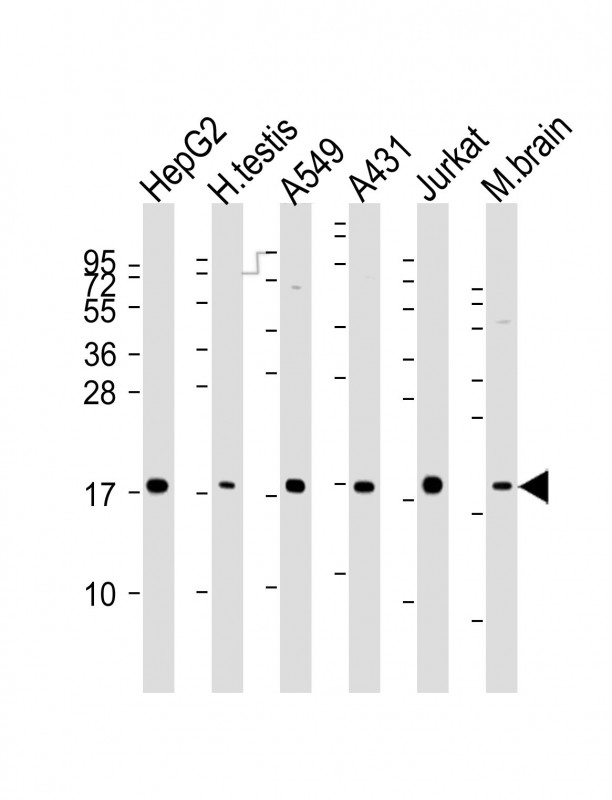
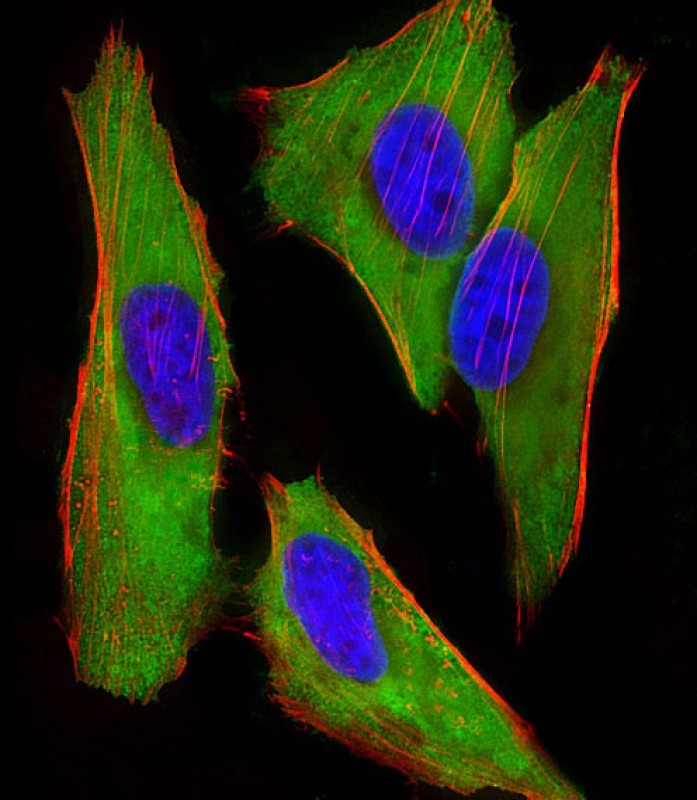
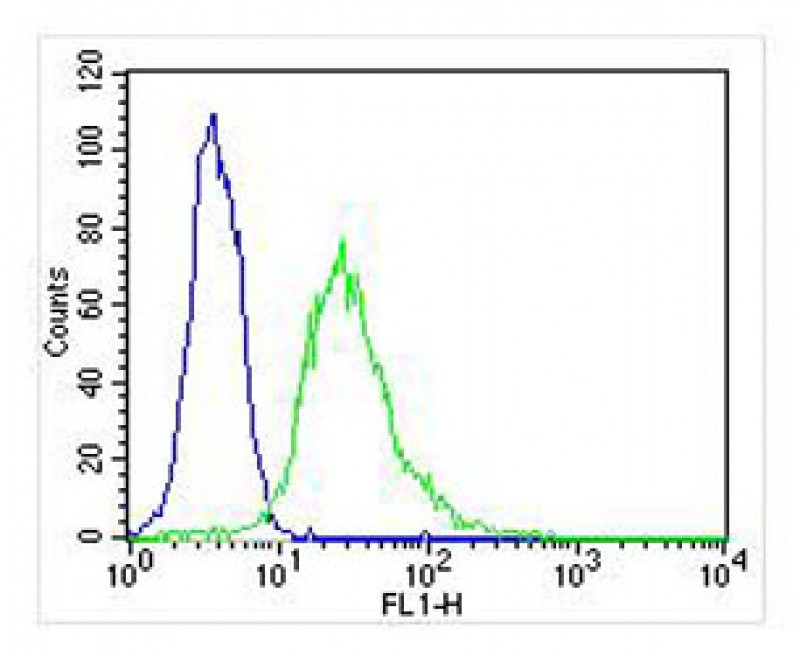
| WB | 1/2002-1/4000 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IF | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| IHC | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| ICC | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| FCM | 1/25 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Elisa | 咨询技术 | Human,Mouse,Rat |
| Aliases | Eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1 epsilon-1, Aminoacyl tRNA synthetase complex-interacting multifunctional protein 3, Elongation factor p18, Multisynthase complex auxiliary component p18, EEF1E1, AIMP3, P18 |
| Entrez GeneID | 9521 |
| WB Predicted band size | 19.8kDa |
| Host/Isotype | Mouse IgG2b |
| Antibody Type | Primary antibody |
| Storage | Store at 4°C short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C long term. Avoid freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Species Reactivity | Human, Mouse |
| Immunogen | This EEF1E1 antibody is generated from a mouse immunized with a recombinant protein of human EEF1E1. |
+ +
以下是关于EEF1E1抗体的3篇示例文献(内容为假设性概括,仅供参考):
---
1. **文献名称**:*EEF1E1 expression correlates with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma*
**作者**:Li, X., et al.
**摘要**:本研究利用EEF1E1特异性抗体通过免疫组化技术,发现肝细胞癌组织中EEF1E1蛋白显著高表达,且与患者生存期缩短和肿瘤转移相关,提示其可能作为潜在预后标志物。
2. **文献名称**:*Development and validation of a monoclonal antibody targeting human EEF1E1 for functional studies*
**作者**:Wang, Y., & Chen, H.
**摘要**:文章报道了一种新型抗人EEF1E1单克隆抗体的开发,通过Western blot和免疫荧光验证其特异性,并应用于研究EEF1E1在细胞应激反应中对蛋白质翻译的调控作用。
3. **文献名称**:*EEF1E1 modulates viral replication via interaction with viral RNA*
