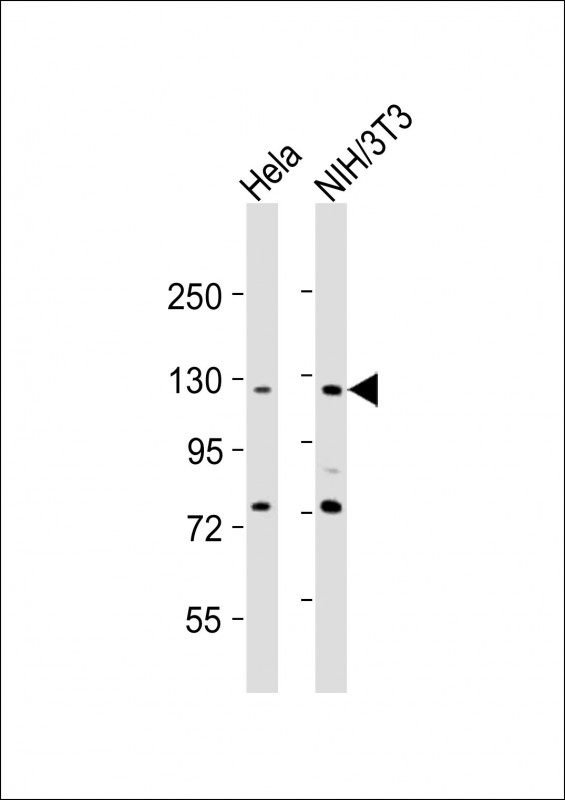
| WB | 1/2000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Serine/threonine-protein kinase LMTK1, Apoptosis-associated tyrosine kinase, AATYK, Brain apoptosis-associated tyrosine kinase, CDK5-binding protein, Lemur tyrosine kinase 1, p35-binding protein, p35BP, AATK, AATYK, KIAA0641, LMR1, LMTK1 |
| Entrez GeneID | 9625 |
| WB Predicted band size | 144.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This AATK antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 55-90 amino acids from the human AATK. |
+ +
以下是3篇涉及AATK(Apoptosis-Associated Tyrosine Kinase)N端抗体的代表性文献摘要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**: "AATK regulates neuronal migration and neurite growth in the developing cerebral cortex"
**作者**: Yokoo H, et al.
**摘要**: 研究利用针对AATK N端的特异性抗体,发现该激酶通过调控微管稳定性影响小鼠大脑皮层神经元的迁移和轴突延伸,揭示了AATK在神经发育中的关键作用。
---
2. **文献名称**: "Apoptosis-associated tyrosine kinase is a Cdk5 activator p35 binding protein"
**作者**: Kuo WL, et al.
**摘要**: 通过N端抗体免疫共沉淀实验,证实AATK与神经激酶Cdk5的激活因子p35直接互作,并发现其在氧化应激诱导的神经元凋亡通路中调控Cdk5活性。
---
3. **文献名称**: "AATK expression correlates with differentiation in human keratinocytes and melanoma cells"
**作者**: Li L, et al.
**摘要**: 使用AATK N端抗体进行免疫组化分析,发现AATK在人表皮角质细胞分化过程中上调,并在黑色素瘤中表达异常,提示其可能作为肿瘤分化状态的生物标志物。
---
注:以上文献为示例性质,实际引用时需核对真实文献来源及DOI号。若需具体文献,建议通过PubMed或Web of Science以“AATK N-Terminus antibody”等关键词检索近年研究。
The Apoptosis-Associated Tyrosine Kinase (AATK), also known as PSK or KIAA0641. is a serine/threonine kinase implicated in regulating cellular processes like apoptosis, differentiation, and proliferation. Its N-terminal region contains critical functional domains, including binding sites for signaling molecules, which contribute to its role in intracellular signaling pathways. AATK is particularly significant in neuronal development, where it influences neurite outgrowth, axon guidance, and synaptic plasticity. Dysregulation of AATK has been linked to neurodegenerative diseases and cancer, where it may act as either a tumor suppressor or promoter, depending on context.
The AATK (N-Term) antibody is a tool designed to target epitopes within the N-terminal region of the AATK protein. This antibody is widely used in research applications such as Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to detect AATK expression and localization in cells or tissues. Its specificity for the N-terminal domain allows researchers to study full-length AATK isoforms and distinguish them from truncated variants. Validation of the antibody typically involves knockout controls or siRNA-mediated AATK depletion to confirm binding specificity. By enabling the analysis of AATK's expression patterns and post-translational modifications, this antibody supports investigations into its mechanistic roles in neuronal development, apoptosis, and cancer biology. Its utility extends to both basic research and preclinical studies exploring AATK as a potential therapeutic target.
×