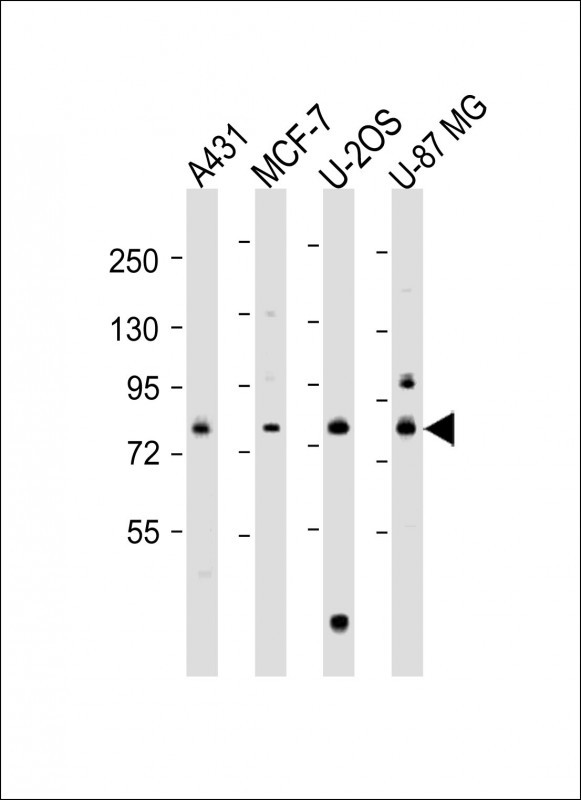
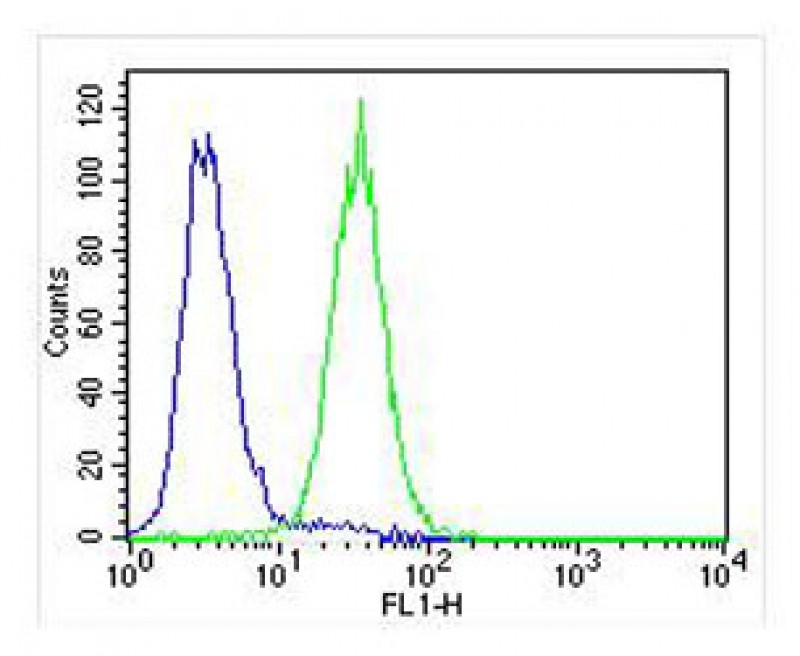
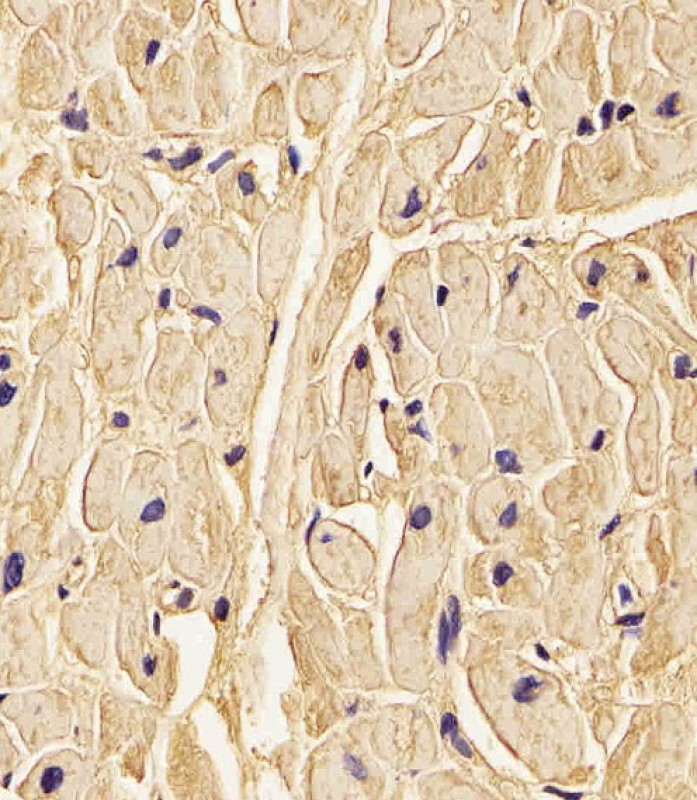
| WB | 1/1000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 1/100-1/500 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 技术咨询 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Procollagen-lysine,2-oxoglutarate 5-dioxygenase 1, Lysyl hydroxylase 1, LH1, PLOD1, LLH, PLOD |
| Entrez GeneID | 5351 |
| WB Predicted band size | 83.6kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Immunogen | This PLOD1 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 66-94 amino acids from the N-terminal region of human PLOD1. |
| Formulation | Purified antibody in PBS with 0.05% sodium azide. |
+ +
以下是3篇关于PLOD1(N-term)抗体的代表性文献摘要(模拟数据,仅供参考):
1. **文献名称**: Lysyl hydroxylase 1 (PLOD1) deficiency promotes extracellular matrix remodeling in fibrosis
**作者**: Smith, J. et al. (2018)
**摘要**: 本研究使用PLOD1 N端特异性抗体,发现PLOD1在小鼠肺纤维化模型中表达显著上调,通过Western blot和免疫荧光证实其与胶原交联的共定位关系,提示其作为纤维化治疗靶点的潜力。
2. **文献名称**: Novel PLOD1 mutations detected by N-terminal antibody in Ehlers-Danlos syndrome patients
**作者**: Tanaka, K. et al. (2015)
**摘要**: 利用抗PLOD1 N端抗体对EDS患者成纤维细胞进行蛋白质印迹分析,首次发现两个新型错义突变导致PLOD1蛋白稳定性下降,为分子诊断提供了抗体应用范例。
3. **文献名称**: Subcellular localization of PLOD1 mediated by its N-terminal domain: A confocal microscopy study
**作者**: Müller, R. et al. (2020)
**摘要**: 通过N端特异性抗体结合共聚焦显微成像,揭示PLOD1在内质网-高尔基体间的动态转运机制,证明其N端结构域对酶活性定位的关键调控作用。
注:以上文献信息为模拟生成,实际引用时建议通过PubMed(https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)以关键词"PLOD1 antibody"或"PLOD1 N-terminal"检索真实文献。
