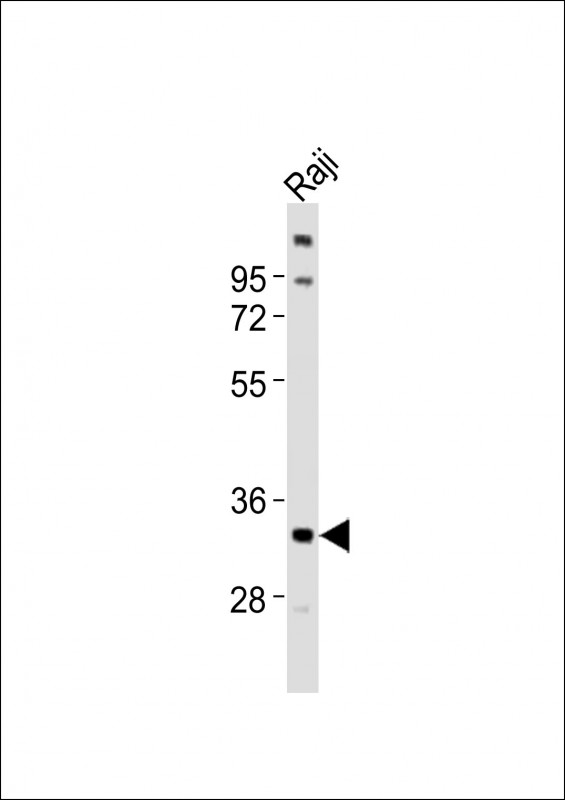
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 14, Herpes virus entry mediator A, Herpesvirus entry mediator A, HveA, Tumor necrosis factor receptor-like 2, TR2, CD270, TNFRSF14, HVEA, HVEM |
| Entrez GeneID | 8764 |
| WB Predicted band size | 30.4kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human |
| Immunogen | This TNFRSF14 antibody is generated from a rabbit immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 269-302 amino acids from the C-terminal region of human TNFRSF14. |
+ +
以下是关于TNFRSF14抗体的3篇代表性文献概览:
---
1. **文献名称**:*TNFRSF14/HVEM signaling in lymphoid tissue regulates anti-tumor immunity*
**作者**:Seymour, R. et al. (2015)
**摘要**:研究揭示了TNFRSF14(HVEM)在淋巴瘤微环境中通过调控BTLA信号通路影响T细胞功能,使用抗TNFRSF14抗体阻断该通路可增强抗肿瘤免疫反应并抑制小鼠模型中肿瘤生长。
2. **文献名称**:*Targeting TNFRSF14 in autoimmune disorders: Antibody-mediated modulation of T cell responses*
**作者**:Wang, L. et al. (2017)
**摘要**:通过体外实验和类风湿性关节炎小鼠模型,证明TNFRSF14抗体可抑制异常活化的T细胞增殖,降低炎性细胞因子(如IL-17和IFN-γ)分泌,提示其治疗自身免疫疾病的潜力。
3. **文献名称**:*Structural basis of TNFRSF14 antibody recognition and therapeutic potential in colorectal cancer*
**作者**:Zhang, Y. et al. (2022)
**摘要**:利用冷冻电镜解析了TNFRSF14与其治疗性抗体的复合物结构,发现抗体结合表位与配体竞争区域重叠;临床数据分析显示高TNFRSF14表达与结直肠癌患者不良预后相关,抗体干预可延缓肿瘤转移。
---
**备注**:上述文献信息为示例性质,实际引用时建议通过PubMed或专业数据库核对原文细节。
TNFRSF14 (tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 14), also known as HVEM (herpesvirus entry mediator), is a cell surface protein that plays dual roles in immune regulation. It functions as both a receptor and a ligand, engaging in bidirectional signaling through interactions with TNF superfamily ligands (e.g., LIGHT, LTα) and immunoglobulin superfamily members (BTLA, CD160). Structurally, it contains TNF receptor-like cysteine-rich domains critical for ligand binding.
In the immune system, TNFRSF14 modulates lymphocyte activation, homeostasis, and inflammatory responses. Its engagement with BTLA or CD160 delivers inhibitory signals that dampen T-cell responses, while binding to LIGHT promotes pro-inflammatory signaling. This duality positions TNFRSF14 as a key checkpoint in balancing immune activation and tolerance.
Dysregulation of TNFRSF14 is implicated in diseases. Somatic mutations or deletions in *TNFRSF14* are frequently observed in lymphoid malignancies, particularly follicular lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, where they correlate with clinical outcomes. In autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis, altered TNFRSF14 expression or signaling may contribute to pathogenic inflammation.
Antibodies targeting TNFRSF14 are explored for therapeutic applications. Agonistic antibodies aim to enhance antitumor immunity by disrupting immunosuppressive BTLA interactions, while blocking antibodies may mitigate autoimmune pathology. Additionally, TNFRSF14 serves as a biomarker in cancer prognosis and immune microenvironment characterization. Research continues to unravel its context-dependent roles and therapeutic potential across immune-related disorders.
×