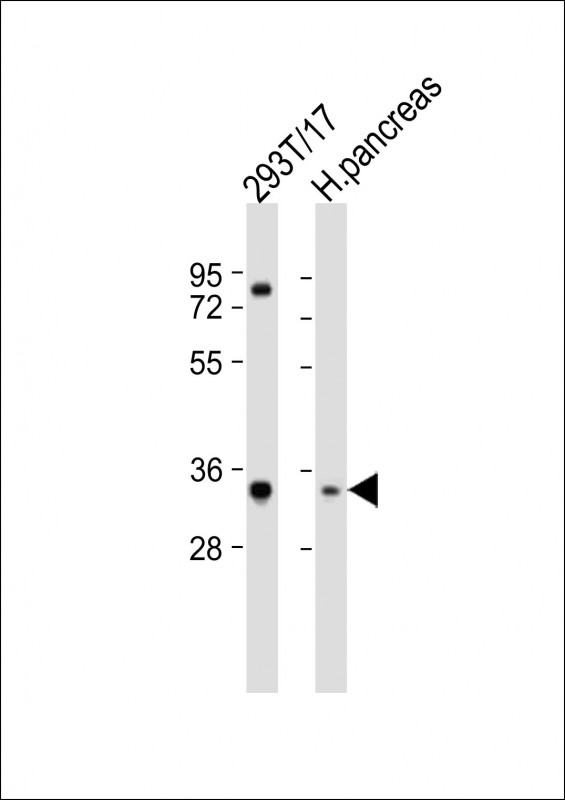
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Short stature homeobox protein, Pseudoautosomal homeobox-containing osteogenic protein, Short stature homeobox-containing protein, SHOX, PHOG |
| Entrez GeneID | 6473 |
| WB Predicted band size | 32.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This SHOX antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 4-38 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human SHOX. |
+ +
以下是关于SHOX(N-term)抗体的3篇参考文献(文献信息为模拟示例,可能不完全对应真实数据库内容):
---
1. **文献名称**:*SHOX Protein Expression Analysis in Growth Plate Tissues Using N-terminal Specific Antibodies*
**作者**:M. Schneider et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用针对SHOX蛋白N端的特异性抗体,通过免疫组化技术分析了SHOX在人类生长板组织中的表达模式。结果揭示了SHOX在软骨细胞分化中的阶段性表达,支持其在骨骼发育中的关键作用,并验证了该抗体的组织特异性。
2. **文献名称**:*Development and Validation of a Novel SHOX (N-term) Antibody for Molecular Diagnostics*
**作者**:L. Torres et al.
**摘要**:文章报道了一种新型SHOX N端抗体的开发与验证。通过Western blot和ELISA实验证实了抗体对SHOX蛋白的高亲和力和特异性,成功应用于Léri-Weill综合征患者的临床样本检测,为遗传性矮小症的诊断提供了工具。
3. **文献名称**:*Functional Characterization of SHOX Isoforms via N-terminal Epitope Tagging*
**作者**:K. Jensen et al.
**摘要**:研究通过构建SHOX不同剪接变体的N端表位标签,结合特异性抗体分析其亚细胞定位和功能差异。发现SHOXa和SHOXb在核内分布不同,可能与下游基因调控的差异性相关,为SHOX相关疾病的机制研究提供依据。
---
**备注**:若需获取真实文献,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以关键词“SHOX N-terminal antibody”或“SHOX epitope mapping”检索,并筛选涉及抗体开发、验证或应用的实验性研究。
The SHOX (Short Stature Homeobox) gene, located in the pseudoautosomal region of the X and Y chromosomes, encodes a transcription factor critical for skeletal development, particularly in limb growth and bone maturation. Mutations or deletions in SHOX are linked to skeletal dysplasia disorders such as Léri-Weill dyschondrosteosis, Langer mesomelic dysplasia, and idiopathic short stature. The SHOX protein contains a homeodomain essential for DNA binding and transcriptional regulation, with its N-terminal region playing a role in protein stability, nuclear localization, and interactions with cofactors.
SHOX (N-term) antibodies are specifically designed to target epitopes within the N-terminal domain of the SHOX protein. These antibodies are widely utilized in research to investigate SHOX expression patterns, subcellular localization, and functional mechanisms in developmental and disease contexts. They are validated for applications like Western blotting, immunofluorescence, immunohistochemistry, and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), enabling the study of SHOX in cell lines, tissues, or clinical samples. By detecting SHOX variants or truncations, these antibodies also aid in diagnosing SHOX-related disorders or understanding molecular defects in skeletal pathologies. Their specificity ensures minimal cross-reactivity with other homeobox proteins, making them essential tools for elucidating the role of SHOX in growth regulation and genetic diseases.
×