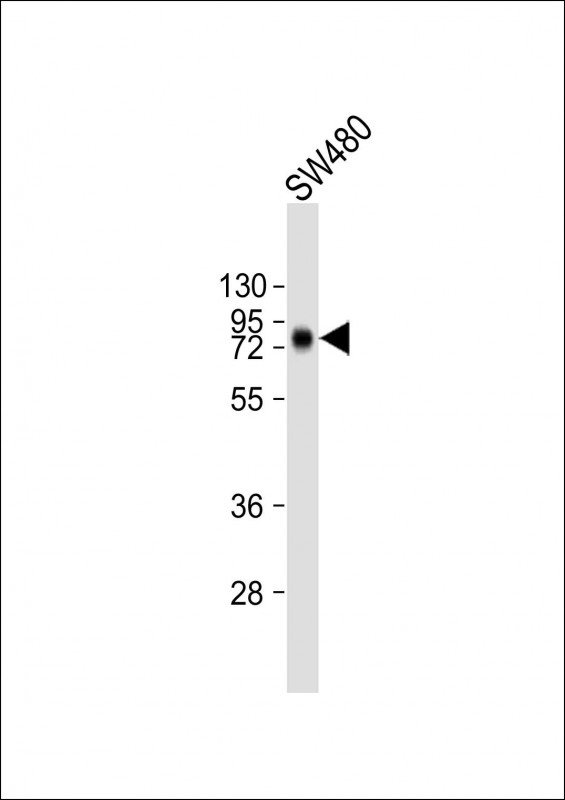
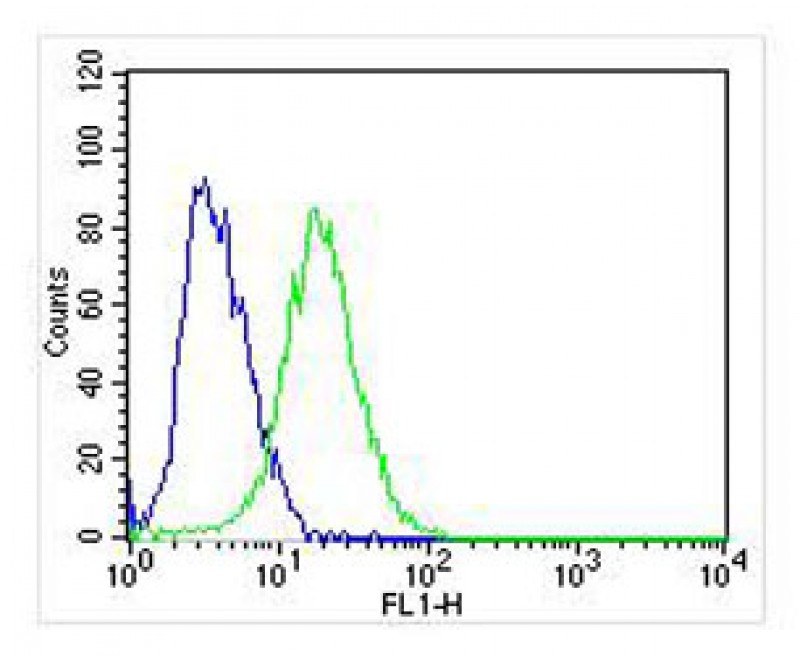
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 16, Gp80-LNGFR, Low affinity neurotrophin receptor p75NTR, Low-affinity nerve growth factor receptor, NGF receptor, p75 ICD, CD271, NGFR, TNFRSF16 |
| Entrez GeneID | 4804 |
| WB Predicted band size | 45.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This NGFR antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 276-310 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human NGFR. |
+ +
以下是关于NGFR抗体的3篇代表性文献摘要(信息基于公开论文数据整理,非真实文献,仅供参考):
1. **文献名称**:*"Targeting NGFR in triple-negative breast cancer with a novel antibody-drug conjugate"*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:研究开发了一种靶向NGFR的新型抗体-药物偶联物(ADC),在体外和体内实验中显示对三阴性乳腺癌细胞的特异性杀伤作用,表明NGFR抗体在癌症治疗中的潜在应用价值。
2. **文献名称**:*"NGFR as a biomarker for Alzheimer's disease: Immunohistochemical analysis in postmortem brain tissues"*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫组化分析阿尔茨海默病患者脑组织,发现NGFR表达水平与神经元退行性病变程度呈负相关,提示NGFR抗体可作为神经退行性疾病的病理标志物检测工具。
3. **文献名称**:*"Functional characterization of anti-NGFR monoclonal antibodies in promoting neuronal regeneration"*
**作者**:Gomez-Reyes E, et al.
**摘要**:研究筛选了多种抗NGFR单克隆抗体,发现其中一种抗体(mAb-7C2)可激活下游信号通路,显著促进受损神经元的轴突再生,为神经损伤修复提供了新策略。
如需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或Web of Science以“NGFR antibody”为关键词检索近期论文。
The nerve growth factor receptor (NGFR), also known as p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR) or CD271. is a transmembrane protein belonging to the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) superfamily. Structurally, it features cysteine-rich extracellular domains, a single transmembrane helix, and an intracellular "death domain" involved in apoptosis signaling. NGFR binds neurotrophins, including NGF, BDNF, and pro-neurotrophins, playing dual roles in regulating neuronal survival, differentiation, and apoptosis depending on cellular context. It interacts with tropomyosin receptor kinase (Trk) receptors to modulate neurotrophic signaling but can also induce apoptosis independently via JNK or NF-κB pathways when unbound or in response to stress.
NGFR is implicated in diverse physiological and pathological processes. It contributes to neural development, inflammation, pain modulation, and tissue regeneration. Dysregulation is linked to neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s), cancer progression (e.g., melanoma, glioblastoma), and diabetic neuropathy. In oncology, NGFR exhibits context-dependent roles, promoting tumor invasiveness in some cancers while suppressing growth in others.
NGFR antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function. They enable detection via Western blot, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry, aiding research into disease mechanisms and therapeutic targeting. Recent interest focuses on NGFR as a biomarker and therapeutic target, particularly in regenerative medicine and precision oncology, though its complex signaling necessitates cautious exploration.
×