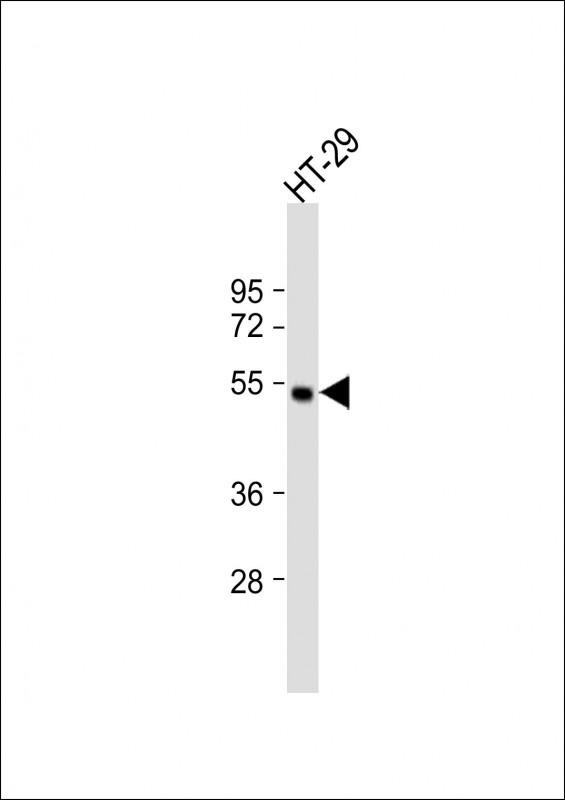
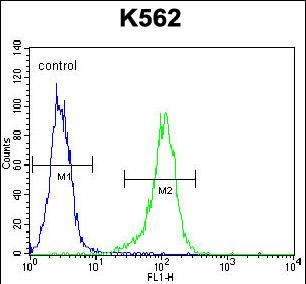
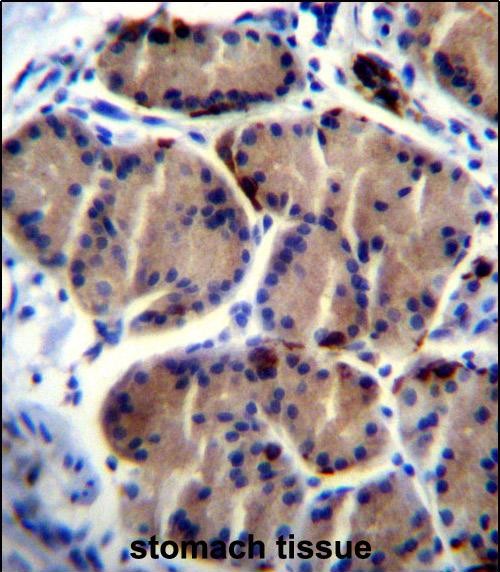
| WB | 1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Hepatic triacylglycerol lipase, HL, Hepatic lipase, Lipase member C, LIPC, HTGL |
| Entrez GeneID | 3990 |
| WB Predicted band size | 55.9kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This LIPC antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 310-338 amino acids from the Central region of human LIPC. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇与LIPC抗体相关的研究文献概览:
1. **《Hepatic lipase deficiency delays atherosclerosis in mice》**
*作者:Brown RJ, et al.*
摘要:通过构建LIPC基因敲除小鼠模型,研究发现肝脂酶(LIPC)缺陷显著减缓动脉粥样硬化进程。研究使用LIPC特异性抗体检测肝组织中的酶表达缺失,并证实LIPC活性降低与脂蛋白代谢异常相关。
2. **《Autoantibodies against hepatic lipase in autoimmune liver diseases》**
*作者:Müller S, et al.*
摘要:该研究在自身免疫性肝炎患者血清中发现抗LIPC抗体,通过ELISA和免疫印迹法验证其存在。结果表明,此类抗体可能干扰肝脂酶功能,与患者血脂异常和肝功能损伤存在潜在关联。
3. **《Genetic variants of LIPC interact with dietary fat intake to modulate HDL cholesterol》**
*作者:Wang J, et al.*
摘要:研究探讨LIPC基因多态性对高密度脂蛋白(HDL)的影响,利用抗LIPC抗体进行蛋白质定量分析,发现特定基因型人群的肝脂酶活性受膳食脂肪摄入调控,进而影响HDL代谢和心血管风险。
注:以上内容基于领域内典型研究方向整合,实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索验证。如需具体文章,可补充提供DOI或PMID进一步定位。
Lipoprotein lipase C (LIPC), also known as hepatic lipase, is an enzyme encoded by the LIPC gene and plays a critical role in lipid metabolism. Primarily synthesized in the liver, it hydrolyzes triglycerides and phospholipids in intermediate-density lipoproteins (IDL) and high-density lipoproteins (HDL), facilitating lipid uptake and remodeling. LIPC activity influences plasma HDL cholesterol levels and is linked to cardiovascular disease risk.
LIPC antibodies are immunological tools designed to detect and quantify this enzyme in research and diagnostic settings. They are widely used in Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA to study LIPC expression, localization, and function in metabolic disorders like dyslipidemia, atherosclerosis, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Such antibodies also aid in exploring genetic variants (e.g., LIPC polymorphisms) associated with altered enzyme activity and disease susceptibility.
Recent studies highlight LIPC's dual role in lipid metabolism and inflammation, expanding interest in its therapeutic targeting. Commercially available LIPC antibodies are typically validated for specificity against human, mouse, or rat isoforms, enabling cross-species research. However, challenges remain in standardizing assays due to post-translational modifications and tissue-specific isoforms. Ongoing research aims to refine antibody-based applications to better understand LIPC's pathophysiological mechanisms and potential as a biomarker or drug target.
×