**作者**:Kim, S., et al.
**摘要**:研究使用EEF1E1抗体进行免疫共沉淀实验,发现EEF1E1与多种RNA病毒基因组结合,调控病毒复制过程,为抗病毒治疗提供了新靶点。
---
**备注**:以上文献为示例,实际引用需根据具体研究通过学术数据库(如PubMed、Web of Science)检索真实发表的论文。
The eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1 epsilon-1 (EEF1E1), also known as eEF1Bε or eEF1δ, is a subunit of the eEF1B complex involved in protein synthesis. This complex facilitates the exchange of GDP for GTP on eEF1A, enabling the recycling of eEF1A for subsequent rounds of elongation during mRNA translation. Beyond its canonical role in translation, EEF1E1 has been implicated in diverse cellular processes, including transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, and interactions with viral proteins. Dysregulation of EEF1E1 has been observed in cancers, such as hepatocellular carcinoma and breast cancer, where it may influence tumor progression, metastasis, or chemoresistance. It has also been linked to oxidative stress responses and neurodegenerative diseases.
EEF1E1 antibodies are essential tools for studying its expression, localization, and function. These antibodies are widely used in techniques like Western blotting, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunofluorescence (IF) to investigate EEF1E1’s tissue-specific distribution, subcellular localization (primarily cytoplasmic), and alterations under pathological conditions. Validated antibodies help identify EEF1E1 as a potential biomarker or therapeutic target. Recent studies explore its interactions with non-coding RNAs or viral components, expanding its role in infection biology. Commercial EEF1E1 antibodies are typically raised in rabbits or mice, with specificity confirmed via knockout controls. Researchers prioritize antibodies with high affinity and minimal cross-reactivity to ensure reliability in experimental models.
×