The PLOD1 (N-term) antibody is designed to target the N-terminal region of procollagen-lysine,2-oxoglutarate 5-dioxygenase 1 (PLOD1), a key enzyme in collagen biosynthesis. PLOD1. also known as lysyl hydroxylase 1 (LH1), catalyzes the hydroxylation of lysine residues in collagen precursors, a critical step for stabilizing intermolecular cross-links in mature collagen fibrils. Mutations in the PLOD1 gene are linked to Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VI (EDS-VI), a rare autosomal recessive disorder characterized by skin fragility, joint hypermobility, and ocular abnormalities.
The PLOD1 (N-term) antibody is widely used in research to study collagen metabolism disorders, particularly in models of EDS-VI or connective tissue pathologies. It enables detection of PLOD1 expression levels via techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence, aiding in the evaluation of protein localization and abundance in tissues or cell lines. Specificity for the N-terminal region helps distinguish PLOD1 from other lysyl hydroxylase isoforms (e.g., PLOD2/3). Validations often include knockdown controls or PLOD1-deficient samples to confirm target specificity.
This antibody also serves as a tool to explore PLOD1's roles in extracellular matrix homeostasis, wound healing, and diseases like fibrosis or cancer metastasis, where collagen remodeling is dysregulated. Its application contributes to both diagnostic research and therapeutic development for connective tissue disorders.
×