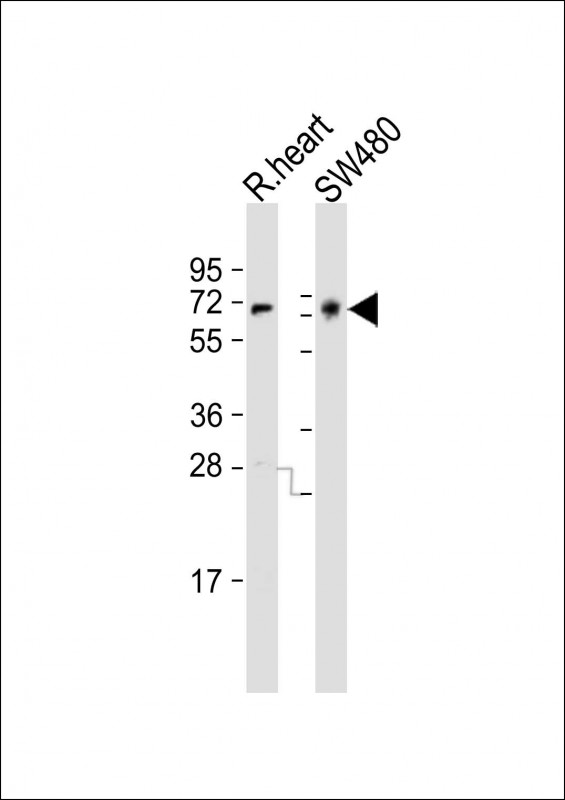
| WB | 1/1000-1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 16, Gp80-LNGFR, Low affinity neurotrophin receptor p75NTR, Low-affinity nerve growth factor receptor, NGF receptor, p75 ICD, CD271, NGFR, TNFRSF16 |
| Entrez GeneID | 4804 |
| WB Predicted band size | 45.2kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This NGFR antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 276-310 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human NGFR. |
+ +
以下是关于NGFR抗体的3篇代表性文献摘要:
1. **《Targeting p75NTR in neuroblastoma neuroblasts with therapeutic intent》**
*作者:Hertwig F. 等人(2016)*
摘要:研究利用特异性抗p75NTR(NGFR)抗体,通过体外和体内实验验证其在神经母细胞瘤中的靶向治疗潜力,显示抗体介导的肿瘤细胞凋亡增强及生长抑制。
2. **《A novel anti-NGFR antibody promotes cell death and inhibits metastasis in osteosarcoma》**
*作者:Zhang Y. 等人(2018)*
摘要:开发一种新型高亲和力NGFR单克隆抗体,可特异性抑制骨肉瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭,并通过激活JNK信号通路诱导肿瘤细胞程序性死亡。
3. **《p75NTR antibody reveals endogenous expression patterns and highlights axonal damage in Alzheimer’s disease brain》**
*作者:Knowles J.K. 等人(2020)*
摘要:通过优化抗p75NTR抗体的免疫组化方法,揭示阿尔茨海默病患者脑组织中NGFR的异常分布,提示其与轴突退行性变的相关性,为病理机制研究提供工具。
The nerve growth factor receptor (NGFR), also known as p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR) or CD271. is a transmembrane protein belonging to the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily. It binds to neurotrophins, including NGF, BDNF, and NT-3/4/5. playing dual roles in regulating cell survival, apoptosis, differentiation, and axonal guidance. NGFR is expressed in neural crest-derived cells (e.g., neurons, glia), stem cells, and certain cancers (e.g., melanoma, neuroblastoma). Its signaling outcomes depend on cellular context, co-receptor interactions (e.g., Trk receptors), and ligand binding.
NGFR antibodies are critical tools for studying its expression, localization, and function. They are widely used in neuroscience, cancer research, and regenerative medicine. Commercially available antibodies include polyclonal and monoclonal types, validated for techniques like Western blot, immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunofluorescence (IF), and flow cytometry. Specificity remains a key consideration, as NGFR shares structural homology with other TNF receptors. Researchers often use knockout controls or epitope mapping to confirm antibody reliability.
Dysregulation of NGFR signaling is linked to neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s) and cancer progression. Antibodies enable exploration of NGFR’s role in these pathologies and its potential as a therapeutic target. Recent studies also highlight its involvement in stem cell maintenance and tissue regeneration, expanding its biomedical relevance.
×