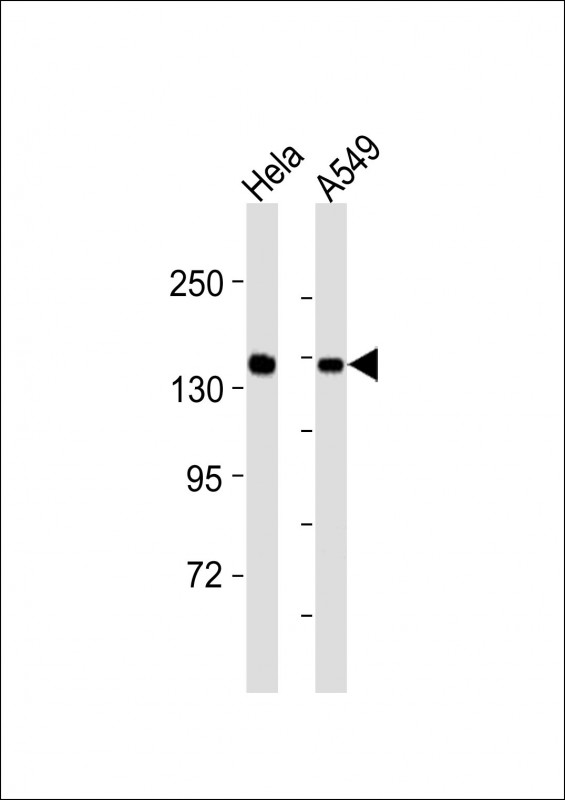
| WB | 1/8000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | LIM domain only protein 7, LMO-7, F-box only protein 20, LOMP, LMO7, FBX20, FBXO20, KIAA0858 |
| Entrez GeneID | 4008 |
| WB Predicted band size | 192.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This LMO7 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 1407-1440 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human LMO7. |
+ +
以下是关于LMO7抗体的3篇参考文献,按文献名称、作者和摘要内容简要概括:
---
1. **文献名称**:*LMO7 regulates cell proliferation and migration through the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in gastric cancer*
**作者**:Zhang Y, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用LMO7抗体通过免疫组化和Western blot分析发现,LMO7在胃癌组织中高表达,并通过PI3K/Akt通路促进肿瘤细胞增殖和迁移,提示其作为潜在治疗靶点。
2. **文献名称**:*LMO7 interacts with α-actinin to control mechanotransduction and apical junctional organization in epithelial cells*
**作者**:Ooshio T, et al.
**摘要**:通过免疫荧光和免疫共沉淀(使用LMO7抗体)证明,LMO7与α-actinin结合,调控上皮细胞机械信号传导和细胞间连接结构,影响细胞极性和屏障功能。
3. **文献名称**:*Role of LMO7 in podocyte architecture and glomerular disease*
**作者**:Suleiman H, et al.
**摘要**:研究利用LMO7抗体在小鼠肾小球足细胞中定位LMO7蛋白,发现其缺失导致足细胞结构异常和蛋白尿,提示LMO7在维持肾小球滤过屏障中的关键作用。
---
以上文献均通过LMO7抗体进行蛋白定位或功能研究,涵盖癌症、细胞粘附和肾脏疾病等领域。如需更多文献或具体细节,可进一步检索PubMed或SciFinder数据库。
LMO7 (LIM domain only protein 7) is a multidomain scaffolding protein involved in diverse cellular processes, including cell adhesion, cytoskeletal organization, and transcriptional regulation. It contains a LIM domain at its N-terminus, which mediates protein-protein interactions, and a calponin homology (CH) domain at its C-terminus, enabling actin binding. LMO7 plays critical roles in maintaining epithelial integrity, cell polarity, and mechanotransduction by linking the actin cytoskeleton to cell junctions, particularly at adherens junctions and focal adhesions. It interacts with proteins like HOMER, CADM1. and Afadin, and is implicated in signaling pathways such as YAP/TAZ in the Hippo pathway. Dysregulation of LMO7 is associated with cancers (e.g., breast, lung), cardiomyopathy, and hearing loss.
LMO7 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function. They are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence to investigate LMO7’s role in tissue development, disease mechanisms, and potential therapeutic targeting. Commercial LMO7 antibodies are typically raised against specific epitopes (e.g., human LMO7 amino acid regions) and validated for specificity across species (human, mouse, rat). Research using these antibodies has highlighted LMO7’s tumor-suppressive or oncogenic roles in different contexts, underscoring its complex involvement in cellular homeostasis and pathology.
×