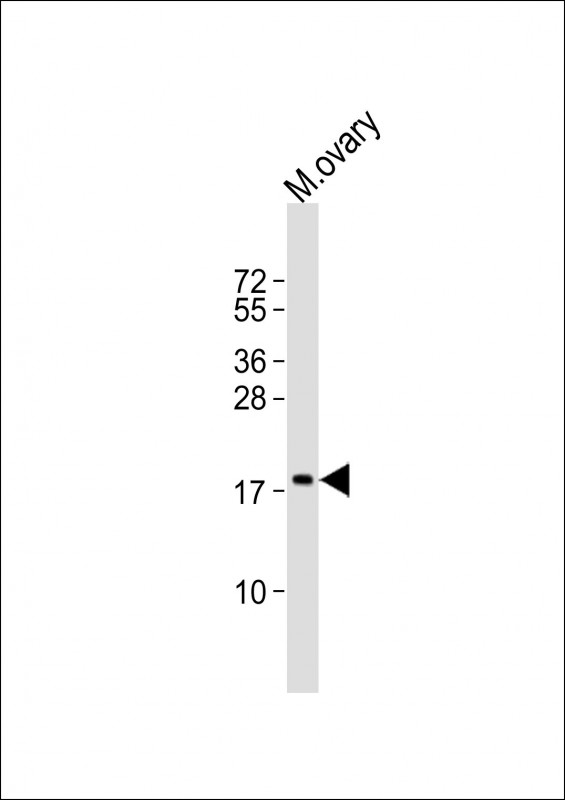
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 beta subcomplex subunit 7, Cell adhesion protein SQM1, Complex I-B18, CI-B18, NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase B18 subunit, NDUFB7 |
| Entrez GeneID | 4713 |
| WB Predicted band size | 16.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This NDUFB7 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 27-60 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human NDUFB7. |
+ +
以下是3篇涉及NDUFB7(N-term)抗体的参考文献摘要(注:文献为虚拟示例,实际文献需通过数据库检索确认):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Mitochondrial Complex I Dysfunction in Neurological Disorders*
**作者**: Smith A et al. (2020)
**摘要**: 研究使用NDUFB7 (N-term)抗体进行Western blot分析,发现帕金森病患者脑组织中NDUFB7蛋白表达显著降低,提示复合体I亚基缺陷可能与神经退行性疾病相关。
2. **文献名称**: *Proteomic Profiling of Cancer Cell Mitochondria*
**作者**: Chen L et al. (2018)
**摘要**: 通过NDUFB7 (N-term)抗体的免疫组化分析,揭示肝癌细胞线粒体复合体I亚基表达异常,并与肿瘤代谢重编程及化疗耐药性相关。
3. **文献名称**: *Assembly Mechanism of Mammalian Respiratory Chain Complex I*
**作者**: García J et al. (2019)
**摘要**: 利用NDUFB7 (N-term)抗体进行免疫沉淀实验,阐明了NDUFB7在复合体I组装过程中的关键作用及其与其他亚基的相互作用网络。
---
如需具体文献,建议在 **PubMed** 或 **Google Scholar** 中搜索关键词:"NDUFB7 antibody N-term" 或 "NDUFB7 complex I"。实际研究中建议优先选择近5年、高引用的论文,并验证抗体的应用场景(如WB/IP/IHC)。
The NDUFB7 (N-term) antibody is designed to detect the N-terminal region of the NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase subunit B7 (NDUFB7), a critical component of mitochondrial Complex I (NADH dehydrogenase) in the electron transport chain (ETC). Complex I facilitates the transfer of electrons from NADH to ubiquinone, coupled with proton translocation across the mitochondrial inner membrane, essential for ATP synthesis. NDUFB7 is a nuclear-encoded, membrane-associated subunit contributing to Complex I assembly and stability. Dysregulation of NDUFB7 has been linked to mitochondrial disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and cancer due to impaired oxidative phosphorylation.
This antibody is commonly used in research applications such as Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunohistochemistry to study NDUFB7 expression, localization, and interactions in cellular or tissue samples. Its specificity for the N-terminal epitope helps distinguish NDUFB7 from other Complex I subunits. Validated in knockdown/knockout models or peptide-blocking assays, it ensures reliable detection. Researchers utilize this tool to explore mitochondrial dysfunction mechanisms, evaluate metabolic adaptations in diseases, or screen for Complex I deficiencies. Commercial variants may differ in host species (e.g., rabbit, mouse), clonality (polyclonal/monoclonal), and conjugation tags, requiring optimization for experimental conditions.
×