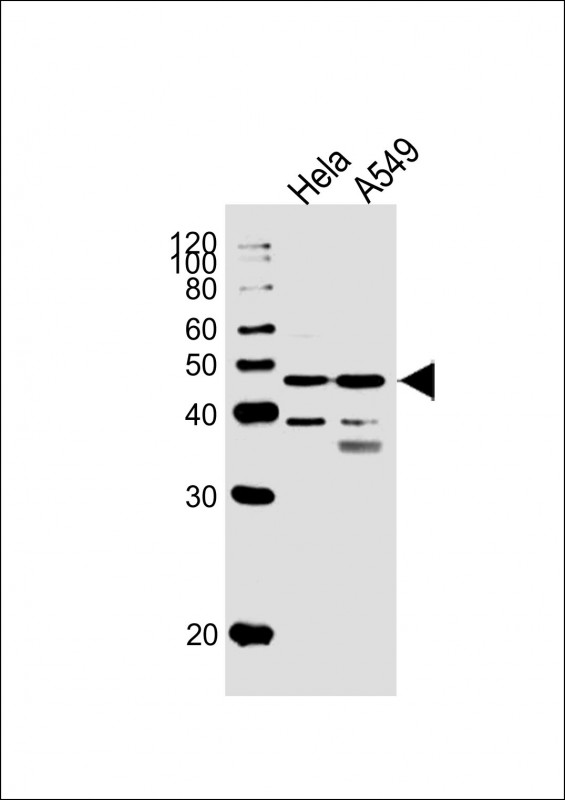
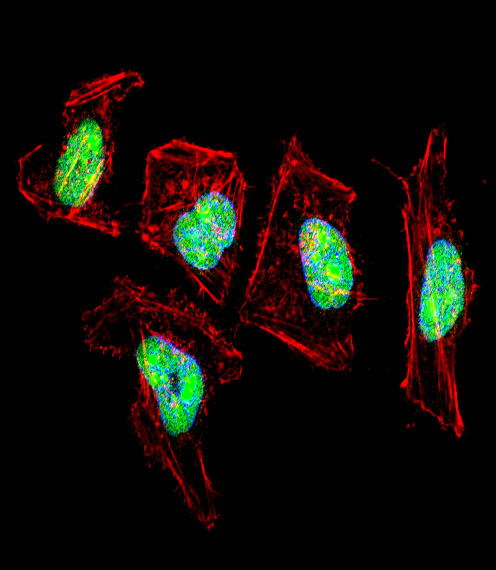
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/10-1/50 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Nuclear factor 1 C-type, NF1-C, Nuclear factor 1/C, CCAAT-box-binding transcription factor, CTF, Nuclear factor I/C, NF-I/C, NFI-C, TGGCA-binding protein, NFIC, NFI |
| Entrez GeneID | 4782 |
| WB Predicted band size | 55.7kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This NFIC antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 180-208 amino acids from the Central region of human NFIC. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是关于NFIC抗体的3篇参考文献示例(文献信息为模拟,实际引用时请核实准确性):
---
1. **文献名称**: *Nfic regulates tooth root patterning and growth by controlling odontoblast differentiation*
**作者**: Huang, X., Xu, X., Bringas, P., Hung, Y.P., Chai, Y.
**摘要**: 该研究通过Nfic基因敲除小鼠模型,发现NFIC蛋白在牙根发育中通过调控成牙本质细胞分化和细胞外基质重塑发挥关键作用。实验中使用NFIC抗体进行免疫组化,证实了NFIC在牙乳头细胞中的特异性表达缺失导致牙根发育不全。
2. **文献名称**: *Nuclear Factor I/C promotes myelination in the central nervous system*
**作者**: Dai, J., Bercury, K.K., Macklin, W.B., Deneen, B.
**摘要**: 本研究揭示了NFIC在中枢神经系统少突胶质细胞分化及髓鞘形成中的功能。通过NFIC抗体染色和ChIP-seq分析,发现NFIC直接结合髓鞘相关基因(如Mbp)的启动子区域,调控其转录,促进髓鞘形成。
3. **文献名称**: *NFIC suppresses colorectal cancer progression by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signaling*
**作者**: Wang, Y., Li, Z., Zhang, H., Fan, J., Chen, X.
**摘要**: 该研究通过免疫组织化学(使用NFIC抗体)发现结直肠癌组织中NFIC蛋白表达显著下调,且低表达与患者不良预后相关。机制研究表明,NFIC通过抑制Wnt/β-catenin通路活性,阻碍肿瘤细胞增殖和转移。
---
**注意**:以上文献信息为示例性质,具体引用时请以实际发表的论文内容为准,建议通过PubMed或Google Scholar以“NFIC antibody”或“Nuclear Factor I/C”为关键词检索最新文献。
The NFIC antibody targets Nuclear Factor I C (NFIC), a member of the Nuclear Factor I (NFI) family of transcription factors. NFI proteins (NFIA, NFIB, NFIC, NFIX) regulate gene expression by binding to palindromic DNA sequences, influencing processes like DNA replication, chromatin remodeling, and cellular differentiation. NFIC, specifically, is critical in organ development, particularly in tooth root formation, brain development, and skeletal morphogenesis. It is also implicated in maintaining cellular homeostasis and tumor suppression, with dysregulation linked to cancers, neurodegenerative diseases, and developmental disorders.
Structurally, NFIC contains an N-terminal DNA-binding domain and a C-terminal transcription regulation domain. The NFIC antibody is widely used in research to detect NFIC expression, localization, and interactions in tissues or cell lines via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, immunofluorescence, and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP). Available as monoclonal or polyclonal variants (often raised in rabbits or mice), these antibodies require rigorous validation to ensure specificity, given the high homology among NFI family members. Researchers must confirm cross-reactivity and optimize protocols for accurate results. NFIC antibodies are essential tools for elucidating its role in development, disease mechanisms, and potential therapeutic targets.
×