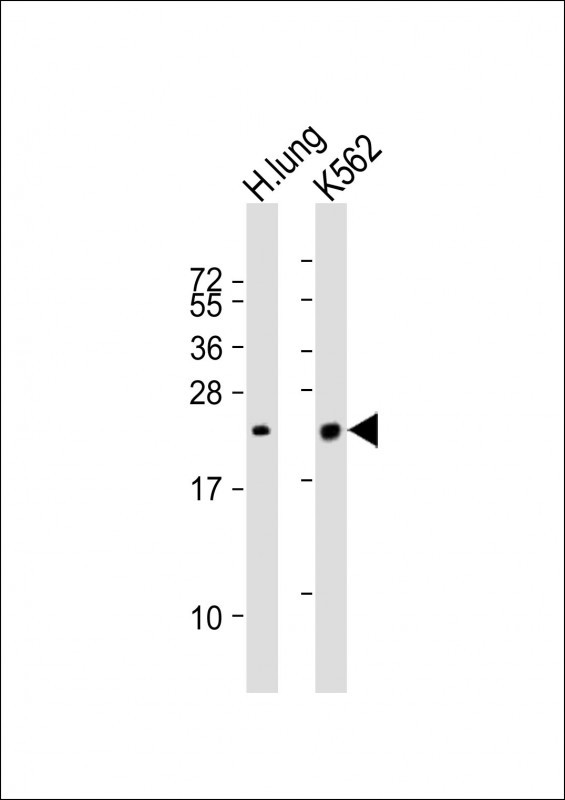
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
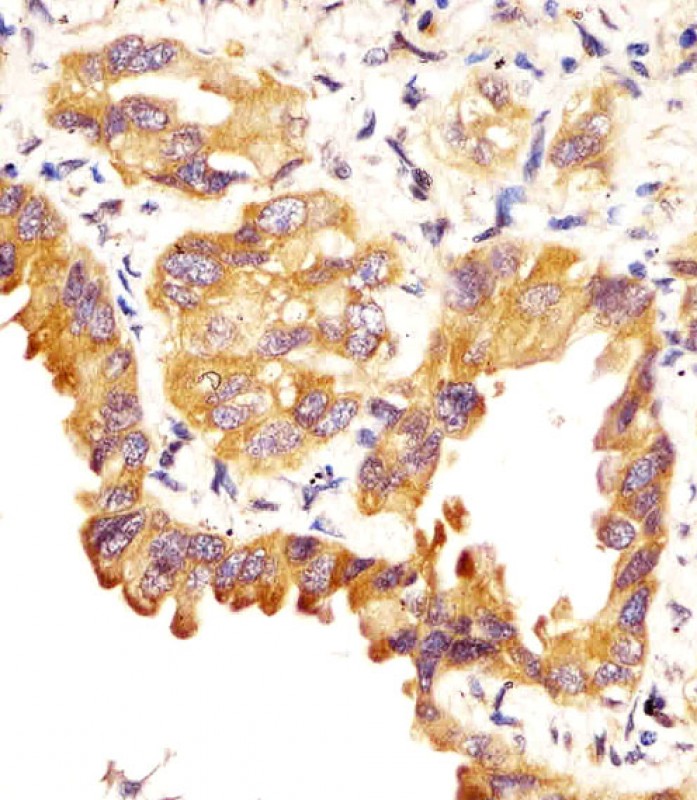
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Pulmonary surfactant-associated protein C, SP-C, Pulmonary surfactant-associated proteolipid SPL(Val), SP5, SFTPC, SFTP2 |
| Entrez GeneID | 6440 |
| WB Predicted band size | 21.1kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This SFTPC antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 144-173 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human SFTPC. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇与SFTPC抗体相关的文献概览:
1. **"Mutations in the Surfactant Protein C Gene Associated with Interstitial Lung Disease"**
*作者:Nogee LM et al. (2001)*
摘要:该研究首次发现SFTPC基因突变与家族性间质性肺病(ILD)的关联,通过免疫组化技术结合SFTPC特异性抗体,证实突变导致肺泡II型细胞中SP-C前体蛋白异常积累。
2. **"Aberrant SP-C Processing in Fibrotic Lung Disease"**
*作者:Korfei M et al. (2018)*
摘要:探讨特发性肺纤维化(IPF)患者中SFTPC的异常代谢途径,利用Western blot和免疫荧光(SFTPC抗体)揭示SP-C前体蛋白的错误折叠与肺泡上皮细胞应激的关系。
3. **"Autoantibodies Against Surfactant Protein C in Pediatric Lung Disease"**
*作者:Gupta A et al. (2012)*
摘要:研究儿童间质性肺病(chILD)患者血清中抗SFTPC自身抗体的存在,通过ELISA和蛋白质印迹验证抗体与SP-C的结合,提示其可能作为疾病活动的生物标志物。
4. **"Intracellular Pathways of SP-C Trafficking and Misfolding in Lung Injury"**
*作者:Mulugeta S, Beers MF (2015)*
摘要:综述SFTPC蛋白从合成到分泌的调控机制,强调使用特异性抗体追踪突变SP-C在细胞内的错误定位及毒性作用,为遗传性ILD提供分子机制解释。
以上文献均涉及SFTPC抗体的实验应用,涵盖基因突变、疾病机制及诊断研究。
The SFTPC antibody targets surfactant protein C (SP-C), a critical component of pulmonary surfactant essential for reducing alveolar surface tension and maintaining respiratory function. Encoded by the SFTPC gene, SP-C is synthesized primarily by type II alveolar epithelial cells as a precursor protein (proSP-C) that undergoes post-translational processing to become the mature, hydrophobic peptide stabilizing alveoli during breathing cycles.
Mutations in SFTPC are linked to hereditary interstitial lung diseases, particularly in infants and children, including idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and childhood interstitial lung disease (chILD). These mutations often lead to protein misfolding, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and cellular dysfunction. SFTPC antibodies are valuable tools in research and diagnostics, enabling detection of SP-C expression patterns in lung tissues through techniques like immunohistochemistry and Western blotting. They help characterize SP-C processing abnormalities in genetic disorders and assess alveolar type II cell health in conditions such as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) or drug-induced lung injury. Additionally, these antibodies aid in differentiating pulmonary pathologies and investigating surfactant metabolism dysregulation, contributing to both mechanistic studies and clinical diagnostics.
×