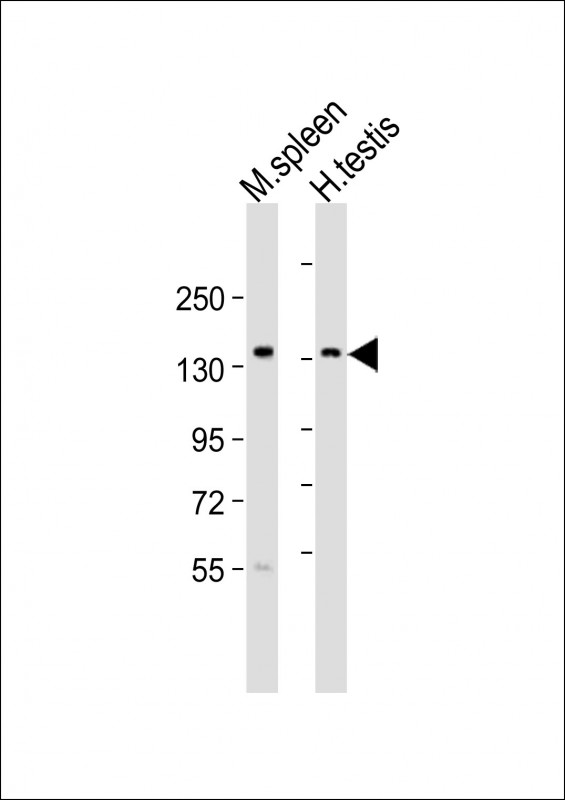
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
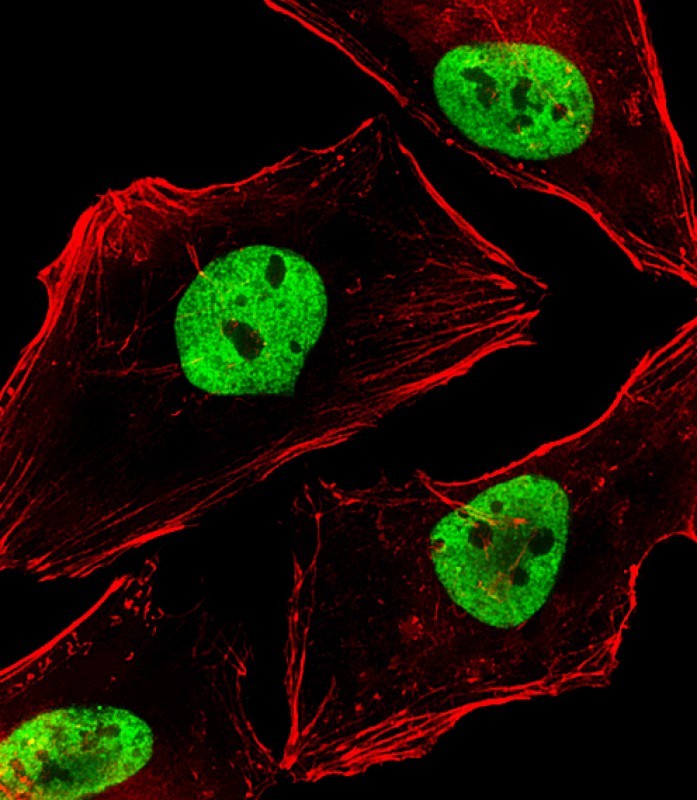
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | B-cell CLL/lymphoma 9 protein, B-cell lymphoma 9 protein, Bcl-9, Protein legless homolog, BCL9 |
| Entrez GeneID | 607 |
| WB Predicted band size | 149.3kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This BCL9 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 272-304 amino acids from human BCL9. |
+ +
以下是关于BCL9(N-Term)抗体的3篇参考文献的简要总结:
1. **"BCL9 is a critical component of the Wnt/β-catenin transcriptional complex"**
- **作者**: Kramps T. et al.
- **摘要**: 研究揭示了BCL9通过N端结构域与β-catenin结合,增强Wnt信号通路的转录活性,并开发了针对BCL9 N端的抗体用于阻断该相互作用,抑制结直肠癌细胞增殖。
2. **"Targeting BCL9-mediated protein interactions suppresses Wnt-driven cancers"**
- **作者**: Manolopoulou M. et al.
- **摘要**: 报道了一种特异性靶向BCL9 N端的单克隆抗体,可破坏BCL9与β-catenin的复合体形成,抑制Wnt信号传导,在多种肿瘤模型中显著减少转移和肿瘤生长。
3. **"BCL9 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through Wnt/β-catenin signaling activation"**
- **作者**: Zhang Y. et al.
- **摘要**: 通过使用抗BCL9(N-Term)抗体的免疫组化分析,发现BCL9在肝癌组织中高表达,且其表达水平与患者预后不良相关,提示其作为治疗靶点的潜力。
如需具体文献来源,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索上述标题及作者获取全文信息。
The BCL9 (N-Term) antibody is a tool used to study the role of B-cell lymphoma 9 (BCL9), a critical transcriptional coactivator in the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. BCL9 interacts with β-catenin to regulate the transcription of Wnt target genes involved in cell proliferation, differentiation, and oncogenesis. Dysregulation of BCL9 is implicated in cancers, particularly colorectal carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, and hematologic malignancies, where hyperactivated Wnt signaling drives tumor progression.
The N-terminal region of BCL9 contains a conserved homology domain (HD1) essential for binding β-catenin, making antibodies targeting this region valuable for investigating BCL9-β-catenin complex formation and its oncogenic functions. Researchers use the BCL9 (N-Term) antibody in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to detect BCL9 expression levels, subcellular localization, and interactions in normal versus cancerous tissues.
Studies employing this antibody have highlighted BCL9's role in promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), metastasis, and cancer stem cell maintenance. Its specificity for the N-terminal epitope helps distinguish BCL9 from its paralog BCL9L or splice variants, ensuring precise mechanistic insights. Additionally, the antibody supports therapeutic research, as disrupting BCL9-β-catenin interactions is a potential strategy for targeting Wnt-dependent cancers. Validation in knockout models or siRNA-treated cells is recommended to confirm signal specificity.
×