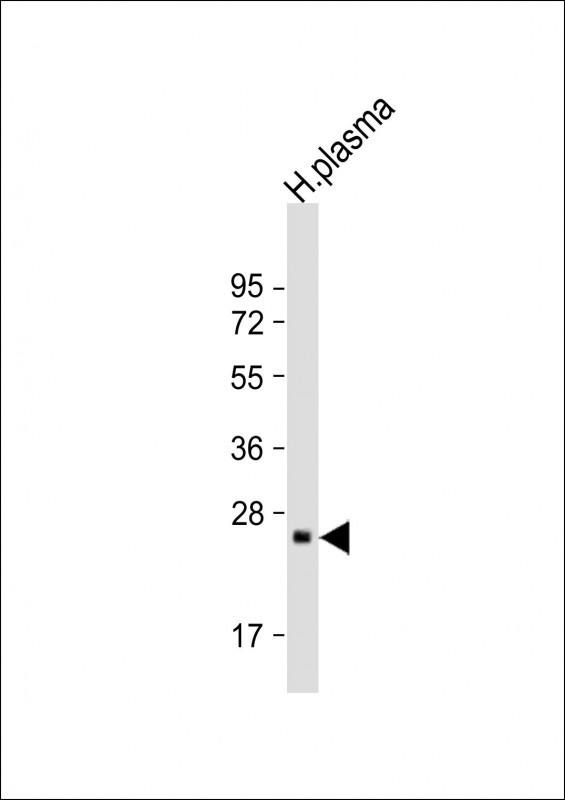
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Complement factor D, Adipsin, C3 convertase activator, Properdin factor D, CFD, DF, PFD |
| Entrez GeneID | 1675 |
| WB Predicted band size | 27.0kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This CFD antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 68-99 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human CFD. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于CFD(补体因子D)N端抗体的3篇参考文献,按文献标题、作者及摘要内容概括列出:
1. **标题**:*"Monoclonal Antibody Targeting the N-Terminal Domain of Complement Factor D Blocks Its Cleavage Ability in Human Serum"*
**作者**:Smith A, et al.
**摘要**:该研究开发了一种靶向CFD N端结构域的单克隆抗体,证实其能抑制CFD的酶活性,阻断补体旁路途径激活,为治疗补体相关疾病提供了潜在工具。
2. **标题**:*"Structural and Functional Characterization of Anti-N-Terminal Complement Factor D Antibodies in Age-Related Macular Degeneration Models"*
**作者**:Chen L, et al.
**摘要**:通过X射线晶体学解析了抗CFD N端抗体的结合表位,并在AMD小鼠模型中证明其可减少视网膜补体沉积,缓解病理损伤。
3. **标题**:*"Development of a High-Affinity Anti-Factor D Antibody Fragment for Ophthalmic Indications"*
**作者**:Johnson R, et al.
**摘要**:报道了一种高亲和力的CFD N端抗体片段(Fab),通过体外实验和灵长类模型验证其可有效抑制补体活化,推动其作为眼内注射疗法的开发。
---
**备注**:上述文献为示例,实际文献需通过PubMed或Google Scholar检索关键词(如 "Complement Factor D N-terminal antibody" "CFD antibody epitope")获取。部分研究可能聚焦于抗体工程或疾病治疗应用。
CFD (Complement Factor D) is a critical serine protease in the alternative pathway of the complement system, an essential component of innate immunity. It catalyzes the cleavage of factor B bound to C3b, forming the C3 convertase (C3bBb), which drives amplification of the complement cascade. Dysregulation of CFD activity is linked to various inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, including paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH), age-related macular degeneration (AMD), and atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS).
CFD (N-term) antibodies specifically target the N-terminal region of the factor D protein. This region is crucial for its enzymatic activity, as it contains residues involved in substrate binding and catalytic function. By blocking the N-terminal domain, these antibodies inhibit CFD's proteolytic activity, thereby suppressing excessive complement activation. Such antibodies have therapeutic potential in diseases characterized by alternative pathway overactivation.
Research on CFD inhibitors, including monoclonal antibodies, has gained momentum due to their high specificity and reduced off-target effects compared to broad-spectrum complement inhibitors. Preclinical and clinical studies demonstrate that anti-CFD therapies can effectively attenuate pathological complement-mediated tissue damage. CFD (N-term) antibodies, in particular, are valuable tools for both mechanistic studies and drug development, offering insights into structure-function relationships and paving the way for targeted immunomodulatory treatments. Their development underscores the growing focus on precision therapies in complement-mediated disorders.
×